Question Number 48745 by peter frank last updated on 28/Nov/18

Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 28/Nov/18
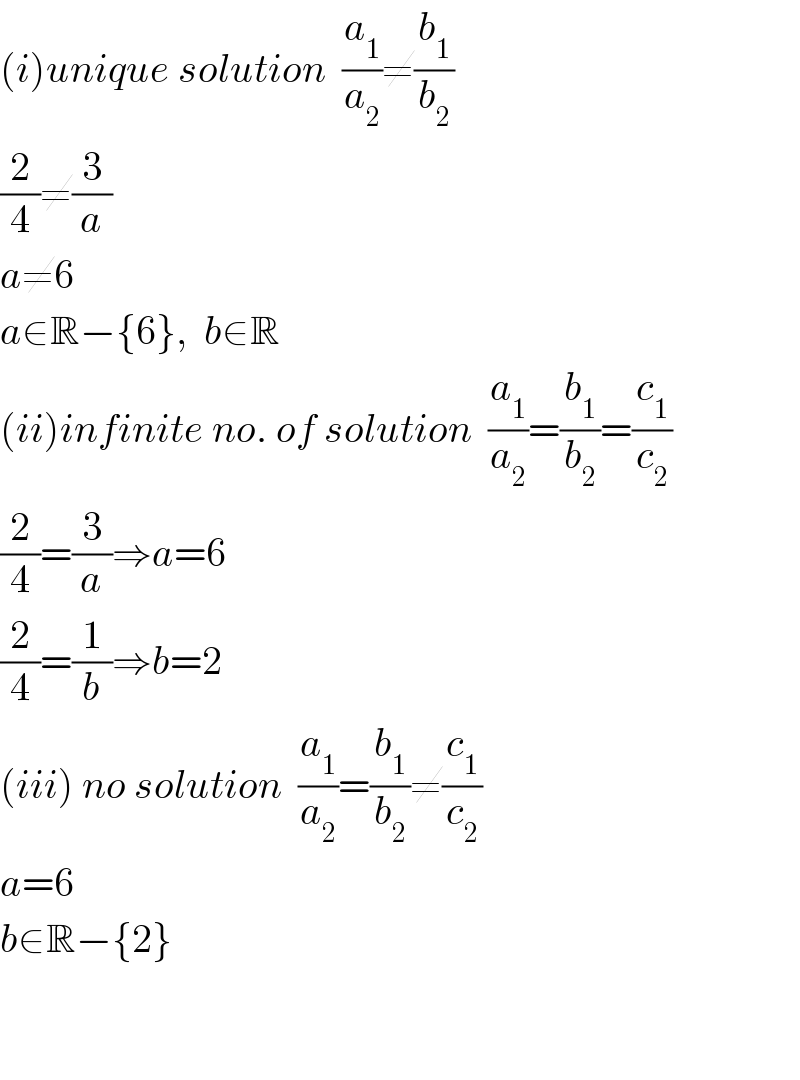
$$\left({i}\right){unique}\:{solution}\:\:\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2}} }\neq\frac{{b}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{b}_{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}\neq\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{a}} \\ $$$${a}\neq\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${a}\in\mathbb{R}−\left\{\mathrm{6}\right\},\:\:{b}\in\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\left({ii}\right){infinite}\:{no}.\:{of}\:{solution}\:\:\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{b}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{b}_{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{c}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{c}_{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{a}}\Rightarrow{a}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{b}}\Rightarrow{b}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\left({iii}\right)\:{no}\:{solution}\:\:\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{a}_{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{b}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{b}_{\mathrm{2}} }\neq\frac{{c}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{c}_{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${b}\in\mathbb{R}−\left\{\mathrm{2}\right\} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
