Question Number 155812 by zainaltanjung last updated on 05/Oct/21

$$\mathrm{Use}\:\mathrm{algebraic}\:\mathrm{simplifications}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{help} \\ $$$$\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{limits},\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{they}\:\mathrm{exist}. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5x}−\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right).\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\: \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Oct/21

$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5x}−\mathrm{7}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{7}\right)} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{7}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{7}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{15}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{15}}=\frac{−\mathrm{20}}{−\mathrm{20}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${You}\:{can}\:{calculate}\:{limit}\:{directly} \\ $$$${because}\:{limit}\:{of}\:{denominator}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right).\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{15}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{Same}\:{as}\:{Q}\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right).\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{12}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by zainaltanjung last updated on 05/Oct/21
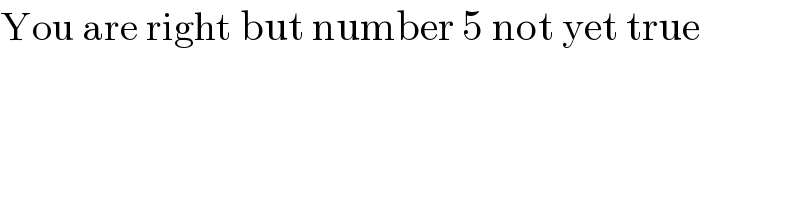
$$\mathrm{You}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{right}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{number}\:\mathrm{5}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{yet}\:\mathrm{true} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Oct/21
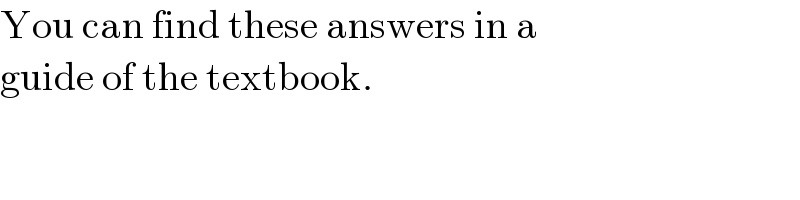
$$\mathrm{You}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{these}\:\mathrm{answers}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{a} \\ $$$$\mathrm{guide}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{textbook}. \\ $$
Commented by zainaltanjung last updated on 05/Oct/21
$$\mathrm{Okey}…\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{lot} \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 05/Oct/21
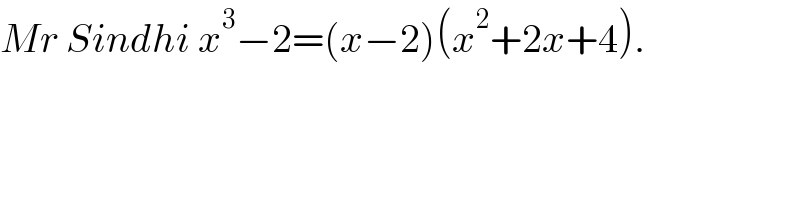
$${Mr}\:{Sindhi}\:{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2}=\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\right). \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Oct/21
$${Yes}\:{sir}\:{you}'{re}\:{right}.{I}\:{have}\:{corrected}. \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 05/Oct/21

$${Thanks} \\ $$
Answered by puissant last updated on 05/Oct/21
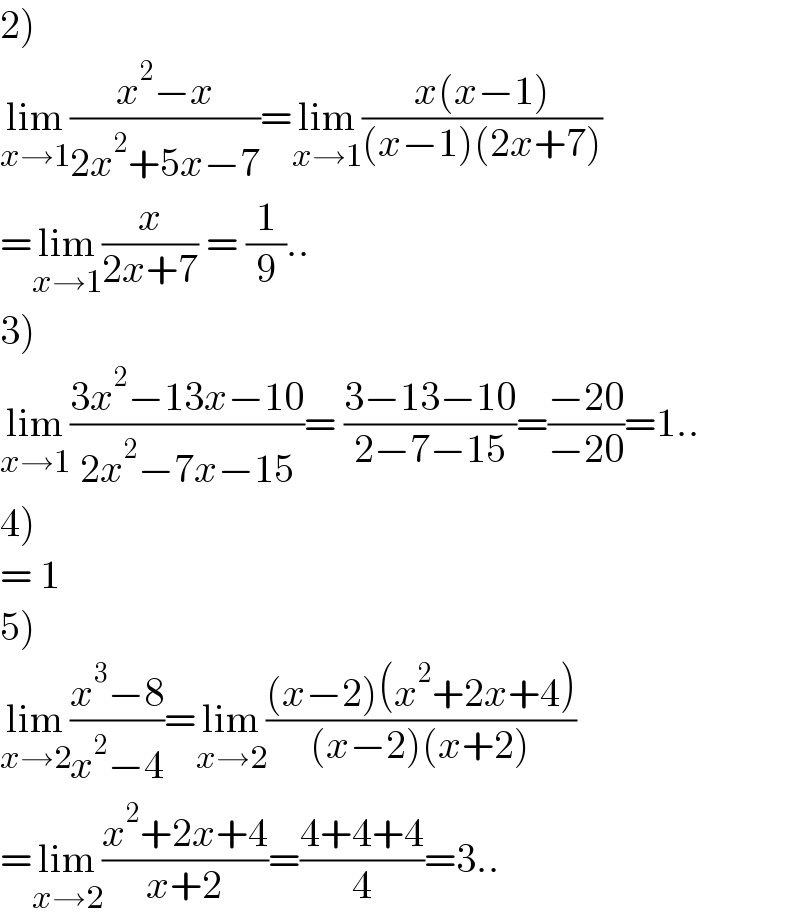
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{7}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{7}\right)} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{7}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}.. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{7}{x}−\mathrm{15}}=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{13}−\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{7}−\mathrm{15}}=\frac{−\mathrm{20}}{−\mathrm{20}}=\mathrm{1}.. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{8}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{3}.. \\ $$
Commented by zainaltanjung last updated on 05/Oct/21

$$\mathrm{okeyMr}\:….\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{answered}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{true}\: \\ $$
