Question Number 53805 by hassentimol last updated on 26/Jan/19

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 26/Jan/19
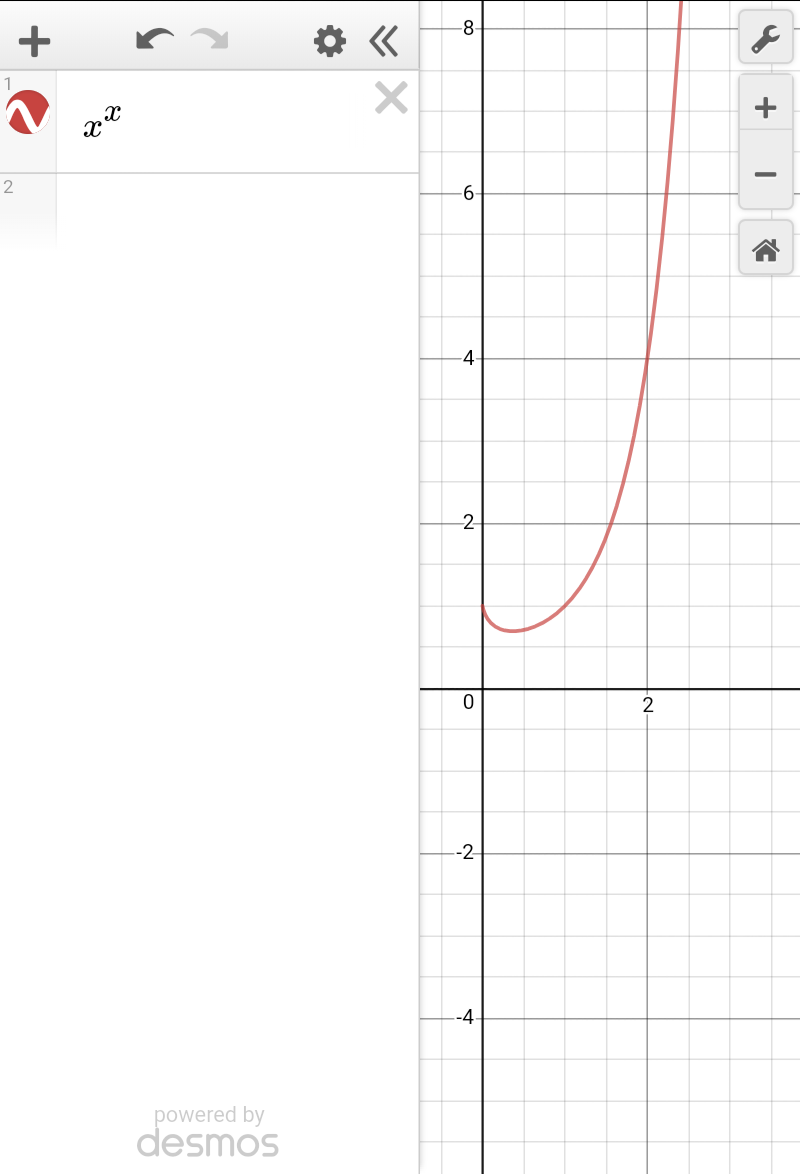
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 26/Jan/19
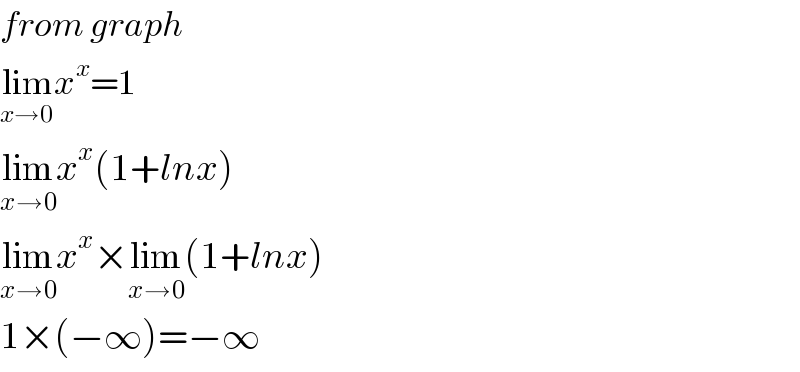
$${from}\:{graph}\: \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{x}^{{x}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{x}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{lnx}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{x}^{{x}} ×\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{lnx}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}×\left(−\infty\right)=−\infty \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 26/Jan/19
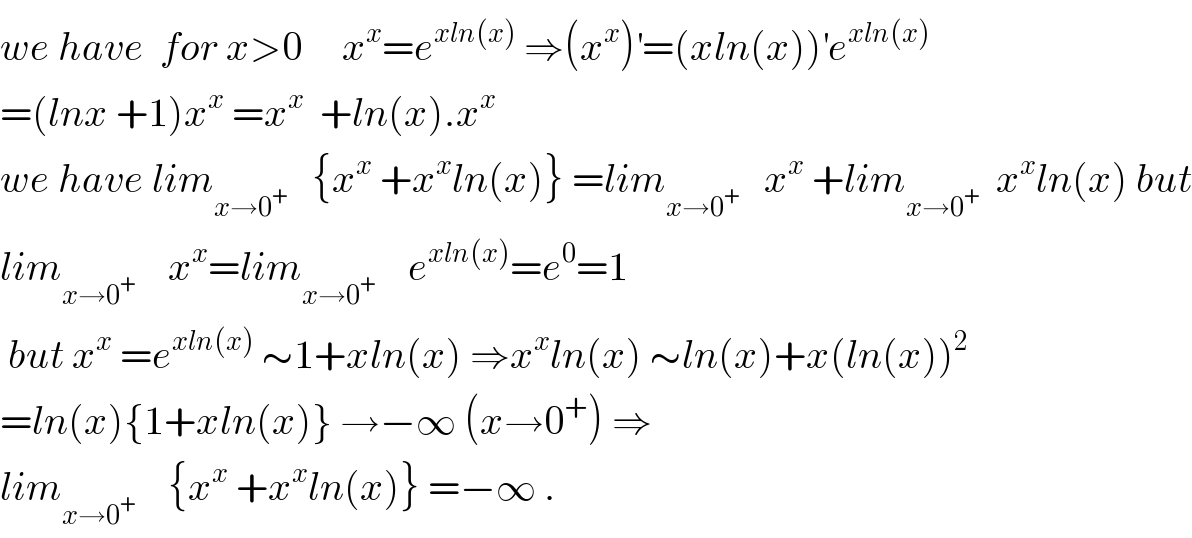
$${we}\:{have}\:\:{for}\:{x}>\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{{x}} ={e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} \:\Rightarrow\left({x}^{{x}} \right)^{'} =\left({xln}\left({x}\right)\right)^{'} {e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} \\ $$$$=\left({lnx}\:+\mathrm{1}\right){x}^{{x}} \:={x}^{{x}} \:\:+{ln}\left({x}\right).{x}^{{x}} \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:\left\{{x}^{{x}} \:+{x}^{{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right)\right\}\:={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:{x}^{{x}} \:+{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:{x}^{{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right)\:{but} \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:\:{x}^{{x}} ={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:\:{e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} ={e}^{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:{but}\:{x}^{{x}} \:={e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} \:\sim\mathrm{1}+{xln}\left({x}\right)\:\Rightarrow{x}^{{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right)\:\sim{ln}\left({x}\right)+{x}\left({ln}\left({x}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$={ln}\left({x}\right)\left\{\mathrm{1}+{xln}\left({x}\right)\right\}\:\rightarrow−\infty\:\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} \right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:\:\left\{{x}^{{x}} \:+{x}^{{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right)\right\}\:=−\infty\:. \\ $$
Commented by hassentimol last updated on 29/Jan/19
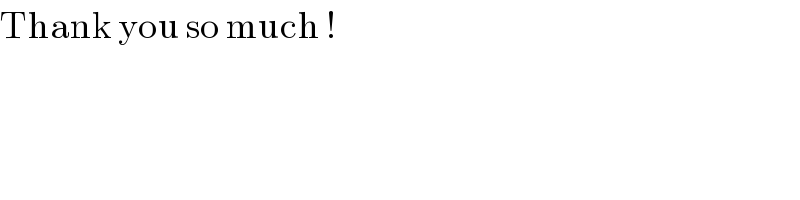
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{much}\:! \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 26/Jan/19
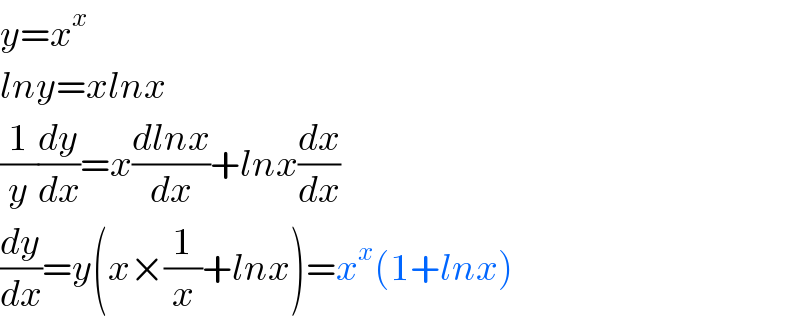
$${y}={x}^{{x}} \\ $$$${lny}={xlnx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={x}\frac{{dlnx}}{{dx}}+{lnx}\frac{{dx}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={y}\left({x}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+{lnx}\right)={x}^{{x}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{lnx}\right) \\ $$
