Question Number 36677 by mondodotto@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 04/Jun/18
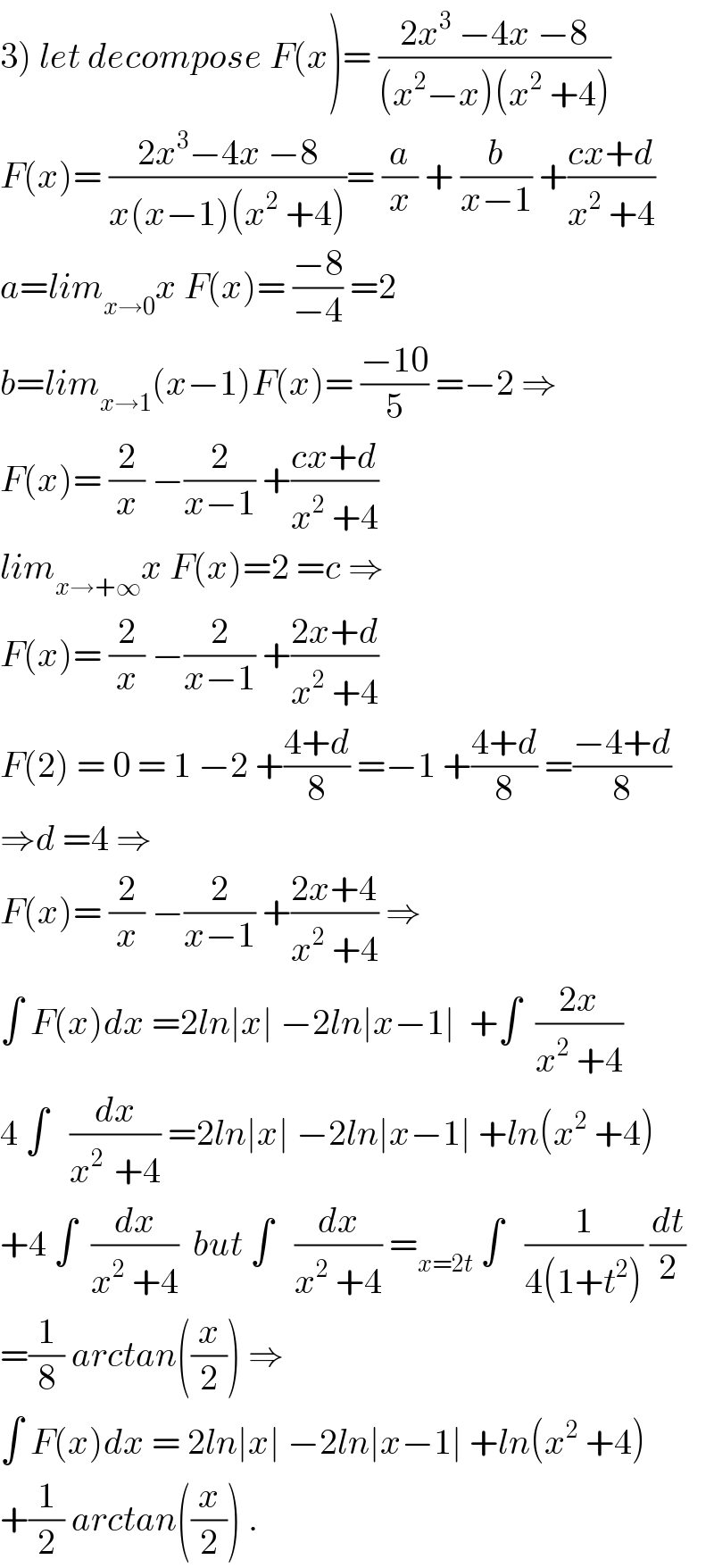
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\:{let}\:{decompose}\:{F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:−\mathrm{4}{x}\:−\mathrm{8}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}\right)} \\ $$$${F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{x}\:−\mathrm{8}}{{x}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}\right)}=\:\frac{{a}}{{x}}\:+\:\frac{{b}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{{cx}+{d}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${a}={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {x}\:{F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{−\mathrm{8}}{−\mathrm{4}}\:=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${b}={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} \left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{5}}\:=−\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{{cx}+{d}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} {x}\:{F}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}\:={c}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+{d}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${F}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:−\mathrm{2}\:+\frac{\mathrm{4}+{d}}{\mathrm{8}}\:=−\mathrm{1}\:+\frac{\mathrm{4}+{d}}{\mathrm{8}}\:=\frac{−\mathrm{4}+{d}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{d}\:=\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${F}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int\:{F}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}\mid\:−\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid\:\:+\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}\:\int\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} \:+\mathrm{4}}\:=\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}\mid\:−\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid\:+{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$+\mathrm{4}\:\int\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}}\:\:{but}\:\int\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}}\:=_{{x}=\mathrm{2}{t}} \:\int\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\:{arctan}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int\:{F}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}\mid\:−\mathrm{2}{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid\:+{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{arctan}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup last updated on 04/Jun/18
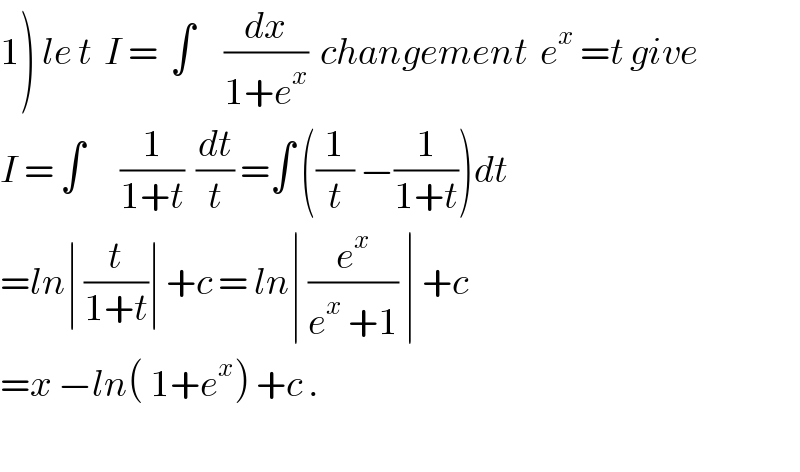
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{le}\:{t}\:\:{I}\:=\:\:\int\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{x}} }\:\:{changement}\:\:{e}^{{x}} \:={t}\:{give} \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\int\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\:\:\frac{{dt}}{{t}}\:=\int\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\right){dt} \\ $$$$={ln}\mid\:\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\mid\:+{c}\:=\:{ln}\mid\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:\mid\:+{c} \\ $$$$={x}\:−{ln}\left(\:\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{x}} \right)\:+{c}\:. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Cheyboy last updated on 04/Jun/18
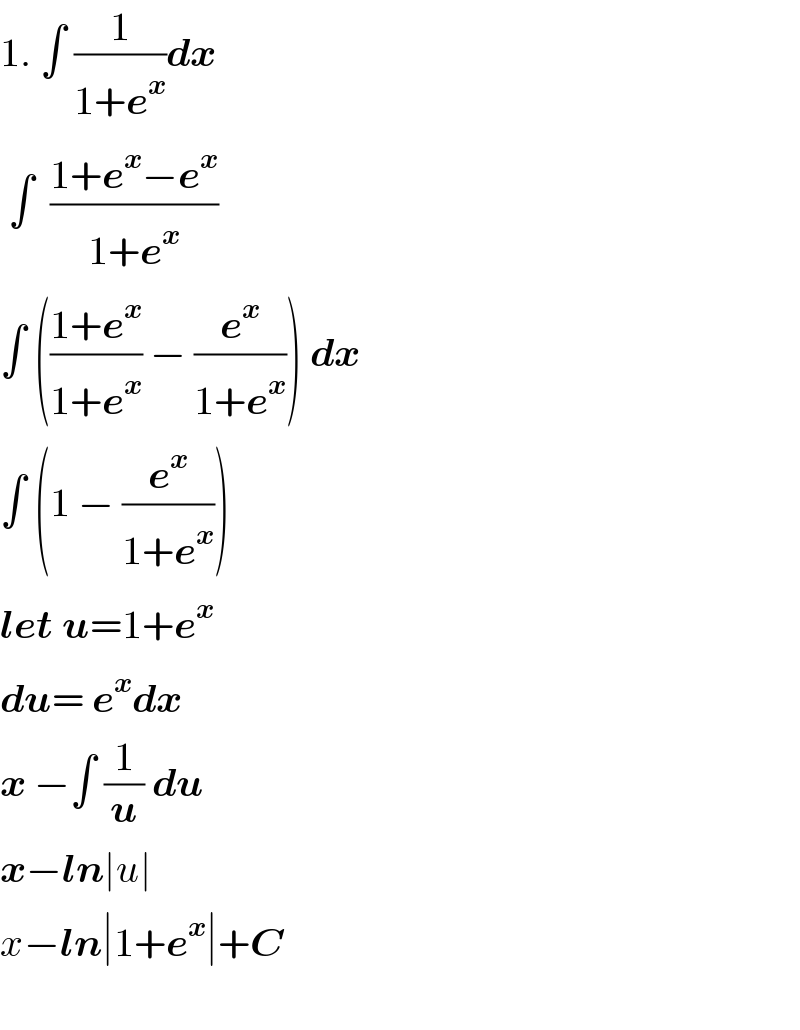
$$\mathrm{1}.\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }\boldsymbol{{dx}} \\ $$$$\:\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }\: \\ $$$$\int\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }\:−\:\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }\right)\:\boldsymbol{{dx}} \\ $$$$\int\:\left(\mathrm{1}\:−\:\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }\right) \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{let}}\:\boldsymbol{{u}}=\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{du}}=\:\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \boldsymbol{{dx}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{x}}\:−\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{u}}}\:\boldsymbol{{du}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{x}}−\boldsymbol{{ln}}\mid{u}\mid \\ $$$${x}−\boldsymbol{{ln}}\mid\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \mid+\boldsymbol{{C}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18
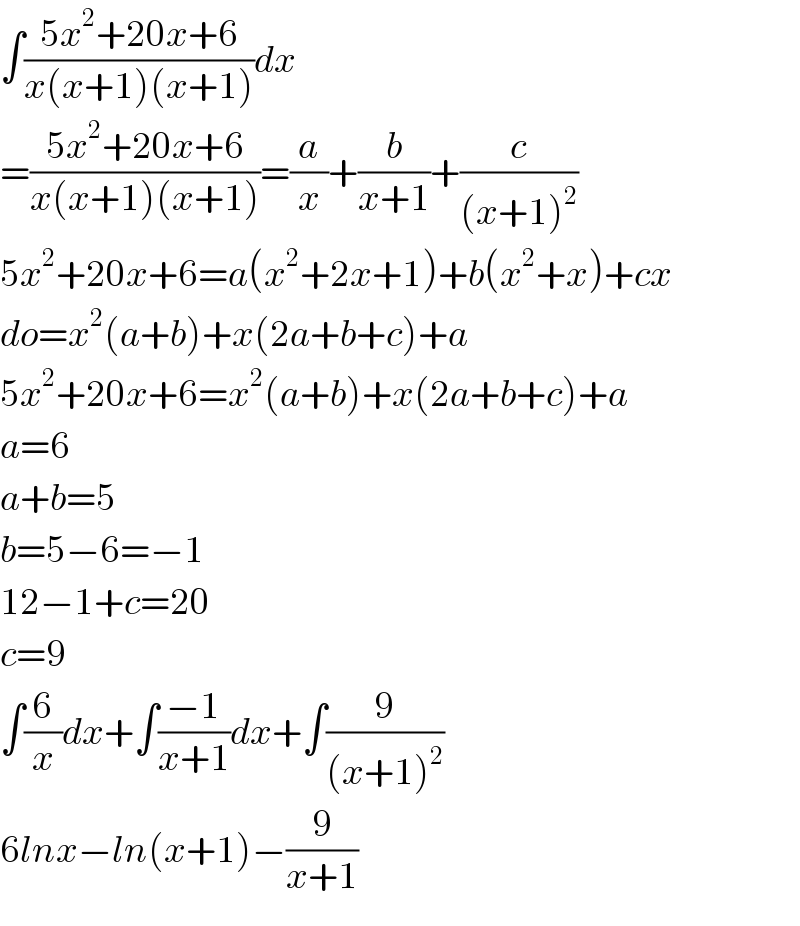
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{x}+\mathrm{6}}{{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{x}+\mathrm{6}}{{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{{a}}{{x}}+\frac{{b}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{{c}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{x}+\mathrm{6}={a}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+{b}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right)+{cx} \\ $$$${do}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({a}+{b}\right)+{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}+{b}+{c}\right)+{a} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{x}+\mathrm{6}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({a}+{b}\right)+{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}+{b}+{c}\right)+{a} \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${b}=\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{6}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{12}−\mathrm{1}+{c}=\mathrm{20} \\ $$$${c}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}{dx}+\int\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx}+\int\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}{lnx}−{ln}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18
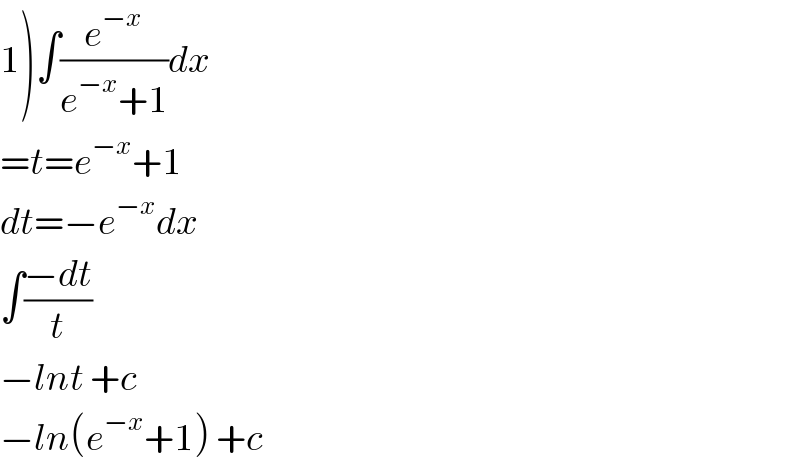
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\int\frac{{e}^{−{x}} }{{e}^{−{x}} +\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$={t}={e}^{−{x}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${dt}=−{e}^{−{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\int\frac{−{dt}}{{t}} \\ $$$$−{lnt}\:+{c} \\ $$$$−{ln}\left({e}^{−{x}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\:+{c} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Jun/18
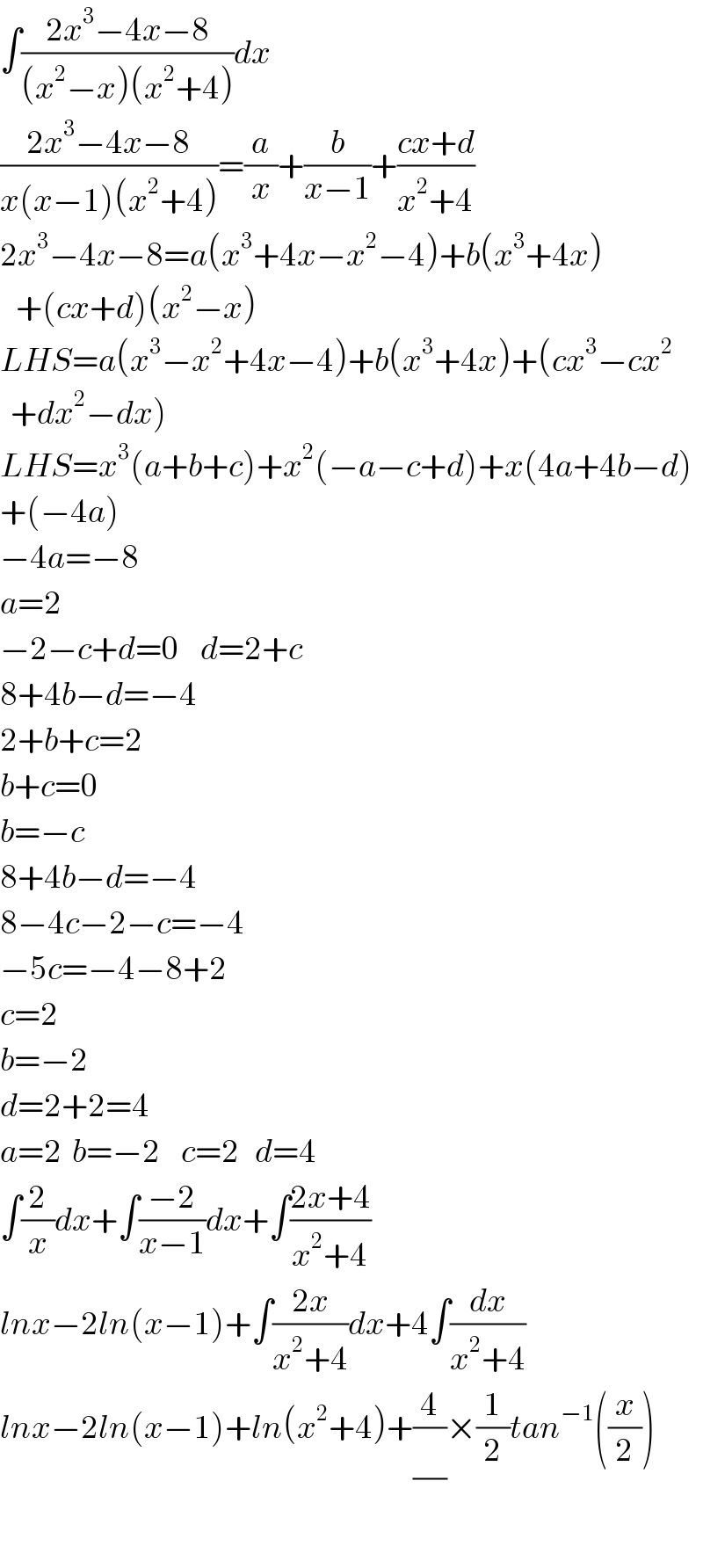
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{8}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)}{dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{8}}{{x}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)}=\frac{{a}}{{x}}+\frac{{b}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}+\frac{{cx}+{d}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{8}={a}\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\right)+{b}\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}{x}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:+\left({cx}+{d}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}\right) \\ $$$${LHS}={a}\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} −{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{4}\right)+{b}\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{4}{x}\right)+\left({cx}^{\mathrm{3}} −{cx}^{\mathrm{2}} \right. \\ $$$$\left.\:\:+{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} −{dx}\right) \\ $$$${LHS}={x}^{\mathrm{3}} \left({a}+{b}+{c}\right)+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(−{a}−{c}+{d}\right)+{x}\left(\mathrm{4}{a}+\mathrm{4}{b}−{d}\right) \\ $$$$+\left(−\mathrm{4}{a}\right) \\ $$$$−\mathrm{4}{a}=−\mathrm{8} \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}−{c}+{d}=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:{d}=\mathrm{2}+{c} \\ $$$$\mathrm{8}+\mathrm{4}{b}−{d}=−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}+{b}+{c}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${b}+{c}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${b}=−{c} \\ $$$$\mathrm{8}+\mathrm{4}{b}−{d}=−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{4}{c}−\mathrm{2}−{c}=−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{5}{c}=−\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{8}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${c}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${b}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${d}=\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{2}\:\:{b}=−\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:{c}=\mathrm{2}\:\:\:{d}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}{dx}+\int\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{dx}+\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${lnx}−\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)+\int\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}}{dx}+\mathrm{4}\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${lnx}−\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)+{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\frac{}{}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 04/Jun/18
![6. ∫((sec^2 x)/(tan x (tan x +1)))dx= [t=tan x → dx=(dt/(sec^2 x))] =∫(dt/(t(t+1)))=∫(A/t)dt+∫(B/(t+1))dt= =∫(dt/t)−∫(dt/(t+1))=ln t −ln(t+1)= =ln∣tan x∣−ln∣tan x +1∣+C 7. ∫((3cos x)/(sin^2 x +sin x −2))dx= [t=sin x → dx=(dt/(cos x))] =∫(3/(t^2 +t−2))dt=∫(3/((t−1)(t+2)))dt= =∫(dt/(t−1))−∫(dt/(t+2))=ln(t−1)−ln(t+2)= [∣sin x −1∣=1−sin x] =ln(1−sin x)−ln(2+sin x)+C](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q36705.png)
$$\mathrm{6}. \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}}{\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:\left(\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{1}\right)}{dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:{dx}=\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}}\right] \\ $$$$=\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\int\frac{\mathcal{A}}{{t}}{dt}+\int\frac{\mathcal{B}}{{t}+\mathrm{1}}{dt}= \\ $$$$=\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}}−\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{ln}\:{t}\:−\mathrm{ln}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)= \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\mid\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\mid−\mathrm{ln}\mid\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{1}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{7}. \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{3cos}\:{x}}{\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\:+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:−\mathrm{2}}{dx}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:{dx}=\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\right] \\ $$$$=\int\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +{t}−\mathrm{2}}{dt}=\int\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)}{dt}= \\ $$$$=\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}−\mathrm{1}}−\int\frac{{dt}}{{t}+\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{ln}\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{ln}\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[\mid\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:−\mathrm{1}\mid=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right] \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)+{C} \\ $$
