Question Number 34205 by rahul 19 last updated on 02/May/18

Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 02/May/18
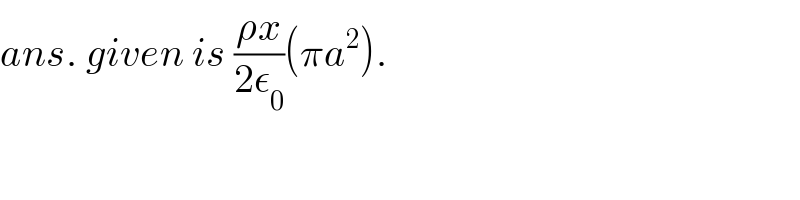
$${ans}.\:{given}\:{is}\:\frac{\rho{x}}{\mathrm{2}\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} }\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right). \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 03/May/18

$${total}\:{flux}\:\phi_{{tot}} =\:\rho\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)/\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$${field}\:{at}\:{r}={x}\:{be}\:{E},\:{then} \\ $$$$\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} {E}\left(\mathrm{2}\pi{rl}\right)=\rho\left(\pi{r}^{\mathrm{2}} {l}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\:{E}=\frac{\rho{r}}{\mathrm{2}\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} } \\ $$$${flux}\:{through}\:{flat}\:{circular}\:{area} \\ $$$${of}\:{small}\:{cylinder}\:{at}\:{r}={x}\:{is} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\phi_{{flat}\:{circular}} \:\:={E}\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\:\frac{\rho{x}}{\mathrm{2}\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} }\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\phi_{{curved}\:{surface}} =\phi_{{tot}} −\phi_{{flat}\:{circular}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{\rho{x}}{\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} }\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\frac{\rho{x}}{\mathrm{2}\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} }\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\phi}_{{curved}} \:=\:\frac{\rho{x}}{\mathrm{2}\epsilon_{\mathrm{0}} }\left(\pi{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:. \\ $$
