Question Number 162804 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 01/Jan/22
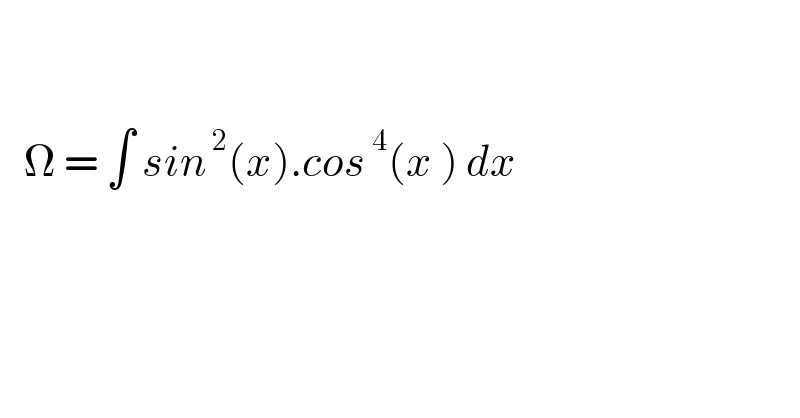
$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\Omega\:=\:\int\:{sin}^{\:\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right).{cos}^{\:\mathrm{4}} \left({x}\:\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 01/Jan/22
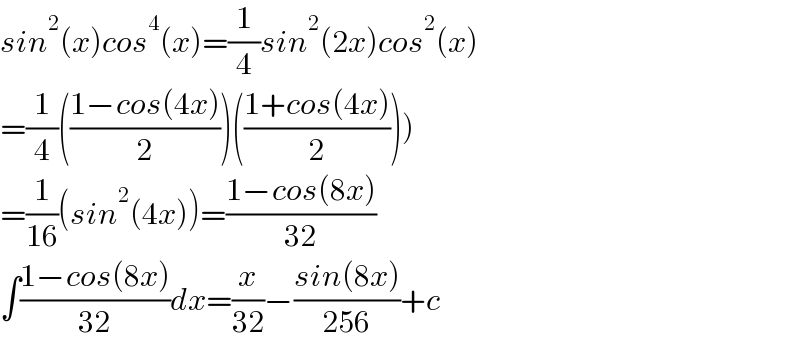
$${sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right){cos}^{\mathrm{4}} \left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right){cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\left.=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+{cos}\left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\left({sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{4}{x}\right)\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{8}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{32}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{8}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{32}}{dx}=\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{32}}−\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{8}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{256}}+{c} \\ $$
Commented by tounghoungko last updated on 02/Jan/22
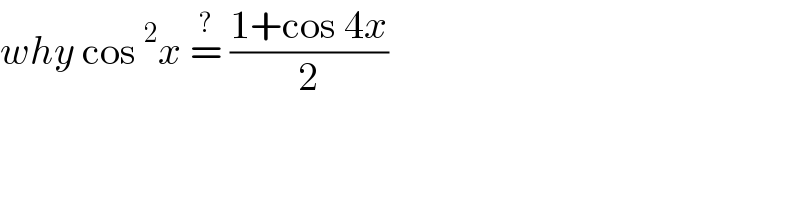
$${why}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:\overset{?} {=}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{4}{x}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by john_santu last updated on 01/Jan/22
![Ω = (1/4)∫ sin^2 2x cos^2 x dx Ω = (1/(16))∫ (2sin 2x cos x)^2 dx Ω= (1/(16))∫ (sin 3x +sin x)^2 dx Ω=(1/(16))∫ [ ((1−cos 6x+1−cos 2x)/2)+2sin 3x sin x ]dx Ω =(1/(32)) (2x−(1/6)sin 6x−(1/2)sin 2x)−(1/(16))∫(cos 4x−cos 2x)dx Ω=(x/(16))−((sin 6x)/(192))−((sin 2x)/(64))−((sin 4x)/(64))+((sin 2x)/(32)) +c Ω= (x/(16))−((sin 6x)/(192))+((sin 2x)/(64))−((sin 4x)/(64))+ c](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q162808.png)
$$\:\Omega\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int\:\mathrm{sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\:\Omega\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\:\left(\mathrm{2sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\Omega=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\:\left(\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}\:+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\Omega=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\:\left[\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\right]{dx} \\ $$$$\:\Omega\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{32}}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{6}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\int\left(\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\Omega=\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{16}}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{6}{x}}{\mathrm{192}}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{64}}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{4}{x}}{\mathrm{64}}+\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{32}}\:+{c} \\ $$$$\:\Omega=\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{16}}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{6}{x}}{\mathrm{192}}+\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{64}}−\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{4}{x}}{\mathrm{64}}+\:{c} \\ $$
