Question Number 97953 by I want to learn more last updated on 10/Jun/20

Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Jun/20
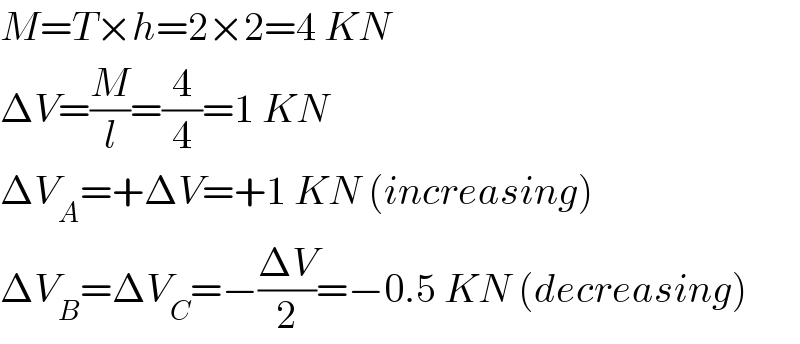
$${M}={T}×{h}=\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4}\:{KN} \\ $$$$\Delta{V}=\frac{{M}}{{l}}=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{1}\:{KN} \\ $$$$\Delta{V}_{{A}} =+\Delta{V}=+\mathrm{1}\:{KN}\:\left({increasing}\right) \\ $$$$\Delta{V}_{{B}} =\Delta{V}_{{C}} =−\frac{\Delta{V}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\:{KN}\:\left({decreasing}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Jun/20

Commented by I want to learn more last updated on 10/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{sir},\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{appreciate} \\ $$
Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 10/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{Here}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{another}\:\mathrm{method}\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{love}.\:\mathrm{Keep}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{mind} \\ $$$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{thesame}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{Mr}\:\mathrm{W}\:\mathrm{method}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{equate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{moments}\:\mathrm{about}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{axis}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{determine}\:\Delta{N}_{\mathrm{A}} \:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{additional}\:\mathrm{reaction}\:\mathrm{force} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\Sigma{M}_{{x}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{4}\Delta{N}_{{A}} \:−\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0}\:×\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0}{kN}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$$\:\Delta{N}_{{A}} \:=\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{0}\:{kN} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{equate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{moments}\:\mathrm{about}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{axis}\:\mathrm{parrallel} \\ $$$$\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{axis}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{goes}\:\mathrm{through}\:\mathrm{point}\:{B}\:\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{zero}.\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{addition}\:\mathrm{reaction}\:\mathrm{force}\:\Delta{N}_{{C}} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\Sigma\:{M}_{{y}} ^{{B}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{8}\Delta{N}_{{C}} \:+\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{4}{N}_{{A}} \:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:{N}_{{C}} \:=\:−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\:{kN} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{equate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{direction}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{zero}\:,\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{determine} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{additional}\:\Delta{N}_{{B}} \:\mathrm{force} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\:\Sigma{F}_{{z}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\:\Delta{N}_{{A}} \:+\:\Delta{N}_{{B}} \:+\:\Delta{N}_{{C}} \:=\:\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$${N}_{{B}} \:=\:−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\:{kN}. \\ $$
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 10/Jun/20

Commented by mr W last updated on 11/Jun/20

$$\Delta{F}_{{B}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Delta{F}_{{C}} =\mathrm{2}\:{KN} \\ $$
