Question Number 20867 by Tinkutara last updated on 05/Sep/17
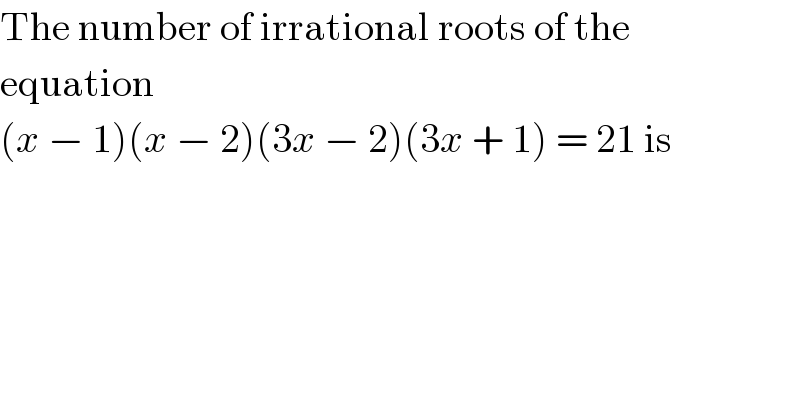
$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{number}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{irrational}\:\mathrm{roots}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$$\left({x}\:−\:\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}\:−\:\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}\:−\:\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}\:+\:\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{21}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$
Answered by alex041103 last updated on 09/Sep/17
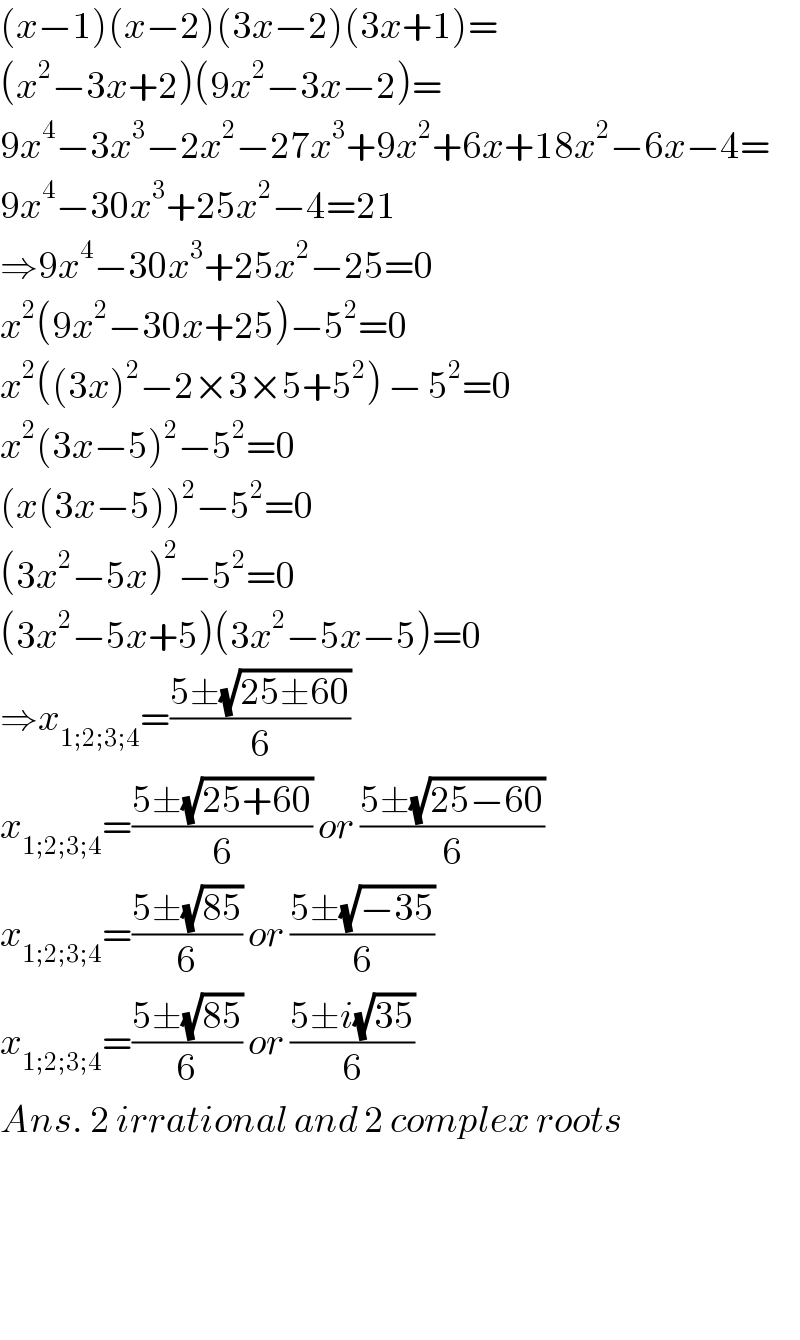
$$\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)= \\ $$$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)= \\ $$$$\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{27}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{18}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{x}−\mathrm{4}= \\ $$$$\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{30}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{25}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{21} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} −\mathrm{30}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{25}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{25}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{30}{x}+\mathrm{25}\right)−\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\left(\mathrm{3}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:−\:\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{5}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{5}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{5}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}_{\mathrm{1};\mathrm{2};\mathrm{3};\mathrm{4}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{25}\pm\mathrm{60}}}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1};\mathrm{2};\mathrm{3};\mathrm{4}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{25}+\mathrm{60}}}{\mathrm{6}}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{25}−\mathrm{60}}}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1};\mathrm{2};\mathrm{3};\mathrm{4}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{85}}}{\mathrm{6}}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{−\mathrm{35}}}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1};\mathrm{2};\mathrm{3};\mathrm{4}} =\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{85}}}{\mathrm{6}}\:{or}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\pm{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{35}}}{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${Ans}.\:\mathrm{2}\:{irrational}\:{and}\:\mathrm{2}\:{complex}\:{roots} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 09/Sep/17
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{much}\:\mathrm{Sir}! \\ $$
