Question Number 96883 by M±th+et+s last updated on 05/Jun/20
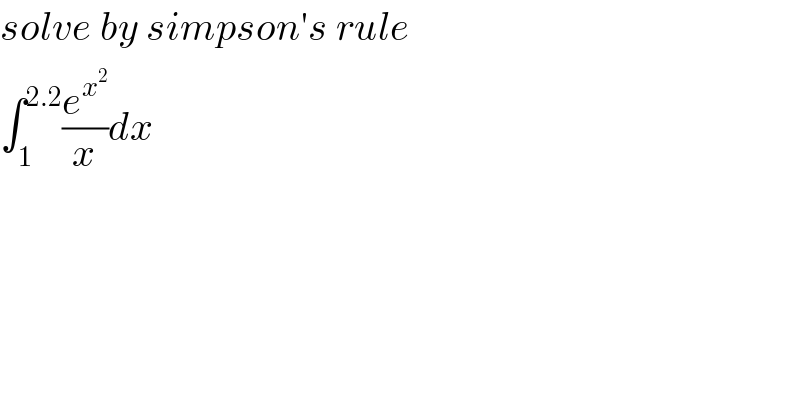
$${solve}\:{by}\:{simpson}'{s}\:{rule}\: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}} \frac{{e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{x}}{dx} \\ $$
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 05/Jun/20
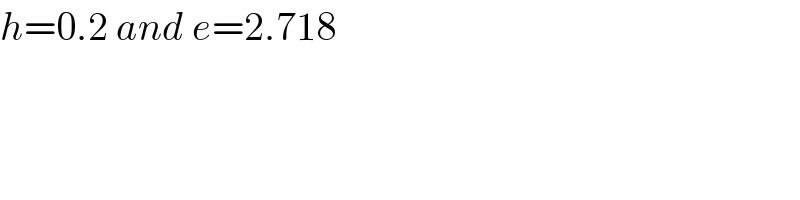
$${h}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}\:{and}\:{e}=\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{718} \\ $$
Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 05/Jun/20

$$\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{2},\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{4},\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{6},\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{8},\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}} \:=\:\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{h}}}{\mathrm{3}}\left\{\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{0}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{6}} \right)+\mathrm{4}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{1}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{3}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{5}} \right)+\mathrm{2}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}_{\mathrm{4}} \right)\right\} \\ $$$$\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\left\{\left(\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{718}+\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{457}\right)+\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{516}+\mathrm{8}.\mathrm{082}+\mathrm{27}.\mathrm{287}\right)\right. \\ $$$$\left.+\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{5}.\mathrm{069}+\mathrm{14}.\mathrm{180}\right)\right\}=\mathrm{16}.\mathrm{947} \\ $$
