Question Number 31794 by mondodotto@gmail.com last updated on 14/Mar/18
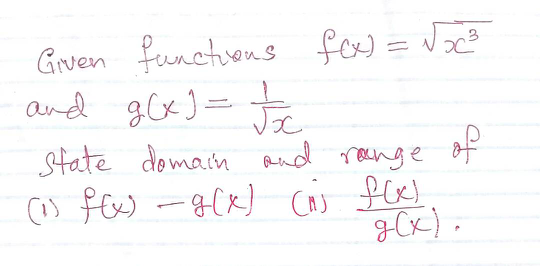
Commented by MJS last updated on 14/Mar/18

$${f}\left({x}\right)=\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }={x}\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{x}}}=\frac{\sqrt{{x}}}{{x}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)−{g}\left({x}\right)={x}\sqrt{{x}}−\frac{\sqrt{{x}}}{{x}}=\left({x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)\sqrt{{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{domain}=\left\{{x}\in\mathbb{R}\mid{x}>\mathrm{0}\right\}=\mathbb{R}^{+} \\ $$$$\mathrm{range}=\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\frac{{f}\left({x}\right)}{{g}\left({x}\right)}={x}\sqrt{{x}}/\frac{\sqrt{{x}}}{{x}}={x}\sqrt{{x}}×\frac{{x}}{\:\sqrt{{x}}}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{looks}\:\mathrm{like}\:\mathrm{domain}=\mathbb{R}\:\mathrm{because} \\ $$$$\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{reduce}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{fraction} \\ $$$$\frac{\sqrt{{x}}}{\:\sqrt{{x}}}\:\mathrm{when}\:{x}<\mathrm{0}\:\left(\mathrm{whatever}\:\mathrm{i}.\mathrm{e}.\right. \\ $$$$\left.\sqrt{−\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{might}\:\mathrm{be},\:\frac{\sqrt{−\mathrm{3}}}{\:\sqrt{−\mathrm{3}}}=\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$$$\mathrm{can}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{when}\:{x}=\mathrm{0}\:\left(\mathrm{although}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{some}\right. \\ $$$$\mathrm{cases}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{might}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{useful}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{add} \\ $$$$\left.\left({x},{y}\right)=\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{close}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{gap}\right),\:\mathrm{so} \\ $$$$\mathrm{domain}=\left\{{x}\in\mathbb{R}\mid{x}\neq\mathrm{0}\right\}=\mathbb{R}\backslash\left\{\mathrm{0}\right\} \\ $$$$\mathrm{range}=\left\{{x}\in\mathbb{R}\mid{x}>\mathrm{0}\right\}=\mathbb{R}^{+} \\ $$
Commented by mondodotto@gmail.com last updated on 15/Mar/18

$$\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}\: \\ $$
