Question Number 153079 by mathdanisur last updated on 04/Sep/21
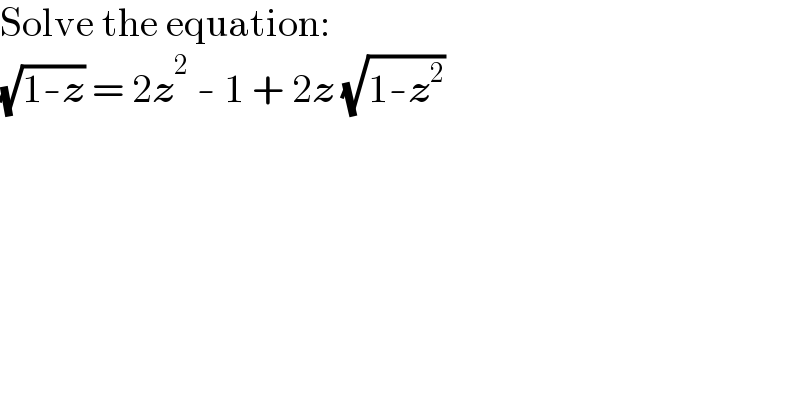
$$\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}: \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{1}-\boldsymbol{{z}}}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{z}}^{\mathrm{2}} \:-\:\mathrm{1}\:+\:\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{z}}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}-\boldsymbol{{z}}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 04/Sep/21
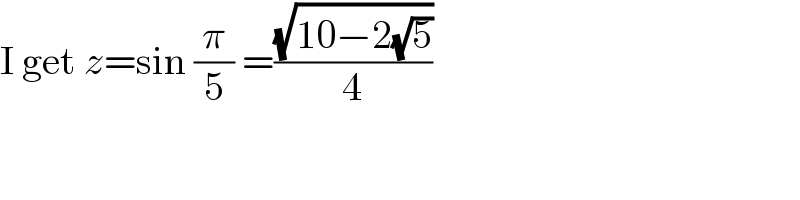
$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{get}\:{z}=\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{5}}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{10}−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Answered by liberty last updated on 04/Sep/21
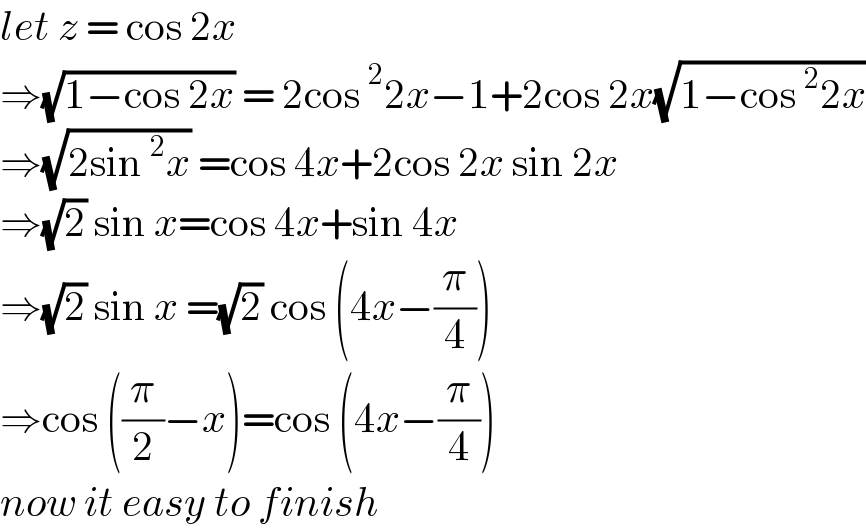
$${let}\:{z}\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}\:=\:\mathrm{2cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2sin}\:^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\:=\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}=\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{4}{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{4}{x}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−{x}\right)=\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{4}{x}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$${now}\:{it}\:{easy}\:{to}\:{finish} \\ $$
