Question Number 118952 by Backer last updated on 21/Oct/20

$$\mathrm{Salut} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Pouvez}\:\mathrm{vous}\:\mathrm{m}'\mathrm{aider}\:\mathrm{avec}\:\mathrm{ce}\:\mathrm{devoir}? \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{Examiner}\:\mathrm{si}\:\mathrm{les}\:\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{suivantes}\:\mathrm{sont}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{absolument}\:\mathrm{convergentes}\:\mathrm{ou}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{semi}−\mathrm{convergentes} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\left(-\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}-\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\left(-\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}-\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{k}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{Etudier}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{convergence}\:\mathrm{des}\:\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{suivantes} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\left(\mathrm{2k}\right)!}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}} } \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Bird last updated on 21/Oct/20
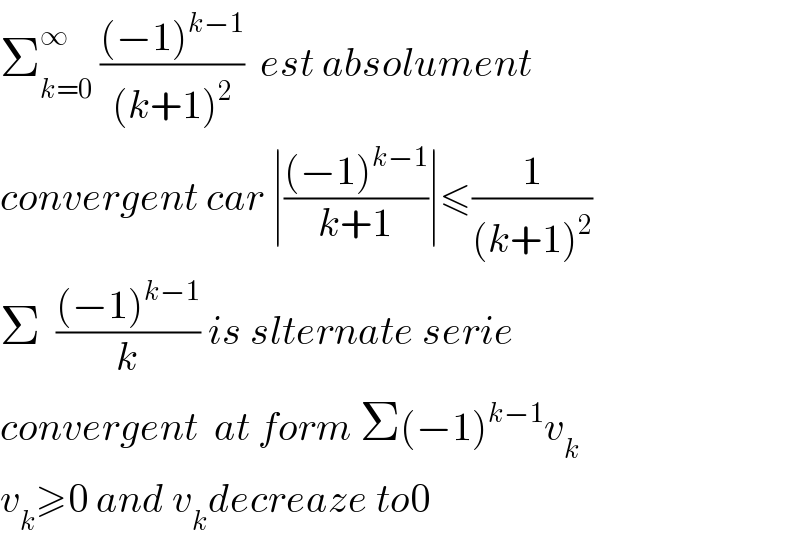
$$\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}−\mathrm{1}} }{\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:{est}\:{absolument} \\ $$$${convergent}\:{car}\:\mid\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}−\mathrm{1}} }{{k}+\mathrm{1}}\mid\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Sigma\:\:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}−\mathrm{1}} }{{k}}\:{is}\:{slternate}\:{serie} \\ $$$${convergent}\:\:{at}\:{form}\:\Sigma\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}−\mathrm{1}} {v}_{{k}} \\ $$$${v}_{{k}} \geqslant\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:{v}_{{k}} {decreaze}\:{to}\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by Bird last updated on 21/Oct/20
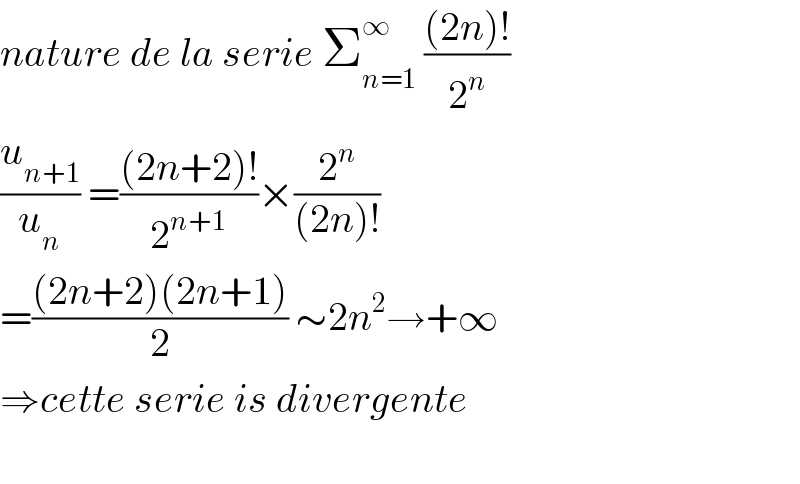
$${nature}\:{de}\:{la}\:{serie}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} } \\ $$$$\frac{{u}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{u}_{{n}} }\:=\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\right)!}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }×\frac{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!} \\ $$$$=\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:\sim\mathrm{2}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \rightarrow+\infty \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{cette}\:{serie}\:{is}\:{divergente} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
