Question Number 96772 by abdomathmax last updated on 04/Jun/20
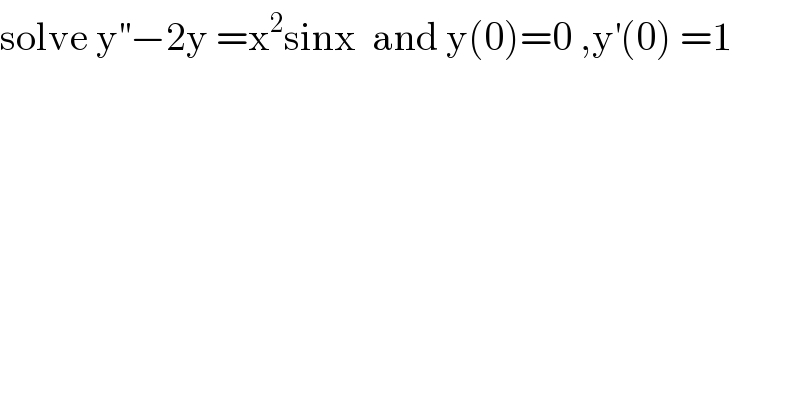
$$\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{y}^{''} −\mathrm{2y}\:=\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:,\mathrm{y}^{'} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 04/Jun/20

$$\left(\mathrm{he}\right)\:\rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{''} −\mathrm{2y}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{r}\:=\overset{−} {+}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{e}^{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{b}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}} \:=\mathrm{au}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{bu}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}\left(\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \:,\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} }\\{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{o}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} }\\{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\:\:\:\:\:−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}}\\{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}}\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{Im}\left(\int\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ix}−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{dx}\right) \\ $$$$\int\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:\mathrm{dx}\:=_{\mathrm{byparts}} \:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\:\mathrm{2x}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \left[\mathrm{dx}\right. \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\left\{\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \right\} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{2x}}{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:=… \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:=….\left(\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{follow}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{way}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} \:+\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/Jun/20
![let use Laplace transform (e) ⇒L(y^((2)) )−2L(y) =L(x^2 sinx) ⇒ x^2 L(y)−y(0)−y^′ (0)−2L(y)=L(x^2 sinx) ⇒ (x^2 −2)L(y)=1+L(x^2 sinx) we have L(x^2 sinx) =∫_0 ^∞ t^2 sint e^(−xt) dt =Im(∫_0 ^∞ t^2 e^(it−xt) dt) but ∫_0 ^∞ t^2 e^((i−x)t) dt =_(by parts) [(t^2 /(i−x))e^((i−x)t) ]_0 ^∞ −∫_0 ^∞ ((2t)/(i−x)) e^((i−x)t) dt =−(2/(i−x)) ∫_0 ^∞ t e^((i−x)t) dt =(2/(x−i)){ [(t/(i−x)) e^((i−x)t) ]_0 ^∞ −∫_0 ^∞ (1/(i−x))e^((i−x)t) dt} =(2/((x−i)^2 )) ×[(1/(i−x)) e^((i−x)t) ]_0 ^∞ = (2/((x−i)^3 )) =((2(x+i)^3 )/((x^2 +1)^3 )) =((2(x^3 +3x^2 i −3x−i))/((x^2 +1)^3 )) =((2x^3 +6x^2 i−6x −2i)/((x^2 +1)^3 )) ⇒L(x^2 sinx) =((6x^2 −2)/((x^2 +1)^3 )) (e)⇒(x^2 −2)L(y) =1+((6x^2 −2)/((x^2 +1)^3 )) ⇒L(y) =(1/(x^2 −2)) +((6x^2 −2)/((x^2 −2)(x^2 +1)^3 )) ⇒ y(x) =L^(−1) ((1/(x^2 −2))) +L^(−1) (((6x^2 −2)/((x^2 −2)(x^2 +1)^3 ))) (1/(x^2 −2)) =(1/(2(√2)))((1/(x−(√2)))−(1/(x+(√2)))) ⇒L^(−1) ((1/(x^2 −2))) =(1/(2(√2)))(e^(x(√2)) −e^(−x(√2)) ) let decompose F(x) =((6x^2 −2)/((x^2 −2)(x^2 +1)^3 )) F(x) =(a/(x−(√2))) +(b/(x+(√2))) +((a_1 x +b_1 )/(x^2 +1)) +((a_2 x +b_2 )/((x^2 +1)^2 )) +((a_3 x +b_3 )/((x^2 +1)^3 )) ...be continued...](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q96810.png)
$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{Laplace}\:\mathrm{transform} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}\right)\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \right)−\mathrm{2L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:=\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sinx}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)−\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)−\mathrm{y}^{'} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)−\mathrm{2L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)=\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sinx}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sinx}\right)\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sint}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{xt}} \:\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{Im}\left(\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{it}−\mathrm{xt}} \:\mathrm{dt}\right)\:\mathrm{but}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \mathrm{dt}\:=_{\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{parts}} \\ $$$$\left[\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{2t}}{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \mathrm{dt}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \:\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{i}}\left\{\:\:\left[\frac{\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \:\mathrm{dt}\right\} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{i}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:×\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{i}−\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{t}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{i}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{i}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{i}\:−\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{i}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{i}−\mathrm{6x}\:−\mathrm{2i}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}\right)\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{L}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}\right)\:+\mathrm{L}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{L}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \:−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{decompose}\:\mathrm{F}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{6x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{F}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{b}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{b}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\frac{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{b}_{\mathrm{3}} }{\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$…\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{continued}… \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/Jun/20
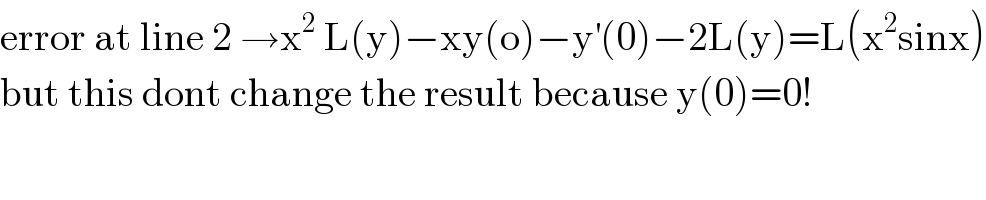
$$\mathrm{error}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{line}\:\mathrm{2}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)−\mathrm{xy}\left(\mathrm{o}\right)−\mathrm{y}^{'} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)−\mathrm{2L}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)=\mathrm{L}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinx}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{dont}\:\mathrm{change}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{result}\:\mathrm{because}\:\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}! \\ $$
