Question Number 40818 by Necxx last updated on 27/Jul/18

$${Two}\:{large}\:{parallel}\:{metal}\:{plates}\:{carrying} \\ $$$${opposite}\:{charges}\:{are}\:{seperated}\:{by}\:{a} \\ $$$${distance}\:{of}\:\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}{m},{and}\:{the}\:{potential} \\ $$$${difference}\:{between}\:{them}\:{is}\:\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{KV}. \\ $$$$\left({a}\right){Calculate}\:{the}\:{magnitude}\:{of}\:{the} \\ $$$${uniform}\:{electric}\:{field}\:{between}\:{them}. \\ $$$$\left({b}\right){Also}\:{calculate}\:{the}\:{workdone}\:{by} \\ $$$${this}\:{field}\:{on}\:{a}\:{charge}\:{of}\:\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{0}×\mathrm{10}^{−\mathrm{9}} {C} \\ $$$${when}\:{it}\:{moves}\:{from}\:{the}\:{plate}\:{of} \\ $$$${higher}\:{potential}\:{to}\:{that}\:{of}\:{lower} \\ $$$${potential}. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 28/Jul/18
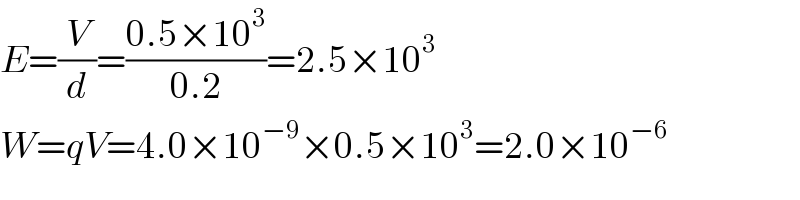
$${E}=\frac{{V}}{{d}}=\frac{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${W}={qV}=\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{0}×\mathrm{10}^{−\mathrm{9}} ×\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{0}×\mathrm{10}^{−\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
