Question Number 65219 by Rio Michael last updated on 26/Jul/19

Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 26/Jul/19
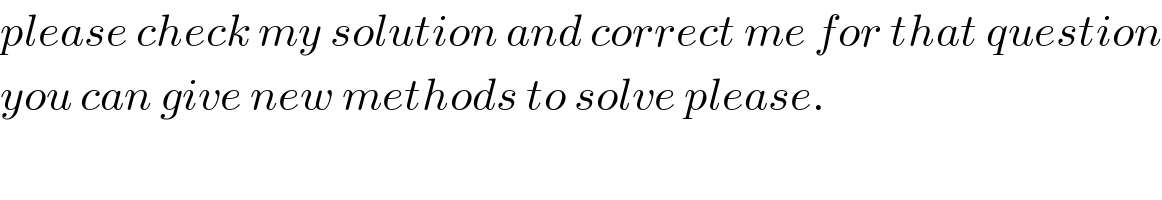
$${please}\:{check}\:{my}\:{solution}\:{and}\:{correct}\:{me}\:{for}\:{that}\:{question} \\ $$$${you}\:{can}\:{give}\:{new}\:{methods}\:{to}\:{solve}\:{please}. \\ $$
Answered by Tanmay chaudhury last updated on 26/Jul/19
![2(d^2 y/dx^2 )−(dy/dx)−3y=5e^(−x) let y=e^(mx) complimentary function 2m^2 −m−3=0 2m^2 −3m+2m−3=0 m(2m−3)+1(2m−3)=0 (2m−3)(m+1)=0 so C.F=C_1 e^((3x)/2) +C_2 e^(−x) P.I y_(p.i) =((5e^(−x) )/(2D^2 −D−3)) [Dy=(dy/dx) and D^2 y=(d^2 y/dx^2 )] y_(p.I) =((5e^(−x) )/((D+1)(2D−3))) y_(p.I) =((5e^(−x) )/(2(−1)−3))×(1/(D−1+1)) y_(p.I) =((5e^(−x) )/(−5))×x =−xe^(−x) complete answer y=C_1 e^((3x)/2) +C_2 e^(−x) −xe^(−x) your answer is correct](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q65221.png)
$$\mathrm{2}\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}−\mathrm{3}{y}=\mathrm{5}{e}^{−{x}} \\ $$$${let}\:{y}={e}^{{mx}} \\ $$$${complimentary}\:{function} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −{m}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{m}+\mathrm{2}{m}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${m}\left(\mathrm{2}{m}−\mathrm{3}\right)+\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{2}{m}−\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}{m}−\mathrm{3}\right)\left({m}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${so}\:\boldsymbol{{C}}.\boldsymbol{{F}}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} \\ $$$${P}.{I} \\ $$$${y}_{\boldsymbol{{p}}.\boldsymbol{{i}}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{D}^{\mathrm{2}} −{D}−\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\left[{Dy}=\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\:\:{and}\:{D}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right] \\ $$$${y}_{\boldsymbol{{p}}.\boldsymbol{{I}}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}^{−{x}} }{\left({D}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{D}−\mathrm{3}\right)} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}.{I}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{3}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}.{I}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}^{−{x}} }{−\mathrm{5}}×{x} \\ $$$$=−{xe}^{−{x}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{complete}}\:\boldsymbol{{answer}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{y}}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} −{xe}^{−{x}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{your}}\:\boldsymbol{{answer}}\:\boldsymbol{{is}}\:\boldsymbol{{correct}} \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 26/Jul/19

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
