Question Number 156684 by mathdave last updated on 14/Oct/21
![solve the D.E [1+e^(x/y) ]dx+e^(x/y) [1−(x/y)]dy=0 any one can help pls](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q156684.png)
$${solve}\:{the}\:{D}.{E}\: \\ $$$$\left[\mathrm{1}+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \right]{dx}+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \left[\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{{y}}\right]{dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${any}\:{one}\:{can}\:{help}\:{pls} \\ $$
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 14/Oct/21
![[1+e^(x/y) ]dx=e^(x/y) [(x/y)−1]dy (dx/dy)=((e^(x/y) [(x/y)−1])/([1+e^(x/y) ])) let (x/y)=v x=vy (dx/dy)=v+y(dv/dy) v+y(dv/dy) =((e^v (v−1))/((1+e^v ))) y(dv/dy) =((ve^v −e^v −v−ve^v )/((1+e^v ))) y(dv/dy)= −(((v+e^v ))/((1+e^v ))) ∫(((1+e^v )dv)/(v+e^v ))= −∫(dy/y) ∫((d(v+e^v ))/(v+e^v ))=−∫(dy/y) ln∣v+e^v ∣=−lny+lnC ln∣v+e^v ∣=ln(C/y) v+e^v =(C/y) y((x/y) +e^(x/y) )=C](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q156688.png)
$$\left[\mathrm{1}+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \right]{dx}={e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \left[\frac{{x}}{{y}}−\mathrm{1}\right]{dy} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{{dy}}=\frac{{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \left[\frac{{x}}{{y}}−\mathrm{1}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{1}+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \right]} \\ $$$${let}\:\frac{{x}}{{y}}={v} \\ $$$$\:{x}={vy} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{{dy}}={v}+{y}\frac{{dv}}{{dy}} \\ $$$${v}+{y}\frac{{dv}}{{dy}}\:=\frac{{e}^{{v}} \left({v}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{v}} \right)} \\ $$$${y}\frac{{dv}}{{dy}}\:=\frac{{ve}^{{v}} −{e}^{{v}} −{v}−{ve}^{{v}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{v}} \right)} \\ $$$${y}\frac{{dv}}{{dy}}=\:−\frac{\left({v}+{e}^{{v}} \right)}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{v}} \right)} \\ $$$$\:\int\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{v}} \right){dv}}{{v}+{e}^{{v}} }=\:−\int\frac{{dy}}{{y}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{d}\left({v}+{e}^{{v}} \right)}{{v}+{e}^{{v}} }=−\int\frac{{dy}}{{y}} \\ $$$${ln}\mid{v}+{e}^{{v}} \mid=−{lny}+{lnC} \\ $$$${ln}\mid{v}+{e}^{{v}} \mid={ln}\frac{{C}}{{y}} \\ $$$${v}+{e}^{{v}} =\frac{{C}}{{y}} \\ $$$${y}\left(\frac{{x}}{{y}}\:+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \right)={C} \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 14/Oct/21
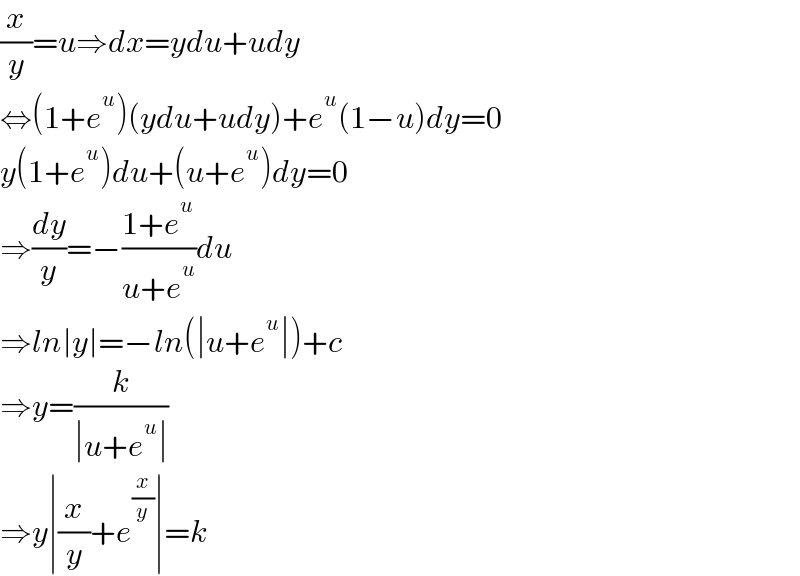
$$\frac{{x}}{{y}}={u}\Rightarrow{dx}={ydu}+{udy} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{u}} \right)\left({ydu}+{udy}\right)+{e}^{{u}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{u}\right){dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${y}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{u}} \right){du}+\left({u}+{e}^{{u}} \right){dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dy}}{{y}}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{{u}} }{{u}+{e}^{{u}} }{du} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{ln}\mid{y}\mid=−{ln}\left(\mid{u}+{e}^{{u}} \mid\right)+{c} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}=\frac{{k}}{\mid{u}+{e}^{{u}} \mid} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}\mid\frac{{x}}{{y}}+{e}^{\frac{{x}}{{y}}} \mid={k} \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 14/Oct/21

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
