Question Number 117728 by syamil last updated on 13/Oct/20
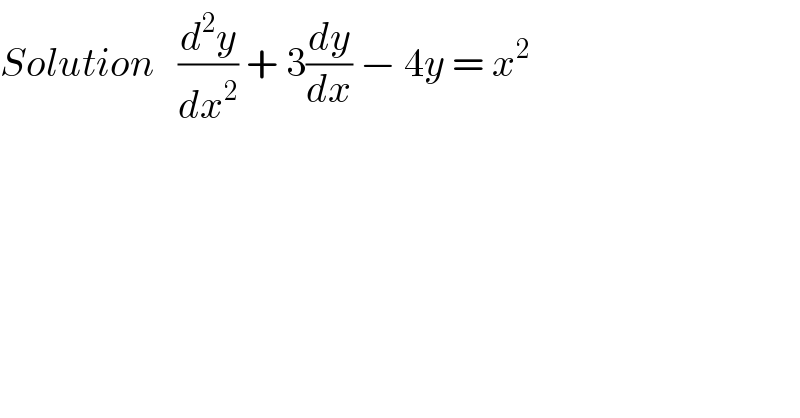
$${Solution}\:\:\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\mathrm{3}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:−\:\mathrm{4}{y}\:=\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 13/Oct/20
![y=e^(mx) (m^2 +3m−4)e^(mx) =0 e^(mx) ≠0 m^2 +4m−m−4=0 (m+4)(m−1)=0→m=1,−4 C.F=C_1 e^x +C_2 e^(−4x) P.I=(x^2 /(D^2 +3D−4))=(x^2 /((D+4)(D−1)))=(1/5)((1/(D−1))−(1/(D+4)))x^2 y=(1/5)[((−1)/(1−D))−(1/(4(1+(D/4))))]x^2 y=((−1)/5)[(1−D)^(−1) +(1/4)(1+(D/4))^(−1) ]x^2 y=((−1)/5)[(1+D+D^2 +D^3 +...)+(1/4)(1−(D/4)+(D^2 /(16))−(D^3 /(64)))]x^2 y=((−1)/5)[(x^2 +2x+2)+(1/4)(x^2 −((2x)/4)+(2/(16)))] =((−1)/5)[((5x^2 )/4)+2x(1−(1/(16)))+2+(2/(64))] =((−1)/5)[((5x^2 )/4)+((15x)/8)+((130)/(64))] y=C_1 e^x +C_2 e^(−4x) −(1/5)(((5x^2 )/4)+((15x)/8)+((65)/(32)))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q117775.png)
$${y}={e}^{{mx}} \\ $$$$\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{m}−\mathrm{4}\right){e}^{{mx}} =\mathrm{0}\:\:\:{e}^{{mx}} \neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{m}−{m}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({m}+\mathrm{4}\right)\left({m}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow{m}=\mathrm{1},−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${C}.{F}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} \\ $$$${P}.{I}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{D}−\mathrm{4}}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({D}+\mathrm{4}\right)\left({D}−\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}−\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}+\mathrm{4}}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{D}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{D}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)}\right]{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\left(\mathrm{1}−{D}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{D}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}} \right]{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\left(\mathrm{1}+{D}+{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +{D}^{\mathrm{3}} +…\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{D}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{{D}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{16}}−\frac{{D}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{64}}\right)\right]{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{16}}\right)\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{2}{x}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\right)+\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{64}}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{15}{x}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\mathrm{130}}{\mathrm{64}}\right] \\ $$$${y}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{15}{x}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\mathrm{65}}{\mathrm{32}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Oct/20
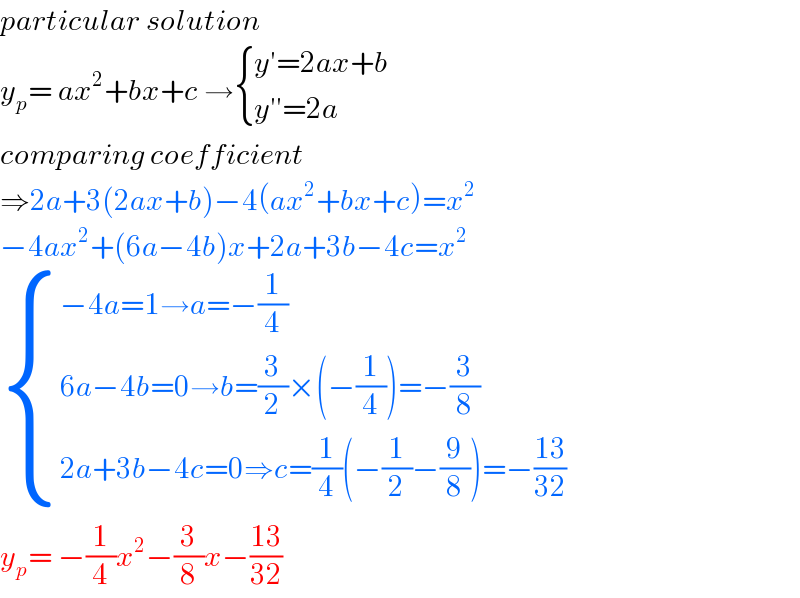
$${particular}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} =\:{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c}\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{y}'=\mathrm{2}{ax}+{b}}\\{{y}''=\mathrm{2}{a}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${comparing}\:{coefficient}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{a}+\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}{ax}+{b}\right)−\mathrm{4}\left({ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{4}{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{6}{a}−\mathrm{4}{b}\right){x}+\mathrm{2}{a}+\mathrm{3}{b}−\mathrm{4}{c}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{−\mathrm{4}{a}=\mathrm{1}\rightarrow{a}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}\\{\mathrm{6}{a}−\mathrm{4}{b}=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow{b}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}×\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}}\\{\mathrm{2}{a}+\mathrm{3}{b}−\mathrm{4}{c}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{c}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{8}}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{32}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} =\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{8}}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{32}} \\ $$
Answered by Bird last updated on 14/Oct/20
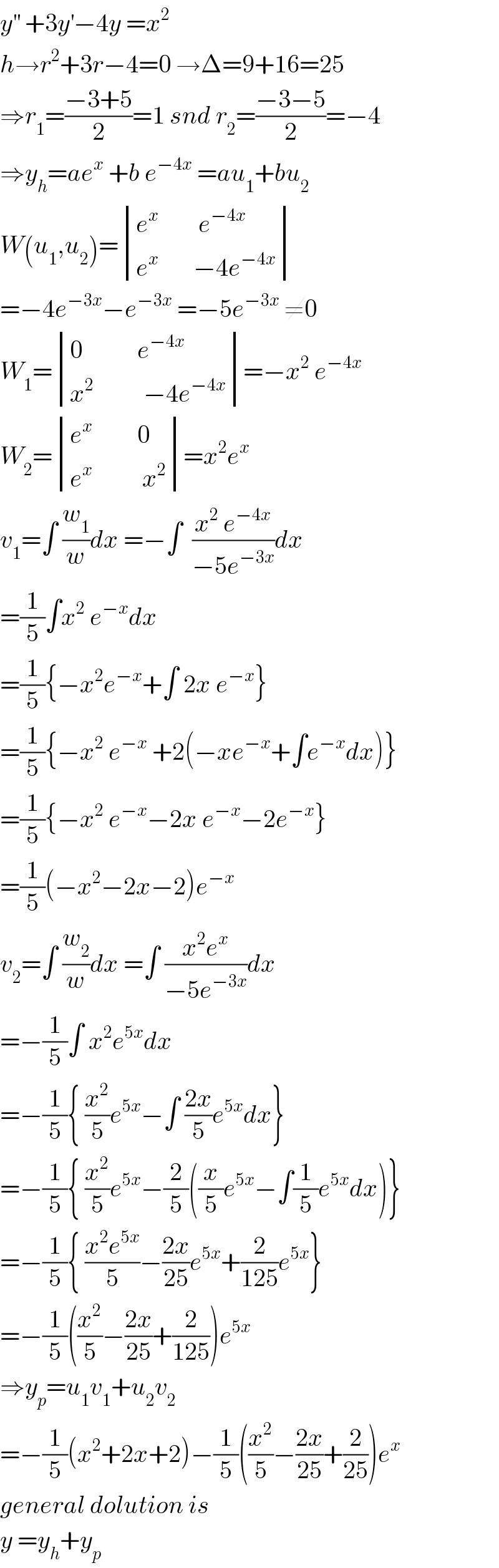
$${y}^{''} \:+\mathrm{3}{y}^{'} −\mathrm{4}{y}\:={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${h}\rightarrow{r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{r}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\Delta=\mathrm{9}+\mathrm{16}=\mathrm{25} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{r}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{−\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}\:{snd}\:{r}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{−\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}_{{h}} ={ae}^{{x}} \:+{b}\:{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} \:={au}_{\mathrm{1}} +{bu}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${W}\left({u}_{\mathrm{1}} ,{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\begin{vmatrix}{{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} }\\{{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{4}{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} }\end{vmatrix} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{4}{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{x}} −{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{x}} \:=−\mathrm{5}{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{x}} \:\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} }\\{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{4}{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} \\ $$$${W}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}}\\{{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\end{vmatrix}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\:\frac{{w}_{\mathrm{1}} }{{w}}{dx}\:=−\int\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−\mathrm{4}{x}} }{−\mathrm{5}{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{x}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} +\int\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:{e}^{−{x}} \right\} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−{x}} \:+\mathrm{2}\left(−{xe}^{−{x}} +\int{e}^{−{x}} {dx}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{e}^{−{x}} −\mathrm{2}{x}\:{e}^{−{x}} −\mathrm{2}{e}^{−{x}} \right\} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right){e}^{−{x}} \\ $$$${v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\:\frac{{w}_{\mathrm{2}} }{{w}}{dx}\:=\int\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{x}} }{−\mathrm{5}{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{x}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\int\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} −\int\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} {dx}\right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} −\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} −\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} {dx}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} }{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{25}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{125}}{e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} \right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{25}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{125}}\right){e}^{\mathrm{5}{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}_{{p}} ={u}_{\mathrm{1}} {v}_{\mathrm{1}} +{u}_{\mathrm{2}} {v}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{25}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{25}}\right){e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${general}\:{dolution}\:{is} \\ $$$${y}\:={y}_{{h}} +{y}_{{p}} \\ $$
