Question Number 26574 by abdo imad last updated on 26/Dec/17
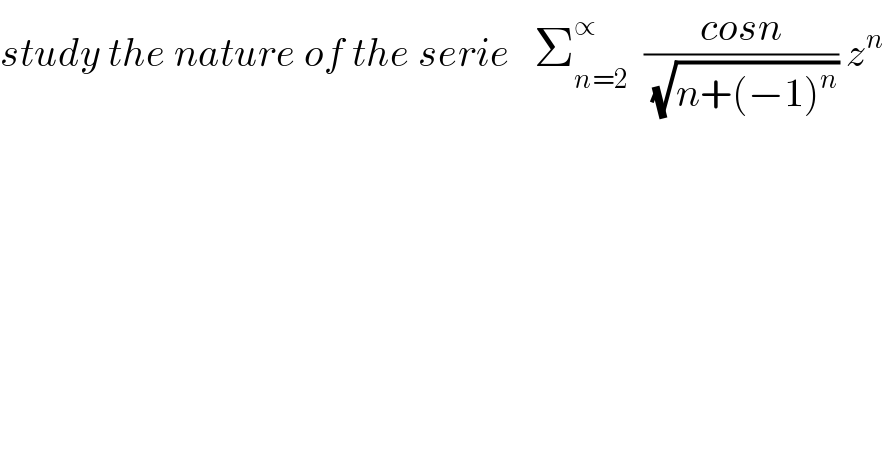
$${study}\:{the}\:{nature}\:{of}\:{the}\:{serie}\:\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\propto} \:\:\frac{{cosn}}{\:\sqrt{{n}+\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }}\:{z}^{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 29/Dec/17
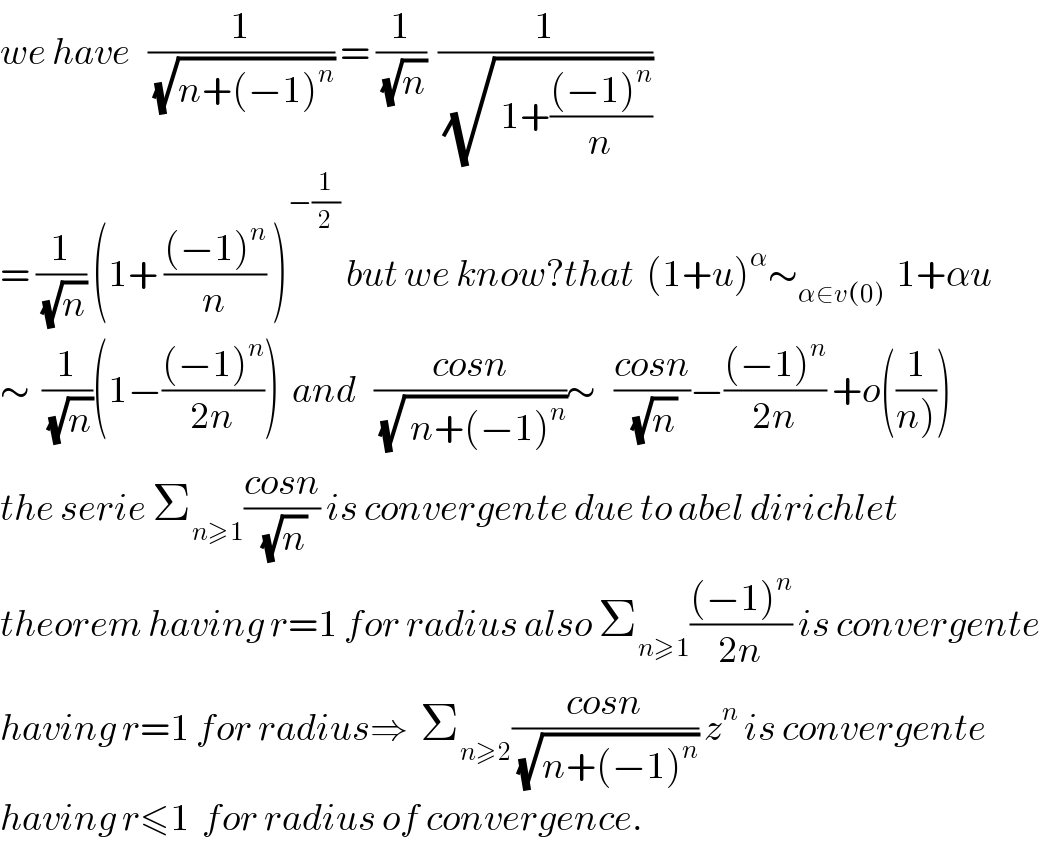
$${we}\:{have}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{n}+\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\:\mathrm{1}+\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}}}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}}\:\right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{but}\:{we}\:{know}?{that}\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)^{\alpha} \sim_{\alpha\in{v}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)} \:\:\mathrm{1}+\alpha{u} \\ $$$$\sim\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}}\right)\:\:{and}\:\:\:\frac{{cosn}}{\:\sqrt{\:{n}+\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }}\sim\:\:\:\frac{{cosn}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}−\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left.{n}\right)}\right) \\ $$$${the}\:{serie}\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \frac{{cosn}}{\:\sqrt{{n}}}\:{is}\:{convergente}\:{due}\:{to}\:{abel}\:{dirichlet}\: \\ $$$${theorem}\:{having}\:{r}=\mathrm{1}\:{for}\:{radius}\:{also}\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:{is}\:{convergente} \\ $$$${having}\:{r}=\mathrm{1}\:{for}\:{radius}\Rightarrow\:\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} \frac{{cosn}}{\:\sqrt{{n}+\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }}\:{z}^{{n}} \:{is}\:{convergente} \\ $$$${having}\:{r}\leqslant\mathrm{1}\:\:{for}\:{radius}\:{of}\:{convergence}. \\ $$
