Question Number 39336 by rahul 19 last updated on 05/Jul/18

Commented by ajfour last updated on 05/Jul/18
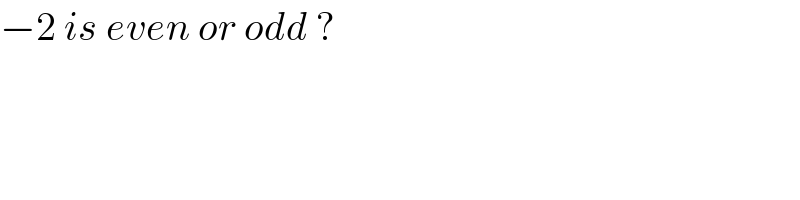
$$−\mathrm{2}\:{is}\:{even}\:{or}\:{odd}\:? \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 05/Jul/18
even.
Commented by ajfour last updated on 05/Jul/18

$${make}\:{sure}. \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 06/Jul/18
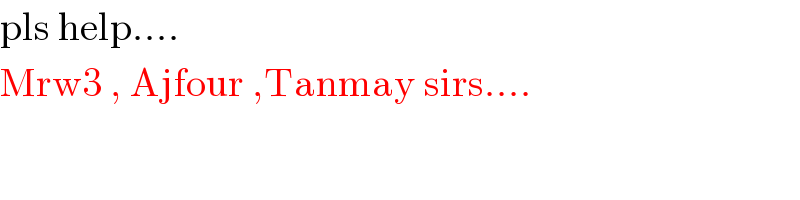
$$\mathrm{pls}\:\mathrm{help}…. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Mrw3}\:,\:\mathrm{Ajfour}\:,\mathrm{Tanmay}\:\mathrm{sirs}…. \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 08/Jul/18
![we have f(x)=∣x−[x]∣ if [x] is odd and f(x)=x−[x+1] if [x] even ∫_(−2) ^4 f(x)dx = Σ_(k=−2) ^3 ∫_k ^(k+1) f(x)dx = ∫_(−2) ^(−1) (x −(−2)−1)dx +∫_(−1) ^0 ∣x−(−1)∣dx + ∫_0 ^1 (x −0−1)dx +∫_1 ^2 ∣x−1∣dx +∫_2 ^3 (x −2−1)dx + ∫_3 ^4 ∣x−3∣dx = ∫_(−2) ^(−1) (x +1)dx + ∫_(−1) ^o (x+1)dx +∫_0 ^1 (x−1)dx + ∫_1 ^2 (x−1)dx + ∫_2 ^3 (x−3)dx +∫_3 ^4 (x−3)dx = ∫_(−2) ^o (x+1)dx + ∫_0 ^2 (x−1)dx + ∫_2 ^4 (x−3)dx =[(x^2 /2) +x]_(−2) ^0 +[ (x^2 /2) −x]_0 ^2 +[ (x^2 /2) −3x]_2 ^4 =−2 +2 + 0 +( 8−12)−(2−6) =−4 +4 =0 ∫_(−2) ^4 f(x)dx =0 .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q39572.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid{x}−\left[{x}\right]\mid\:{if}\:\left[{x}\right]\:{is}\:{odd}\:{and} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={x}−\left[{x}+\mathrm{1}\right]\:{if}\:\left[{x}\right]\:{even} \\ $$$$\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \:{f}\left({x}\right){dx}\:\:=\:\sum_{{k}=−\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{3}} \:\int_{{k}} ^{{k}+\mathrm{1}} \:{f}\left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\:\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\:−\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \mid{x}−\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\mid{dx} \\ $$$$+\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\left({x}\:−\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \mid{x}−\mathrm{1}\mid{dx}\:+\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{3}} \left({x}\:−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx} \\ $$$$+\:\int_{\mathrm{3}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \:\:\mid{x}−\mathrm{3}\mid{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\:+\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:\:\:+\:\int_{−\mathrm{1}} ^{{o}} \left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx} \\ $$$$+\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\:\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{3}} \left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right){dx}\:+\int_{\mathrm{3}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\:\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{{o}} \left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:\:+\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\:\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+{x}\right]_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \:\:+\left[\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:−{x}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\left[\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{3}{x}\right]_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{2}\:+\mathrm{2}\:\:+\:\mathrm{0}\:\:+\left(\:\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{12}\right)−\left(\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{6}\right) \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{4}\:+\mathrm{4}\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\int_{−\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{4}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=\mathrm{0}\:. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
