Question Number 120780 by mathace last updated on 02/Nov/20
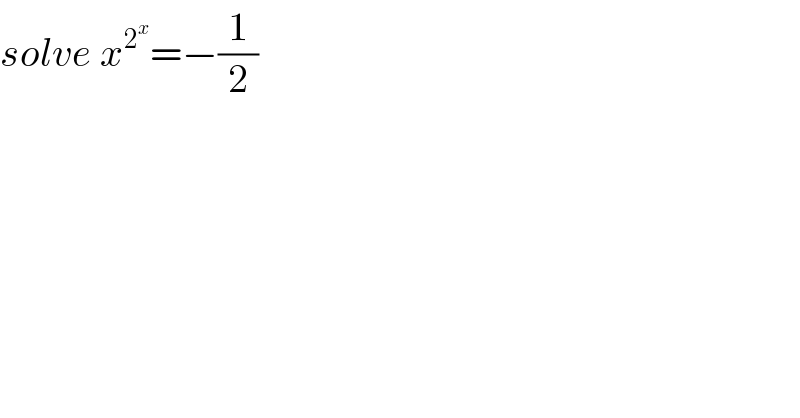
$${solve}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} } =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by Anuragkar last updated on 02/Nov/20

$${Use}\:\:{Lambert}\:{W}\:{function}\:{to}\:{work}\:{it}\:{out}…… \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 02/Nov/20

$${Complex}\:{solution}\:\left({x}\in\mathbb{C}\right).{No}\:{real}\:{solution} \\ $$
Answered by Anuragkar last updated on 14/Nov/20
![2^x ln(x)=ln(e^(iπ) )−ln(2) xln(x)ln(2)=ln(iπ−ln(2)) ln(x)e^(ln(x)) =ln(iπ−ln(2))/ln(2) Now use lambert W function W(ln(x)e^(ln(x)) )=ln(x)=W[ln{iπ−ln(2)}/ln(2)] x=e^(W[ln{iπ−ln(2)}/ln(2)]) .....this is the final answer....calculstw it using Wolframalpha](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q122046.png)
$$\mathrm{2}^{{x}} {ln}\left({x}\right)={ln}\left({e}^{{i}\pi} \right)−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${xln}\left({x}\right){ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)={ln}\left({i}\pi−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$$${ln}\left({x}\right){e}^{{ln}\left({x}\right)} ={ln}\left({i}\pi−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right)/{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${Now}\:{use}\:{lambert}\:{W}\:{function} \\ $$$${W}\left({ln}\left({x}\right){e}^{{ln}\left({x}\right)} \right)={ln}\left({x}\right)={W}\left[{ln}\left\{{i}\pi−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right\}/{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right] \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${x}={e}^{{W}\left[{ln}\left\{{i}\pi−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right\}/{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right]} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$…..{this}\:{is}\:{the}\:{final}\:{answer}….{calculstw}\:{it}\:{using}\: \\ $$$${Wolframalpha} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 13/Nov/20

$${Error}\:{in}\:{second}\:{line} \\ $$
Answered by mathace last updated on 18/Nov/20

$$ \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} } =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\left({e}^{{i}\pi} \right)−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${e}^{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \mathrm{ln}\left({x}\right)={i}\pi−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\left({e}^{{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}\right)\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:\left({i}\pi−\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$$${x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}\right)\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:\left({i}\pi−\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$$${e}^{{e}^{{t}} } \alpha+{t}=\beta\:{where}\:\alpha=\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right),\:\beta=\mathrm{ln}\:\left({i}\pi−\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right) \\ $$$$\alpha+{te}^{−{e}^{{t}} } =\beta{e}^{−{e}^{{t}} } \\ $$$$\left({t}−\beta\right){e}^{−{e}^{{t}} } =−\alpha \\ $$$$\left({t}−\beta\right){e}^{−\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}+{O}\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right)\:} =\:−\alpha \\ $$$$\left({t}−\beta\right){e}^{−\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)\:} =\:−\alpha \\ $$$$\left({t}−\beta\right){e}^{−{t}} =\frac{−\alpha}{{e}^{−\mathrm{1}} }=−\alpha{e} \\ $$$$\left(\beta−{t}\right){e}^{−{t}} =\alpha{e} \\ $$$$\left(\beta−{t}\right){e}^{−{t}} {e}^{\beta} =\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\left(\beta−{t}\right){e}^{\beta−{t}} =\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${W}\left(\left(\beta−{t}\right){e}^{\beta−{t}} \right)={W}\left(\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \right) \\ $$$$\beta−{t}={W}\left(\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \right) \\ $$$${t}=\beta−{W}\left(\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \right) \\ $$$${Now}\:{recalling} \\ $$$${x}={e}^{{e}^{{t}} } \\ $$$${x}={e}^{{e}^{\beta−{W}\left(\alpha{e}^{\beta+\mathrm{1}} \right)} } \\ $$$${Recalling}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:\alpha\:{and}\:\beta,\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$${the}\:{required}\:{solution}. \\ $$$$\left({Omar}\right) \\ $$
