Question Number 29442 by prof Abdo imad last updated on 08/Feb/18
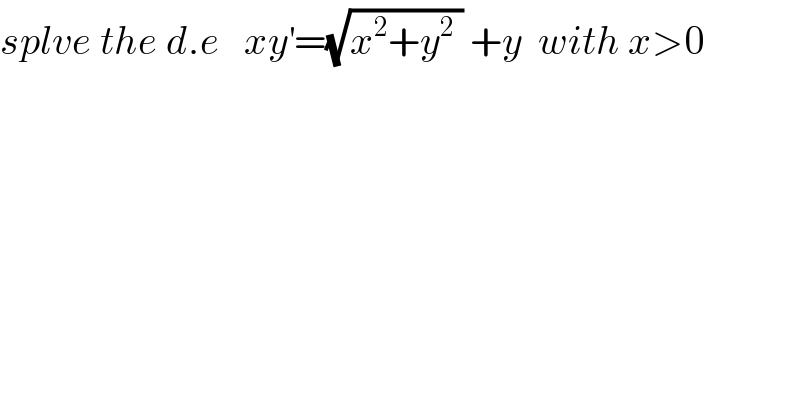
$${splve}\:{the}\:{d}.{e}\:\:\:{xy}^{'} =\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\:+{y}\:\:{with}\:{x}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by mrW2 last updated on 09/Feb/18
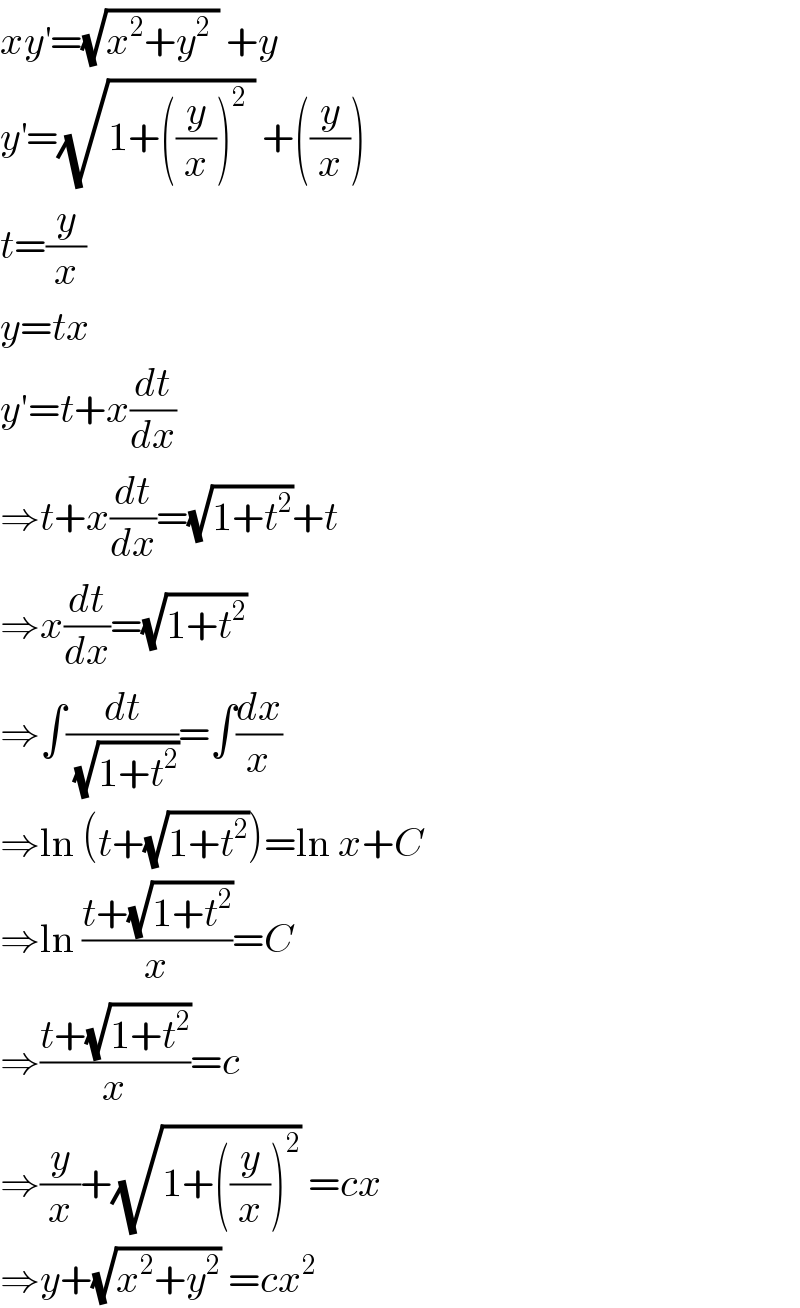
$${xy}^{'} =\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\:+{y} \\ $$$${y}^{'} =\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\left(\frac{{y}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\:+\left(\frac{{y}}{{x}}\right) \\ $$$${t}=\frac{{y}}{{x}} \\ $$$${y}={tx} \\ $$$${y}'={t}+{x}\frac{{dt}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{t}+{x}\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{t} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int\frac{{dt}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}=\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{ln}\:\left({t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:{x}+{C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{x}}={C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{{x}}={c} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{y}}{{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\left(\frac{{y}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:={cx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:={cx}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
