Question Number 166391 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Feb/22
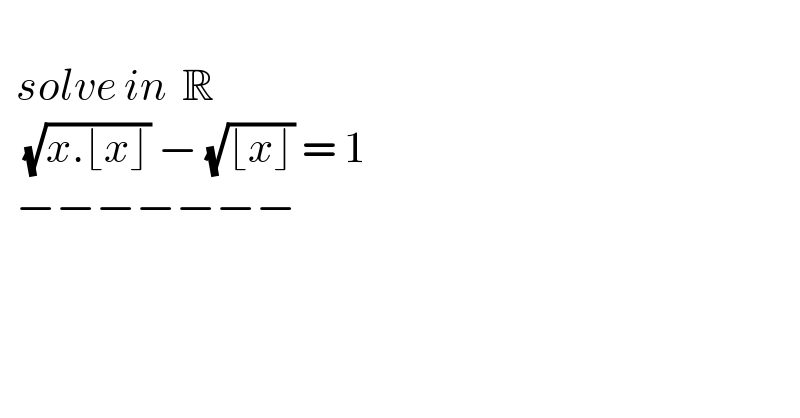
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:{solve}\:{in}\:\:\mathbb{R} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\sqrt{{x}.\lfloor{x}\rfloor}\:−\:\sqrt{\lfloor{x}\rfloor}\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:−−−−−−− \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 19/Feb/22
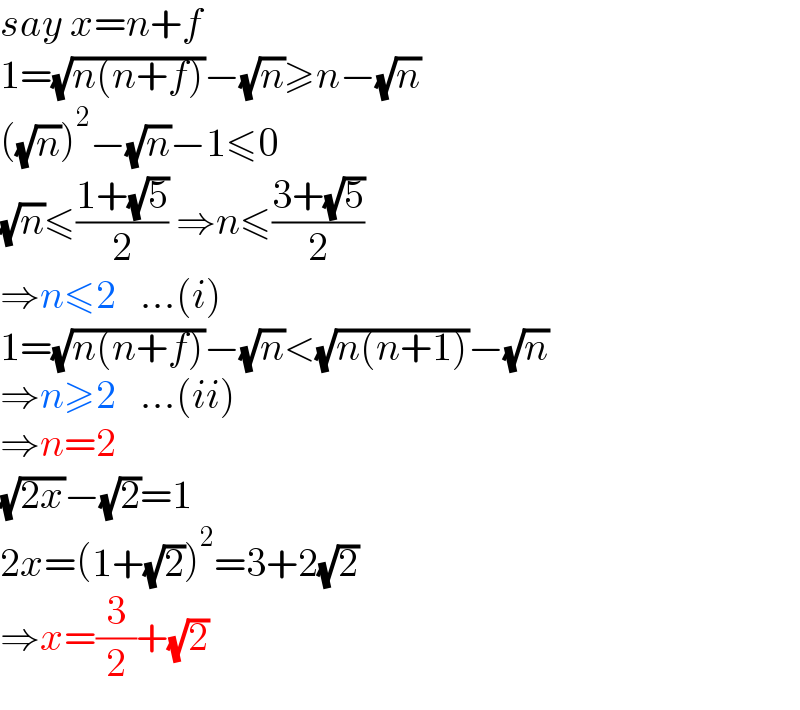
$${say}\:{x}={n}+{f} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=\sqrt{{n}\left({n}+{f}\right)}−\sqrt{{n}}\geqslant{n}−\sqrt{{n}} \\ $$$$\left(\sqrt{{n}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\sqrt{{n}}−\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\sqrt{{n}}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow{n}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\:\:\:…\left({i}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}=\sqrt{{n}\left({n}+{f}\right)}−\sqrt{{n}}<\sqrt{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}−\sqrt{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}\:\:\:…\left({ii}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Feb/22

$${bravo}\:{sir}\:{W} \\ $$
Answered by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Feb/22
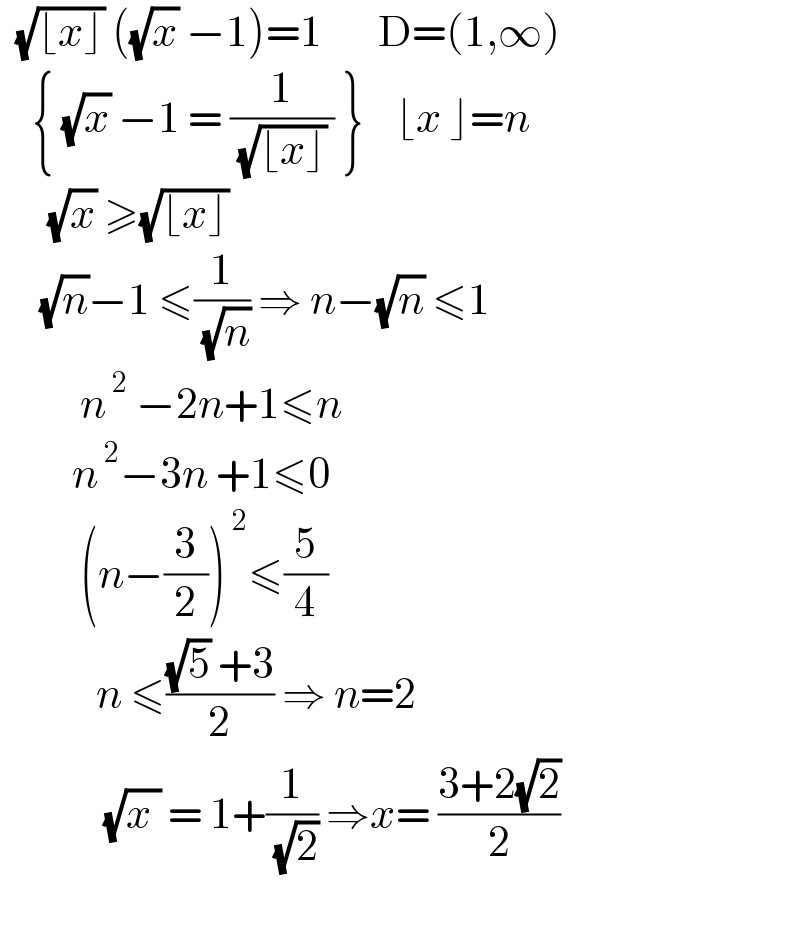
$$\:\:\sqrt{\lfloor{x}\rfloor}\:\left(\sqrt{{x}}\:−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{D}=\left(\mathrm{1},\infty\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\left\{\:\sqrt{{x}}\:−\mathrm{1}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\lfloor{x}\rfloor}\:}\:\right\}\:\:\:\:\lfloor{x}\:\rfloor={n} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\sqrt{{x}}\:\geqslant\sqrt{\lfloor{x}\rfloor} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\sqrt{{n}}−\mathrm{1}\:\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}\:\Rightarrow\:{n}−\sqrt{{n}}\:\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}^{\:\mathrm{2}} \:−\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\leqslant{n} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}^{\:\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{n}\:+\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({n}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\:\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}\:\leqslant\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\:+\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\sqrt{{x}\:}\:=\:\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$
