Question Number 91378 by jagoll last updated on 30/Apr/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 30/Apr/20
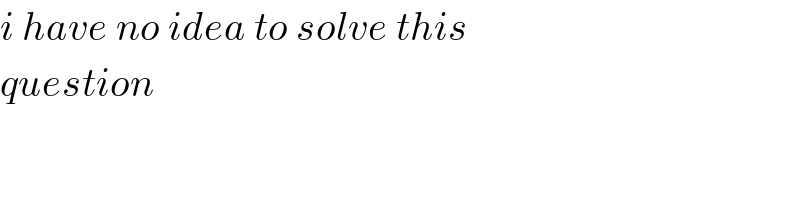
$${i}\:{have}\:{no}\:{idea}\:{to}\:{solve}\:{this}\: \\ $$$${question} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 30/Apr/20
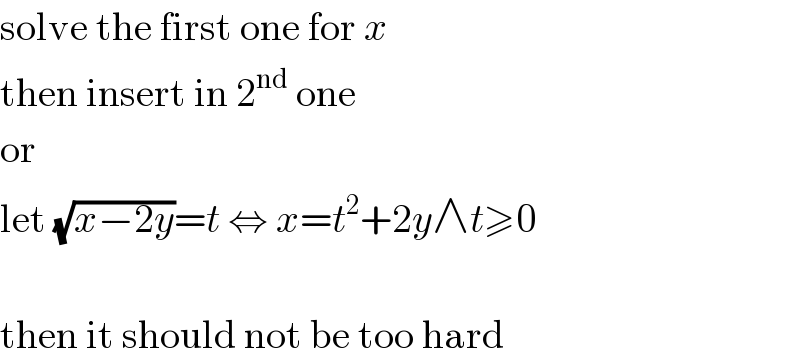
$$\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{first}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{for}\:{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{insert}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{nd}} \:\mathrm{one} \\ $$$$\mathrm{or} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\sqrt{{x}−\mathrm{2}{y}}={t}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}={t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{y}\wedge{t}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{too}\:\mathrm{hard} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 01/May/20
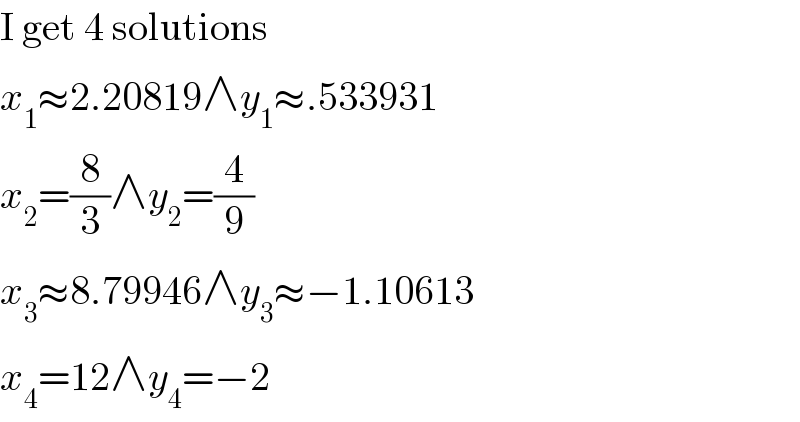
$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{solutions} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} \approx\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{20819}\wedge{y}_{\mathrm{1}} \approx.\mathrm{533931} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{3}}\wedge{y}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{9}} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{3}} \approx\mathrm{8}.\mathrm{79946}\wedge{y}_{\mathrm{3}} \approx−\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{10613} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{4}} =\mathrm{12}\wedge{y}_{\mathrm{4}} =−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 01/May/20
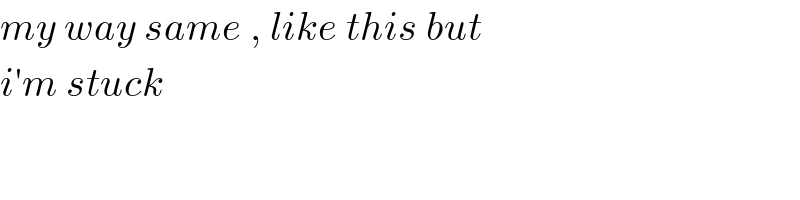
$${my}\:{way}\:{same}\:,\:{like}\:{this}\:{but} \\ $$$${i}'{m}\:{stuck}\: \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 01/May/20
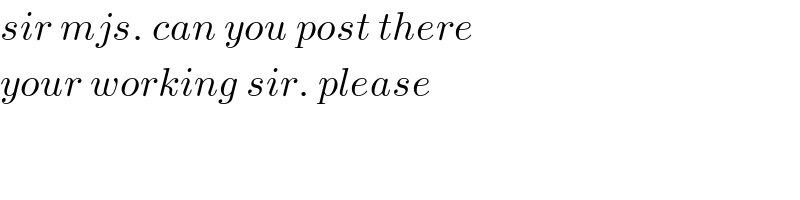
$${sir}\:{mjs}.\:{can}\:{you}\:{post}\:{there} \\ $$$${your}\:{working}\:{sir}.\:{please} \\ $$
Commented by Prithwish Sen 1 last updated on 01/May/20
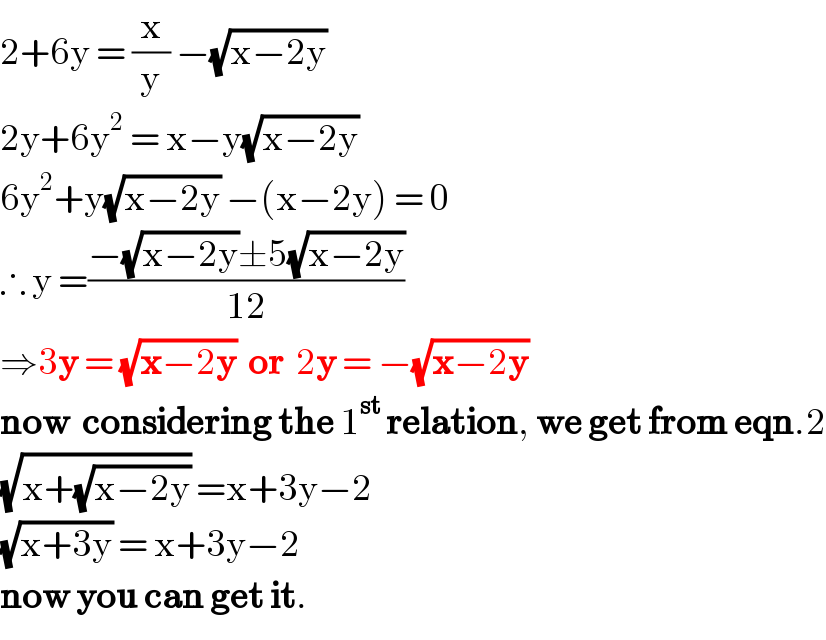
$$\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{6y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{y}}\:−\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2y}+\mathrm{6y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{y}\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{6y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}}\:−\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{y}\:=\frac{−\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}}\pm\mathrm{5}\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}}}{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{3}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}\:=\:\sqrt{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}}\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{or}}\:\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}\:=\:−\sqrt{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{now}}\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{considering}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}}\:\mathrm{1}^{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{st}}} \:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{relation}},\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{we}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{get}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{from}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{eqn}}.\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}}}\:=\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3y}}\:=\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{now}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{you}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{can}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{get}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{it}}. \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 01/May/20

Commented by Prithwish Sen 1 last updated on 01/May/20

$$\mathrm{Nice}. \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 01/May/20
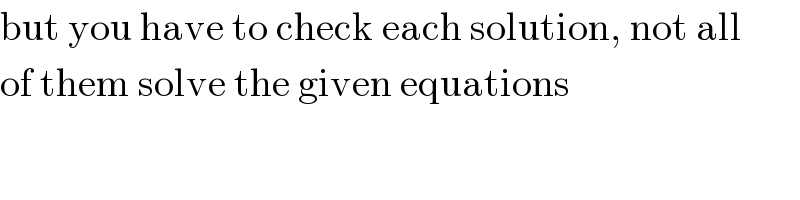
$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{check}\:\mathrm{each}\:\mathrm{solution},\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{all} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{them}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{equations} \\ $$
