Question Number 117585 by syamil last updated on 12/Oct/20
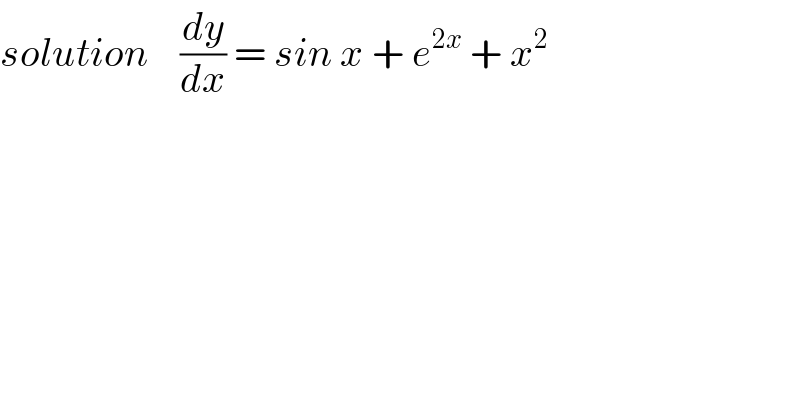
$${solution}\:\:\:\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:{sin}\:{x}\:+\:{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:+\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 12/Oct/20

$${i}\:{can}\:{not}\:{post}\:{question} \\ $$$${so}\:{here}\:{i}\:{am}\:{posting}?{question} \\ $$$$\frac{\boldsymbol{{d}}^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{y}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\boldsymbol{{a}}^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{y}}=\boldsymbol{{cos}}\left(\boldsymbol{{ax}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 12/Oct/20
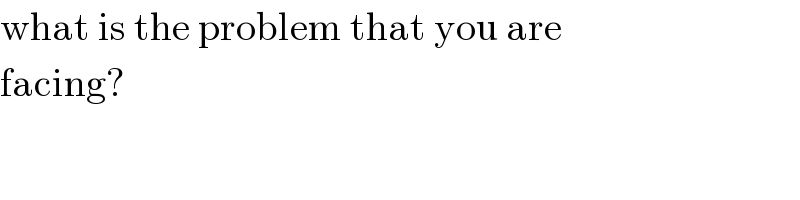
$$\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{problem}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{are} \\ $$$$\mathrm{facing}? \\ $$
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 12/Oct/20
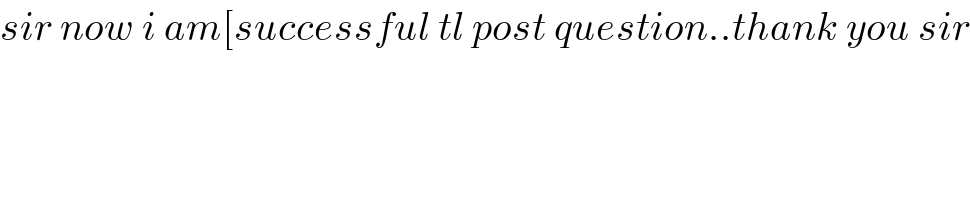
$${sir}\:{now}\:{i}\:{am}\left[{successful}\:{tl}\:{post}\:{question}..{thank}\:{you}\:{sir}\right. \\ $$
Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 12/Oct/20

$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{You}. \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 12/Oct/20
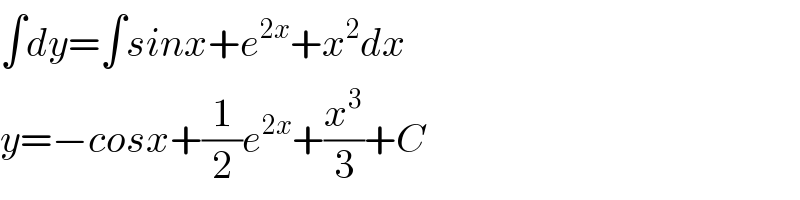
$$\int{dy}=\int{sinx}+{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {dx} \\ $$$${y}=−{cosx}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{C} \\ $$
