Question Number 91010 by jagoll last updated on 27/Apr/20
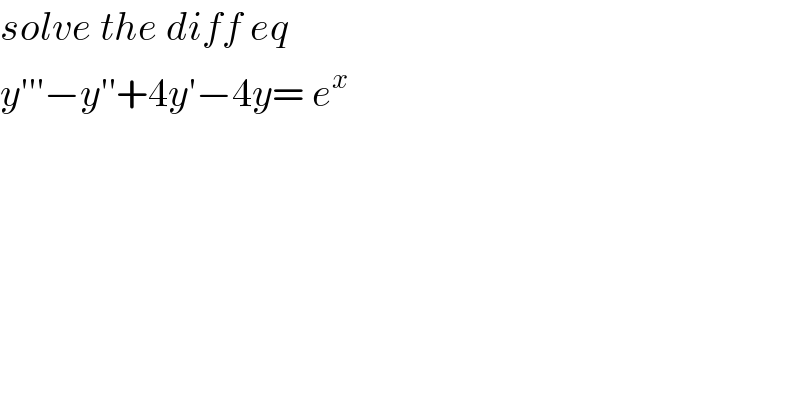
$${solve}\:{the}\:{diff}\:{eq}\: \\ $$$${y}'''−{y}''+\mathrm{4}{y}'−\mathrm{4}{y}=\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 27/Apr/20

$${the}\:{characteristic}\:{equation}\: \\ $$$${w}^{\mathrm{3}} −{w}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{w}\:−\mathrm{4}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${with}\:{roots}\:{are}\:{w}\:=\:\mathrm{1},\:\pm\:\mathrm{2}{i} \\ $$$${complementary}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{{c}} \:=\:{K}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{K}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}+{K}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$${particular}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:{Qxe}^{{x}} +{Re}^{{x}} \\ $$$${y}'=\:{Qxe}^{{x}} +\left({Q}+{R}\right){e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${y}''=\:{Qxe}^{{x}} +\left(\mathrm{2}{Q}+{R}\right){e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${y}'''\:=\:{Qxe}^{{x}} +\left(\mathrm{3}{Q}+{R}\right){e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${comparing}\:{coeff} \\ $$$${y}'''−{y}''+\mathrm{4}{y}'−\mathrm{4}{y}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{Qe}^{{x}} =\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${Q}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$${general}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$${y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{xe}^{{x}} +{K}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{K}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}+{K}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 27/Apr/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{both} \\ $$
Answered by MWSuSon last updated on 27/Apr/20
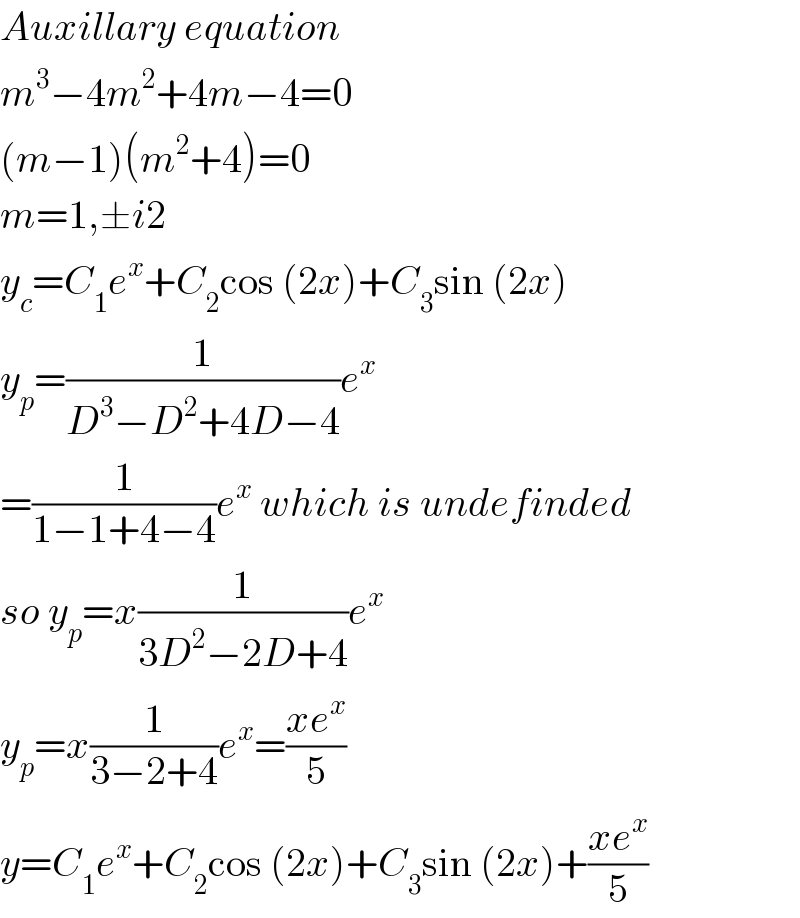
$${Auxillary}\:{equation} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{m}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({m}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${m}=\mathrm{1},\pm{i}\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${y}_{{c}} ={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}^{\mathrm{3}} −{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{D}−\mathrm{4}}{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{4}}{e}^{{x}} \:{which}\:{is}\:{undefinded} \\ $$$${so}\:{y}_{{p}} ={x}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{D}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{4}}{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} ={x}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{4}}{e}^{{x}} =\frac{{xe}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$${y}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)+\frac{{xe}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$
