Question Number 39921 by Raj Singh last updated on 13/Jul/18

Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 13/Jul/18
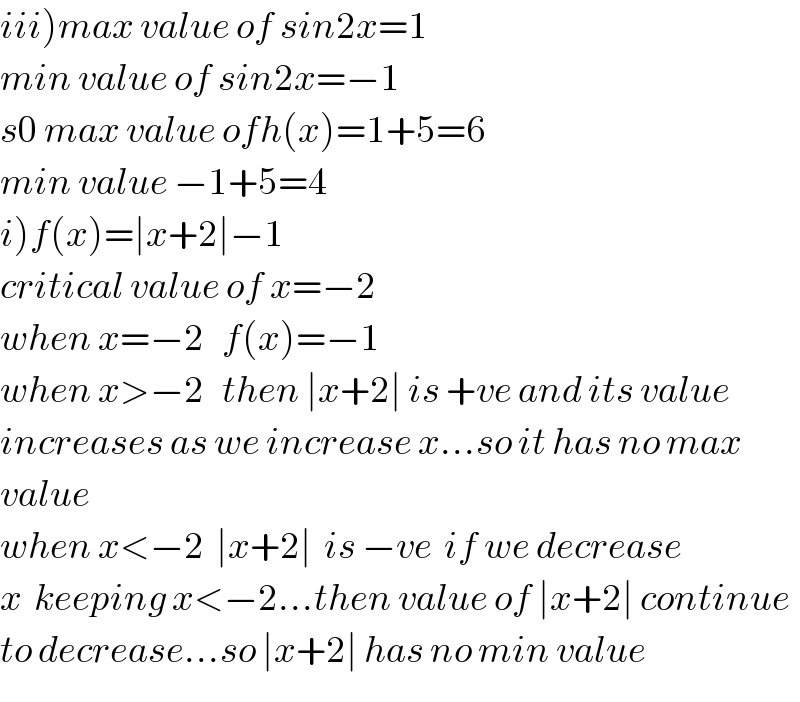
$$\left.{iii}\right){max}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${min}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\mathrm{2}{x}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${s}\mathrm{0}\:{max}\:{value}\:{ofh}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${min}\:{value}\:−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\left.{i}\right){f}\left({x}\right)=\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${critical}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${when}\:{x}=−\mathrm{2}\:\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${when}\:{x}>−\mathrm{2}\:\:\:{then}\:\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid\:{is}\:+{ve}\:{and}\:{its}\:{value} \\ $$$${increases}\:{as}\:{we}\:{increase}\:{x}…{so}\:{it}\:{has}\:{no}\:{max} \\ $$$${value} \\ $$$${when}\:{x}<−\mathrm{2}\:\:\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid\:\:{is}\:−{ve}\:\:{if}\:{we}\:{decrease} \\ $$$${x}\:\:{keeping}\:{x}<−\mathrm{2}…{then}\:{value}\:{of}\:\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid\:{continue} \\ $$$${to}\:{decrease}…{so}\:\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid\:{has}\:{no}\:{min}\:{value} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 13/Jul/18

$$\left.{ii}\right){g}\left({x}\right)=−\mid{x}+\mathrm{1}\mid+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${critical}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${at}\:{x}=−\mathrm{1}\:\:{g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${now}\:{when}\:{x}>−\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{we}\:{increase}\:{x}\:{keeping} \\ $$$${condition}\:{x}>−\mathrm{1}\:{value}\:{of}\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:{decreases} \\ $$$${so}\:{it}\:{has}\:{no}\:{min}\:{value}… \\ $$$${when}\:{x}<−\mathrm{1}\:\:{we}\:{continue}\:{decrease}\:{the} \\ $$$${value}\:{of}\:{x}…{then}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x}+\mathrm{1}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${so}\:−\mid{x}+\mathrm{1}\mid\:{become}\:+{ve}…{thus}\:{the}\:{value} \\ $$$${of}\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:{increases}\:…{thus}\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:{has}\:{no}\:{max}\:{value} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 13/Jul/18

$$\left.{iv}\right){for}\:{any}\:{value}\:{of}\:{x},{min}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\mathrm{4}{x}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${max}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\mathrm{4}{x}=+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${so}\:{min}\:{value}\:{of}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}\mid=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${max}\:{value}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}\mid=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${if}\:{the}\:{problem}\:{is}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid{sin}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{3}\right)\mid \\ $$$${then}\:{min}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{3}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${thdn}\:{max}\:{value}\:{of}\:{sin}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${but}\:{value}\:{of}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mid−\mathrm{1}\mid=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mid\mathrm{1}\mid=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${so}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:{has}\:{no}\:{min}\:{no}\:{max}\:{value}… \\ $$$${so}\: \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 13/Jul/18

$$\left.{v}\right){h}\left({x}\right)={x}+\mathrm{1}\:\:{as}\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}\:\:{h}\left({x}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${x}\rightarrow−\mathrm{1}\:\:{h}\left({x}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${so}\:{value}\:{of}\:{h}\left({x}\right)\:\:{lies}\:{between}\:\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${h}\left({x}\right)\:\:\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}\right)…{but}\:{the}\:{range}\:{of}\:{h}\left({x}\right)\:{does}\:{not} \\ $$$${include}\:{lowes}\:{value}\:\mathrm{0}\:{highest}\:{value}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${thus}\:{h}\left({x}\right)\:{has}\:{no}\:{max}\:{or}\:{min}\:{value}… \\ $$
