Question Number 146791 by puissant last updated on 15/Jul/21
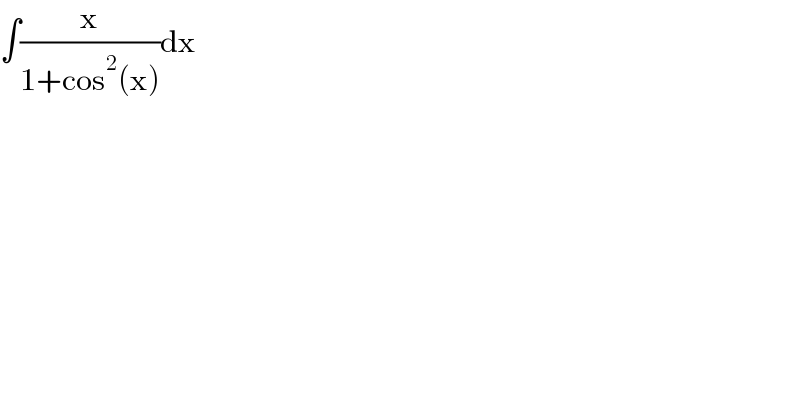
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 15/Jul/21
![I=∫(x/(1+cos^2 x))dx=∫((xsec^2 x)/(sec^2 x+1))dx =∫((xd(tanx))/(2+tan^2 x))=(x/( (√2)))arctan(((tanx)/( (√2))))−(1/( (√2)))∫arctan(((tanx)/( (√2))))dx I=∫_0 ^π (x/(1+cos^2 x))dx=∫_0 ^π ((π−x)/(1+cos^2 x))dx =π∫_0 ^π (dx/(1+cos^2 x))−I=π∫_0 ^π ((d(tanx))/(2+tan^2 x))−I =(π/2)[(1/( (√2)))arctan(((tanx)/( (√2))))]_0 ^π =((π^2 (√2))/4)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q146797.png)
$$\mathrm{I}=\int\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx}=\int\frac{\mathrm{xsec}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:=\int\frac{\mathrm{xd}\left(\mathrm{tanx}\right)}{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tanx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\mathrm{arctan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tanx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathcal{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \frac{\pi−\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\pi\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}−\mathcal{I}=\pi\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \frac{\mathrm{d}\left(\mathrm{tanx}\right)}{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}−\mathcal{I} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{tanx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} =\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} \sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
