Question Number 160558 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 01/Dec/21
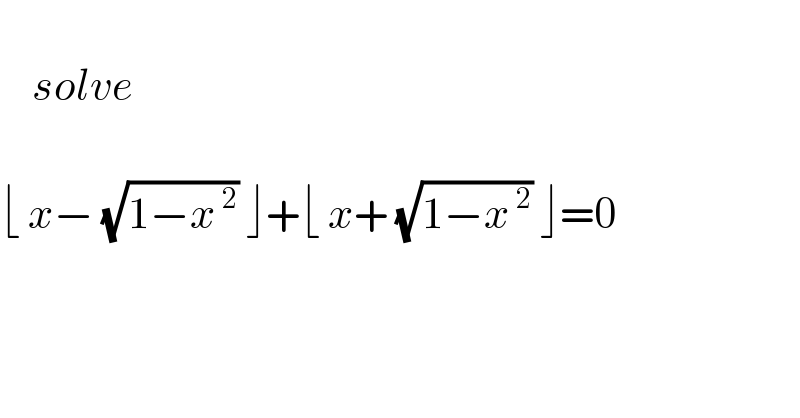
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{solve} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\lfloor\:{x}−\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\:\mathrm{2}} }\:\rfloor+\lfloor\:{x}+\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\:\mathrm{2}} }\:\rfloor=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 02/Dec/21
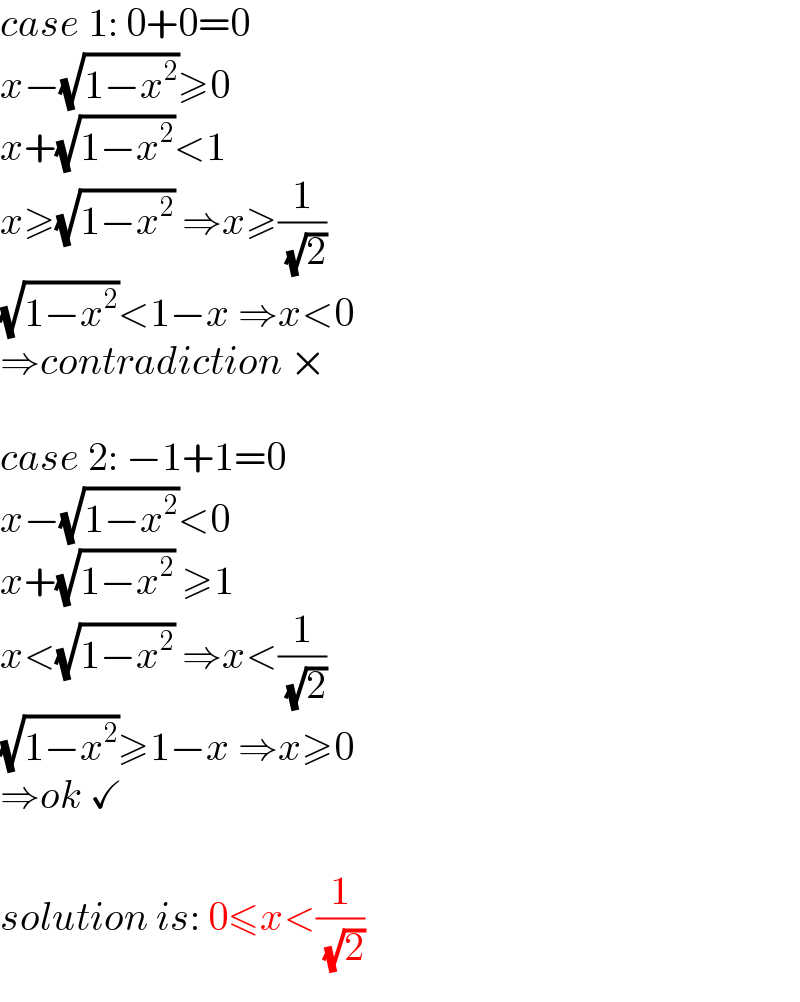
$${case}\:\mathrm{1}:\:\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{0}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}\geqslant\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow{x}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }<\mathrm{1}−{x}\:\Rightarrow{x}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{contradiction}\:× \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{2}:\:−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }<\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}<\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow{x}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\geqslant\mathrm{1}−{x}\:\Rightarrow{x}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{ok}\:\checkmark \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${solution}\:{is}:\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{x}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$
