Question Number 24663 by NECx last updated on 24/Nov/17

$$\boldsymbol{{solve}}\:\mid{x}−\mathrm{3}\mid=\mid\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 24/Nov/17
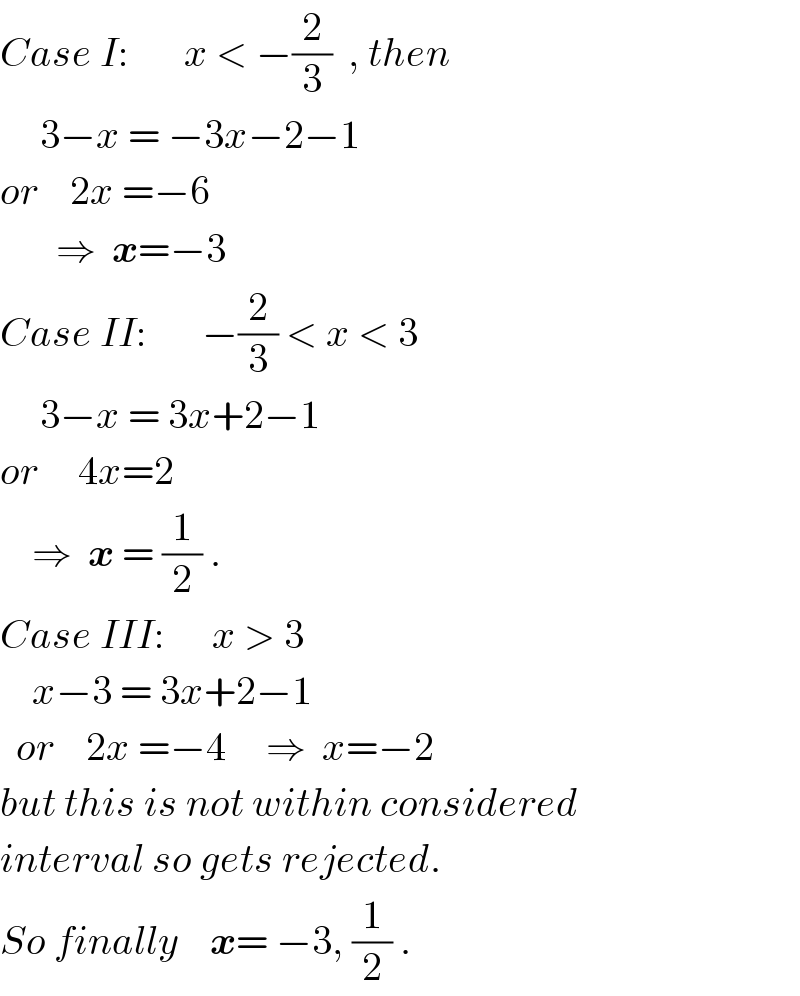
$${Case}\:{I}:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}\:<\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:,\:{then} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}−{x}\:=\:−\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:=−\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\boldsymbol{{x}}=−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${Case}\:{II}:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:<\:{x}\:<\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}−{x}\:=\:\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\boldsymbol{{x}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$$${Case}\:{III}:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}\:>\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{x}−\mathrm{3}\:=\:\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:{or}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:=−\mathrm{4}\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:{x}=−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$${but}\:{this}\:{is}\:{not}\:{within}\:{considered} \\ $$$${interval}\:{so}\:{gets}\:{rejected}. \\ $$$${So}\:{finally}\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{x}}=\:−\mathrm{3},\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 25/Nov/17

$${thanks}\:{boss} \\ $$
