Question Number 152543 by liberty last updated on 29/Aug/21
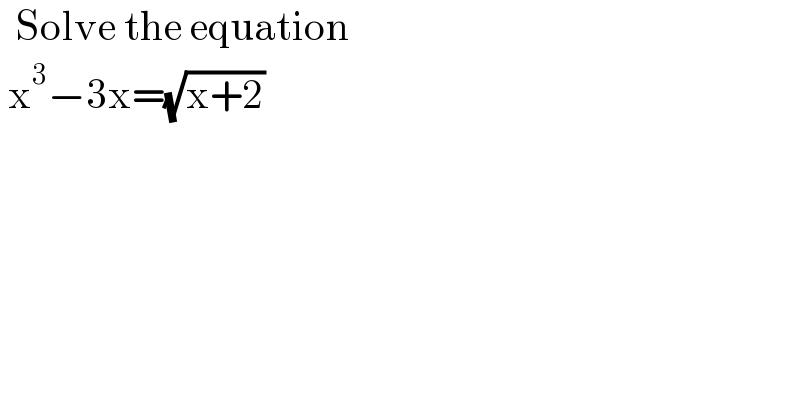
$$\:\:\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{3x}=\sqrt{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by EDWIN88 last updated on 29/Aug/21
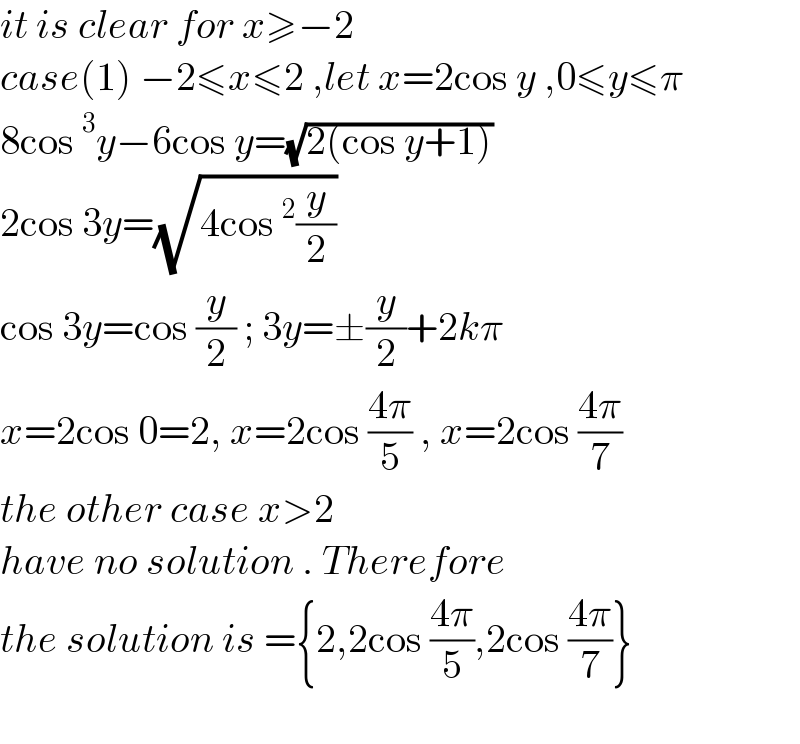
$${it}\:{is}\:{clear}\:{for}\:{x}\geqslant−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${case}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:−\mathrm{2}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}\:,{let}\:{x}=\mathrm{2cos}\:{y}\:,\mathrm{0}\leqslant{y}\leqslant\pi \\ $$$$\mathrm{8cos}\:^{\mathrm{3}} {y}−\mathrm{6cos}\:{y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{cos}\:{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{3}{y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{4cos}\:^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{y}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}{y}=\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{{y}}{\mathrm{2}}\:;\:\mathrm{3}{y}=\pm\frac{{y}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}{k}\pi \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{2cos}\:\mathrm{0}=\mathrm{2},\:{x}=\mathrm{2cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{4}\pi}{\mathrm{5}}\:,\:{x}=\mathrm{2cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{4}\pi}{\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$${the}\:{other}\:{case}\:{x}>\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${have}\:{no}\:{solution}\:.\:{Therefore} \\ $$$${the}\:{solution}\:{is}\:=\left\{\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{4}\pi}{\mathrm{5}},\mathrm{2cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{4}\pi}{\mathrm{7}}\right\} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 29/Aug/21
![squaring (beware of false solutions!) and transforming ⇒ x^6 −6x^4 +9x^2 −x+2=0 (x−2)(x^2 +x−1)(x^3 +x^2 −2x−1)=0 ⇒ x_1 =2 [true] ★ x_2 =−(1/2)−((√5)/2) [true] ★ x_3 =−(1/2)+((√5)/2) [false] x^3 +x^2 −2x−1=0 ⇒ x_4 =−(1/3)−((2(√7))/3)cos ((π/6)+(1/3)arcsin ((√7)/(14))) [false] x_5 =−(1/3)−((2(√7))/3)sin ((1/3)arcsin ((√7)/(14))) [true] ★ x_6 =−(1/3)+((2(√7))/3)sin ((π/3)+(1/3)arcsin ((√7)/(14))) [false]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q152581.png)
$$\mathrm{squaring}\:\left(\mathrm{beware}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{false}\:\mathrm{solutions}!\right)\:\mathrm{and} \\ $$$$\mathrm{transforming}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{6}} −\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}\:\left[\mathrm{true}\right]\:\bigstar \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\left[\mathrm{true}\right]\:\bigstar \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{3}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\left[\mathrm{false}\right] \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{4}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{arcsin}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{14}}\right)\:\left[\mathrm{false}\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{5}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{arcsin}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{14}}\right)\:\left[\mathrm{true}\right]\:\bigstar \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{\mathrm{6}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{arcsin}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}}{\mathrm{14}}\right)\:\left[\mathrm{false}\right] \\ $$
