Question Number 38822 by NECx last updated on 30/Jun/18

$${The}\:{incident}\:{wave}\:{set}\:{up}\:{on}\:{a}\:{string} \\ $$$${of}\:{length}\:{fixed}\:{at}\:{each}\:{end}\:{is}\:{given} \\ $$$${by}:\:\:\:{y}_{\mathrm{1}} ={Asin}\left({kx}−{wt}\right) \\ $$$$\left.{i}\right){what}\:{is}\:{the}\:{equation}\:{of}\:{motion} \\ $$$${of}\:{the}\:{reflected}\:{wave},{y}_{\mathrm{2}} . \\ $$$$\left.{ii}\right){obtain}\:{the}\:{resultant},{y}={y}_{\mathrm{1}} +{y}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${of}\:{the}\:{two}\:{waves}. \\ $$$$\left.{iii}\right){what}\:{type}\:{of}\:{resultant}\:{wave}\:{is} \\ $$$${this}? \\ $$$$\left.{iv}\right){for}\:{what}\:{values}\:{of}\:{x}\:{will}\:{the} \\ $$$${amplitud}\:{of}\:{the}\:{resultant}\:{wave}\: \\ $$$${become}\:{zero}? \\ $$$$\left.{v}\right){for}\:{what}\:{values}\:{of}\:{x}\:{will}\:{y}\:{be} \\ $$$${maximum}? \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 30/Jun/18
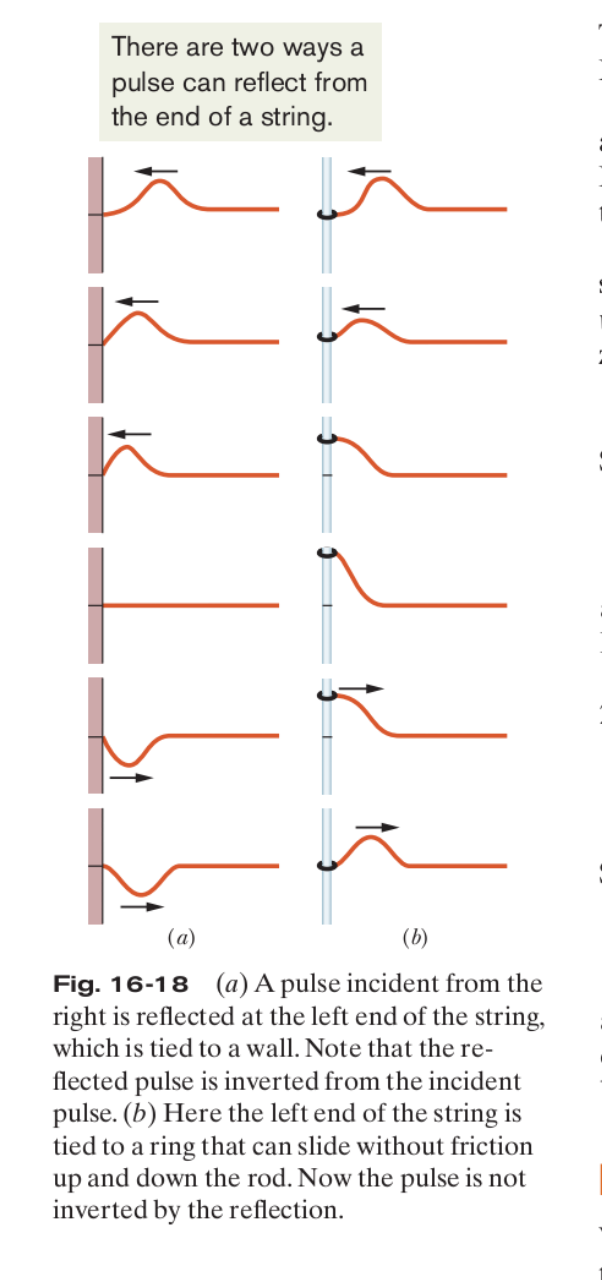
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 30/Jun/18
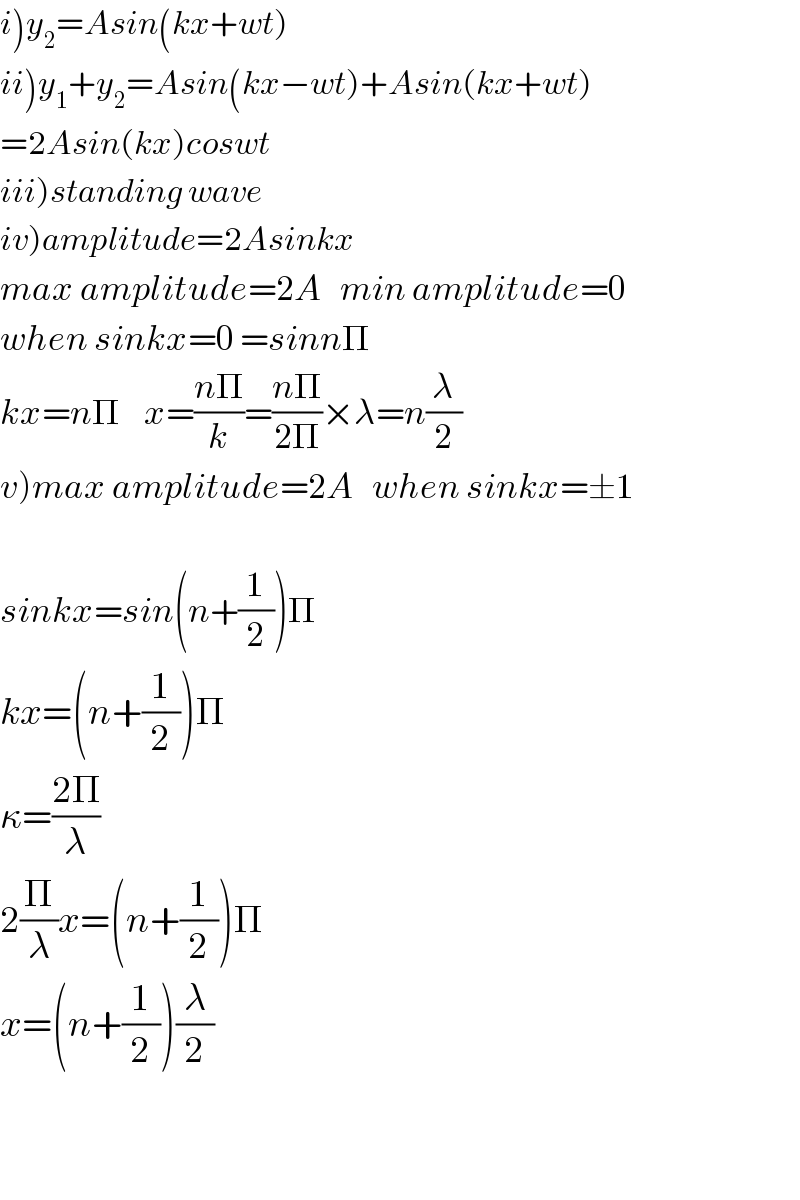
$$\left.{i}\right){y}_{\mathrm{2}} ={Asin}\left({kx}+{wt}\right) \\ $$$$\left.{ii}\right){y}_{\mathrm{1}} +{y}_{\mathrm{2}} ={Asin}\left({kx}−{wt}\right)+{Asin}\left({kx}+{wt}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{Asin}\left({kx}\right){coswt} \\ $$$$\left.{iii}\right){standing}\:{wave} \\ $$$$\left.{iv}\right){amplitude}=\mathrm{2}{Asinkx} \\ $$$${max}\:{amplitude}=\mathrm{2}{A}\:\:\:{min}\:{amplitude}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${when}\:{sinkx}=\mathrm{0}\:={sinn}\Pi \\ $$$${kx}={n}\Pi\:\:\:\:{x}=\frac{{n}\Pi}{{k}}=\frac{{n}\Pi}{\mathrm{2}\Pi}×\lambda={n}\frac{\lambda}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left.{v}\right){max}\:{amplitude}=\mathrm{2}{A}\:\:\:{when}\:{sinkx}=\pm\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${sinkx}={sin}\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Pi \\ $$$${kx}=\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Pi \\ $$$$\kappa=\frac{\mathrm{2}\Pi}{\lambda} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\frac{\Pi}{\lambda}{x}=\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Pi \\ $$$${x}=\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\frac{\lambda}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
