Question Number 53051 by Abror last updated on 16/Jan/19
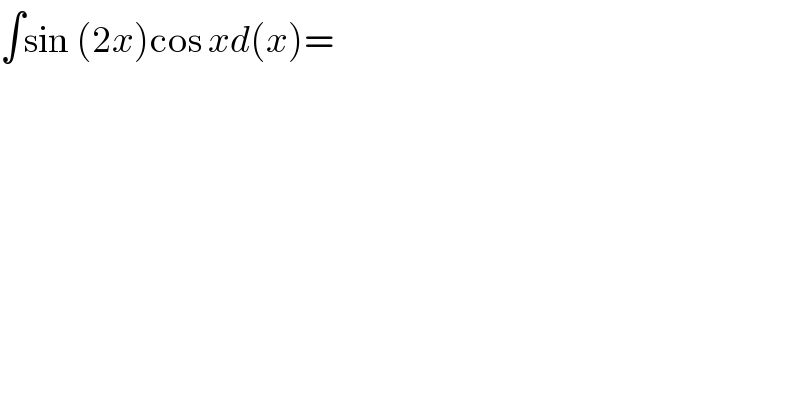
$$\int\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{xd}\left({x}\right)= \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 16/Jan/19
![(1/2)∫2sin2xcosxdx =(1/2)∫(sin3x+sinx)dx =(1/2)[((−cos3x)/3)+((−cosx)/)]+c](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q53053.png)
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{2}{sin}\mathrm{2}{xcosxdx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left({sin}\mathrm{3}{x}+{sinx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{−{cos}\mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{−{cosx}}{}\right]+{c} \\ $$
Answered by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 16/Jan/19
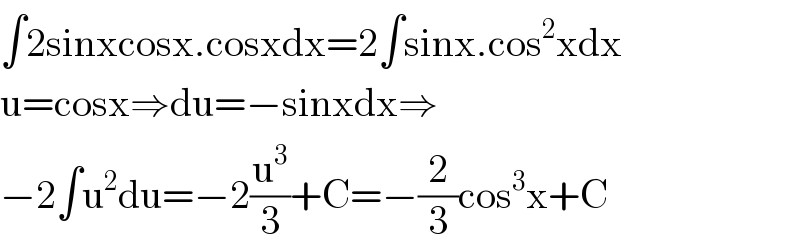
$$\int\mathrm{2sinxcosx}.\mathrm{cosxdx}=\mathrm{2}\int\mathrm{sinx}.\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{xdx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{cosx}\Rightarrow\mathrm{du}=−\mathrm{sinxdx}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}\int\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{du}=−\mathrm{2}\frac{\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{C}=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{C} \\ $$
