Question Number 92925 by frc2crc last updated on 09/May/20
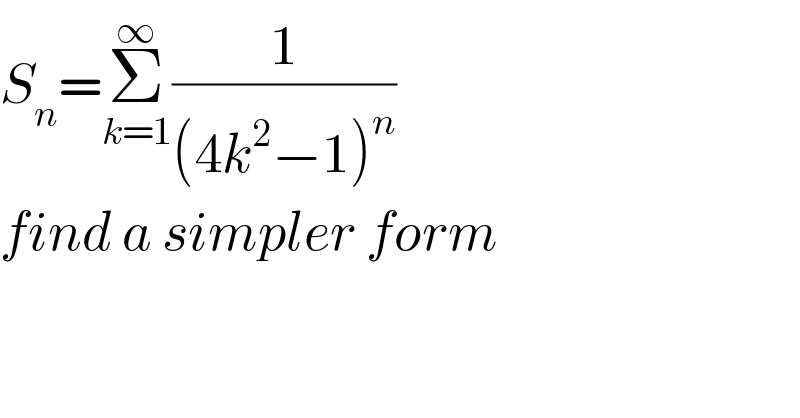
$${S}_{{n}} =\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{4}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} } \\ $$$${find}\:{a}\:{simpler}\:{form} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 09/May/20

$${check}\:{your}\:{question}\:{please}. \\ $$$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}\:{or}\:\infty} {\sum}} \\ $$
Commented by frc2crc last updated on 09/May/20
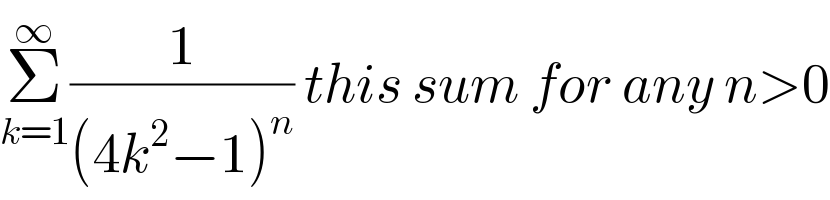
$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{4}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }\:{this}\:{sum}\:{for}\:{any}\:{n}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 09/May/20

$$\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{convergent}\:\mathrm{for}\:{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}.\:\mathrm{We} \\ $$$$\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{limit}\:\mathrm{comparion}\:\mathrm{test}. \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}{k}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{evaluated}\:\mathrm{using} \\ $$$$\mathrm{known}\:\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{expansion}\:\mathrm{for}\:\pi^{\mathrm{2}} . \\ $$$$−−−−− \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{check}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{generic}\:\mathrm{closed} \\ $$$$\mathrm{form}\:\mathrm{formula}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{possible}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{It}\:\mathrm{may}\:\mathrm{exists}\:\mathrm{using}\:\mathrm{zeta}\:\mathrm{function}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 10/May/20
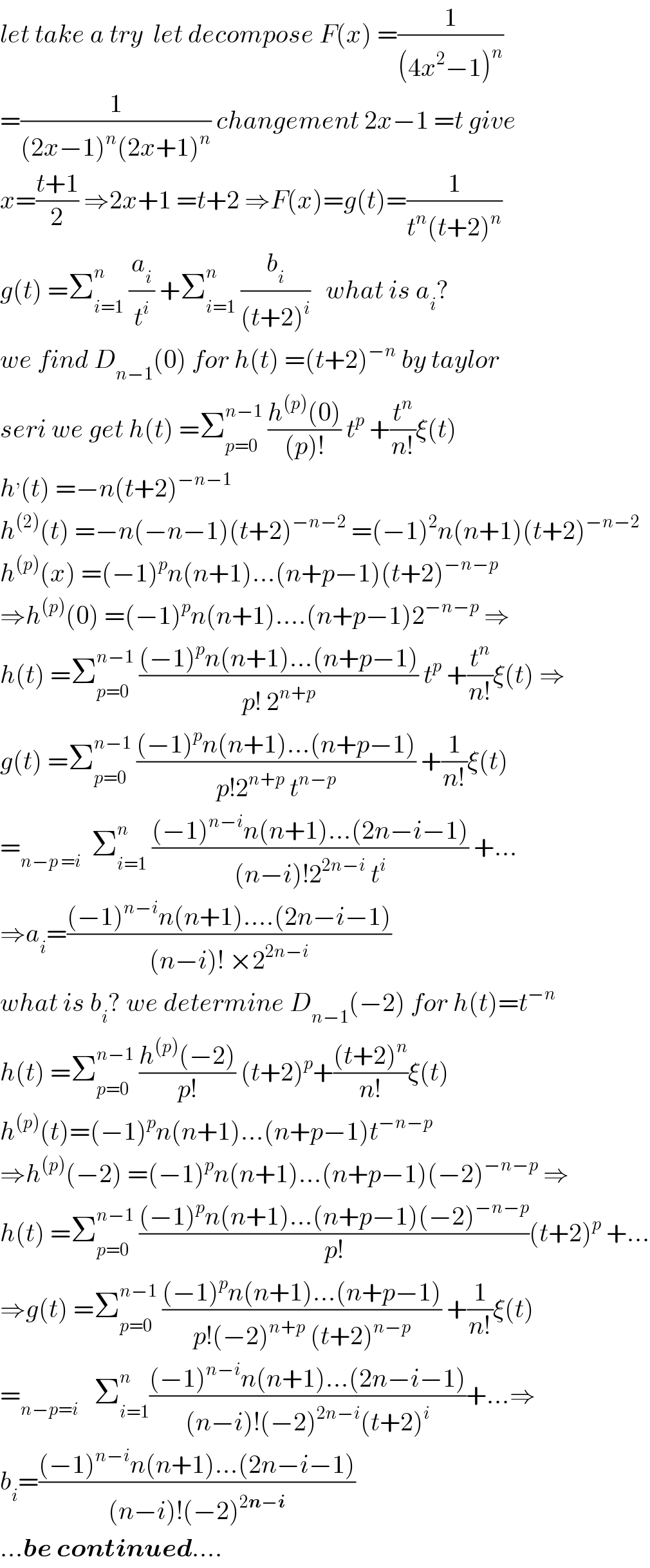
$${let}\:{take}\:{a}\:{try}\:\:{let}\:{decompose}\:{F}\left({x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }\:{changement}\:\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\:={t}\:{give} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{{t}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\:={t}+\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{F}\left({x}\right)={g}\left({t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}^{{n}} \left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}} } \\ $$$${g}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{i}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{a}_{{i}} }{{t}^{{i}} }\:+\sum_{{i}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{b}_{{i}} }{\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{i}} }\:\:\:{what}\:{is}\:{a}_{{i}} ? \\ $$$${we}\:{find}\:{D}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:{for}\:{h}\left({t}\right)\:=\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}} \:{by}\:{taylor} \\ $$$${seri}\:{we}\:{get}\:{h}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{\left({p}\right)!}\:{t}^{{p}} \:+\frac{{t}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\xi\left({t}\right) \\ $$$${h}^{,} \left({t}\right)\:=−{n}\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−\mathrm{1}} \: \\ $$$${h}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({t}\right)\:=−{n}\left(−{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−\mathrm{2}} \:=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left({x}\right)\:=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−{p}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)….\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{2}^{−{n}−{p}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${h}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{{p}!\:\mathrm{2}^{{n}+{p}} }\:{t}^{{p}} \:+\frac{{t}^{{n}} }{{n}!}\xi\left({t}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${g}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{{p}!\mathrm{2}^{{n}+{p}} \:{t}^{{n}−{p}} }\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!}\xi\left({t}\right) \\ $$$$=_{{n}−{p}\:={i}} \:\:\sum_{{i}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−{i}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({n}−{i}\right)!\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}} \:{t}^{{i}} }\:+… \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{{i}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−{i}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)….\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({n}−{i}\right)!\:×\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}} } \\ $$$${what}\:{is}\:{b}_{{i}} ?\:{we}\:{determine}\:{D}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \left(−\mathrm{2}\right)\:{for}\:{h}\left({t}\right)={t}^{−{n}} \\ $$$${h}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left(−\mathrm{2}\right)}{{p}!}\:\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{p}} +\frac{\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}!}\xi\left({t}\right) \\ $$$${h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left({t}\right)=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right){t}^{−{n}−{p}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{h}^{\left({p}\right)} \left(−\mathrm{2}\right)\:=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−{p}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${h}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{−{n}−{p}} }{{p}!}\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{p}} \:+… \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{g}\left({t}\right)\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{p}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left({n}+{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{{p}!\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}+{p}} \:\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}−{p}} }\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}!}\xi\left({t}\right) \\ $$$$=_{{n}−{p}={i}} \:\:\:\sum_{{i}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−{i}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({n}−{i}\right)!\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}} \left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{{i}} }+…\Rightarrow \\ $$$${b}_{{i}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−{i}} {n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)…\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{i}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({n}−{i}\right)!\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{n}}−\boldsymbol{{i}}} } \\ $$$$…\boldsymbol{{be}}\:\boldsymbol{{continued}}…. \\ $$
