Question Number 171743 by Mikenice last updated on 20/Jun/22
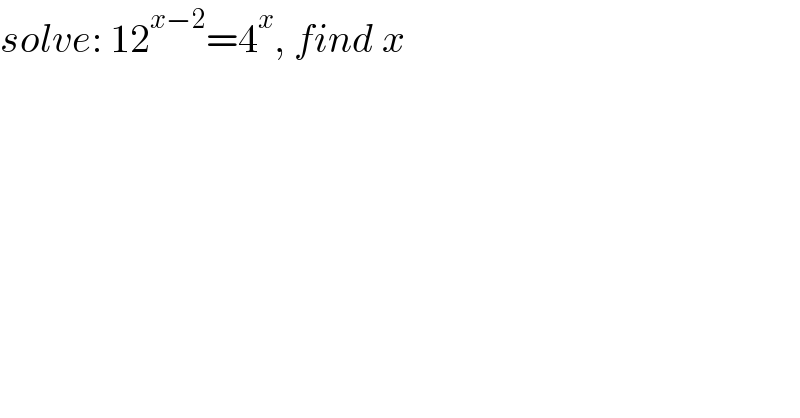
$${solve}:\:\mathrm{12}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4}^{{x}} ,\:{find}\:{x} \\ $$
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 20/Jun/22
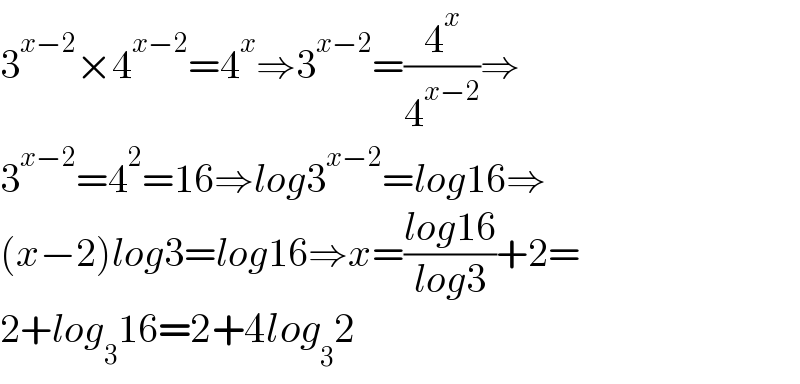
$$\mathrm{3}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} ×\mathrm{4}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4}^{{x}} \Rightarrow\mathrm{3}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{4}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{4}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} }\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{16}\Rightarrow{log}\mathrm{3}^{{x}−\mathrm{2}} ={log}\mathrm{16}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right){log}\mathrm{3}={log}\mathrm{16}\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{{log}\mathrm{16}}{{log}\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{2}= \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}+{log}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{16}=\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{4}{log}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by Mikenice last updated on 20/Jun/22

$${thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$
