Question Number 150533 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 13/Aug/21
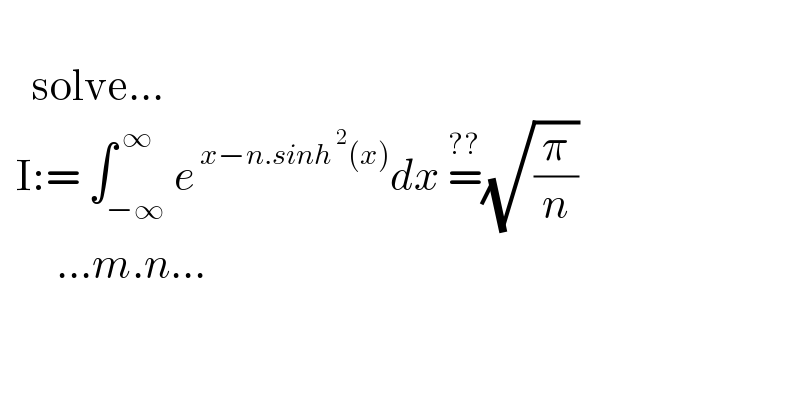
$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\mathrm{solve}… \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{I}:=\:\int_{−\infty} ^{\:\infty} {e}^{\:{x}−{n}.{sinh}^{\:\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)} {dx}\:\overset{??} {=}\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{{n}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:…{m}.{n}… \\ $$
Answered by Kamel last updated on 13/Aug/21
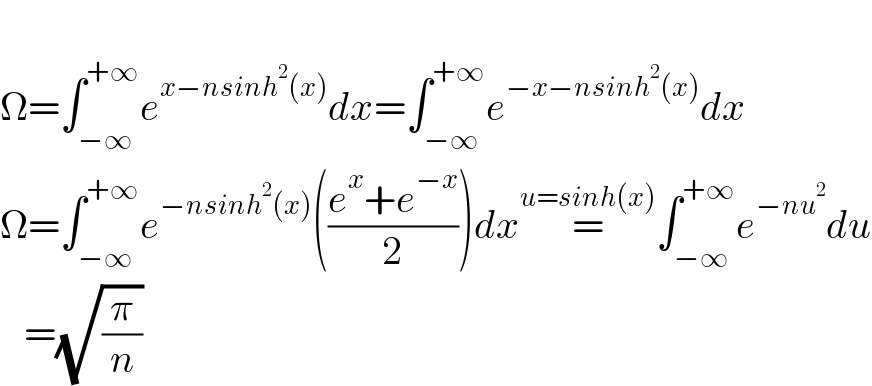
$$ \\ $$$$\Omega=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{{x}−{nsinh}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)} {dx}=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{x}−{nsinh}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)} {dx} \\ $$$$\Omega=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{nsinh}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)} \left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right){dx}\overset{{u}={sinh}\left({x}\right)} {=}\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} {e}^{−{nu}^{\mathrm{2}} } {du} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{{n}}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 13/Aug/21
$${excellent}\:{master}\:\:…{very}\:{nice}.. \\ $$
