Question Number 169526 by ali009 last updated on 01/May/22
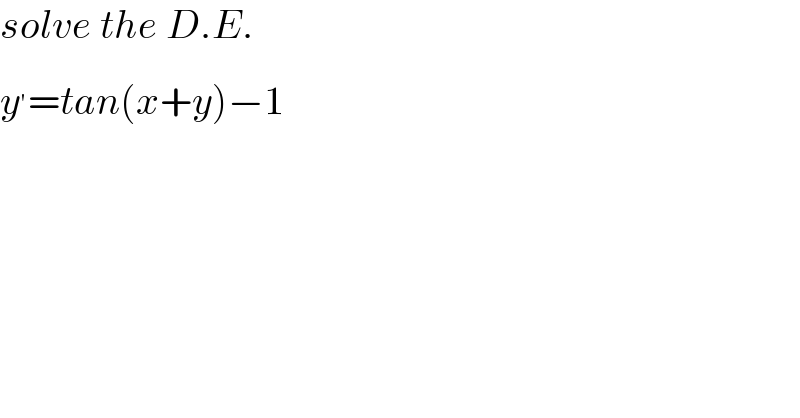
$${solve}\:{the}\:{D}.{E}. \\ $$$${y}^{'} ={tan}\left({x}+{y}\right)−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 01/May/22
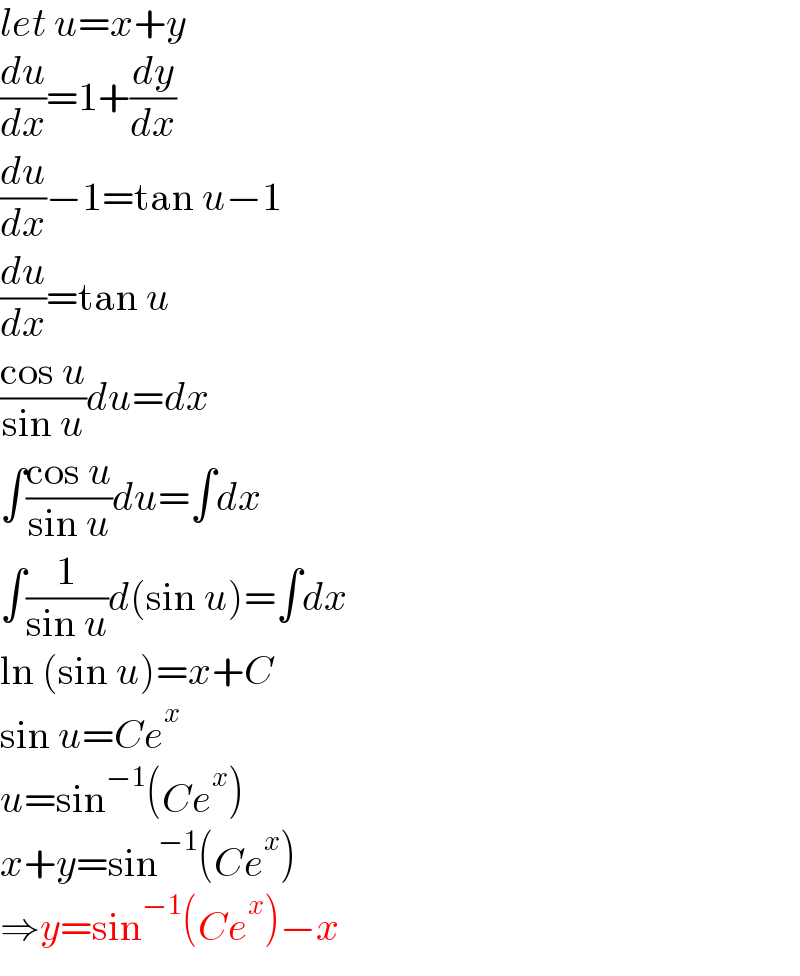
$${let}\:{u}={x}+{y} \\ $$$$\frac{{du}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{du}}{{dx}}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{tan}\:{u}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{{du}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{tan}\:{u} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{u}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{u}}{du}={dx} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{u}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{u}}{du}=\int{dx} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{u}}{d}\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{u}\right)=\int{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{u}\right)={x}+{C} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:{u}={Ce}^{{x}} \\ $$$${u}=\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({Ce}^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$${x}+{y}=\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({Ce}^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}=\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({Ce}^{{x}} \right)−{x} \\ $$
Commented by ali009 last updated on 01/May/22

$${thank}\:{you}\: \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 02/May/22

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
