Question Number 105574 by bemath last updated on 30/Jul/20
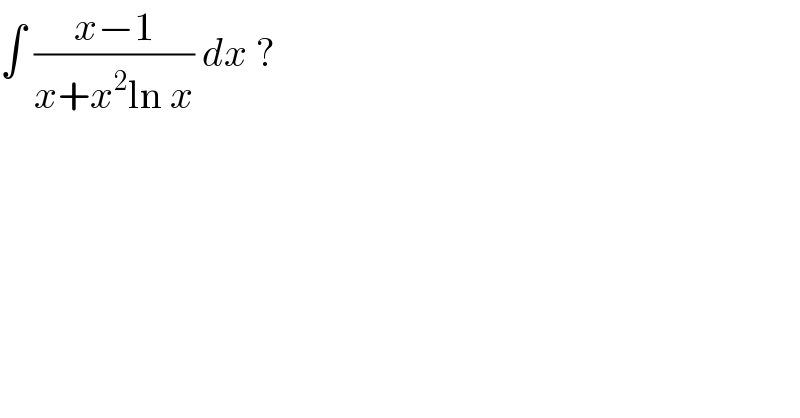
$$\int\:\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{ln}\:{x}}\:{dx}\:?\: \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 30/Jul/20
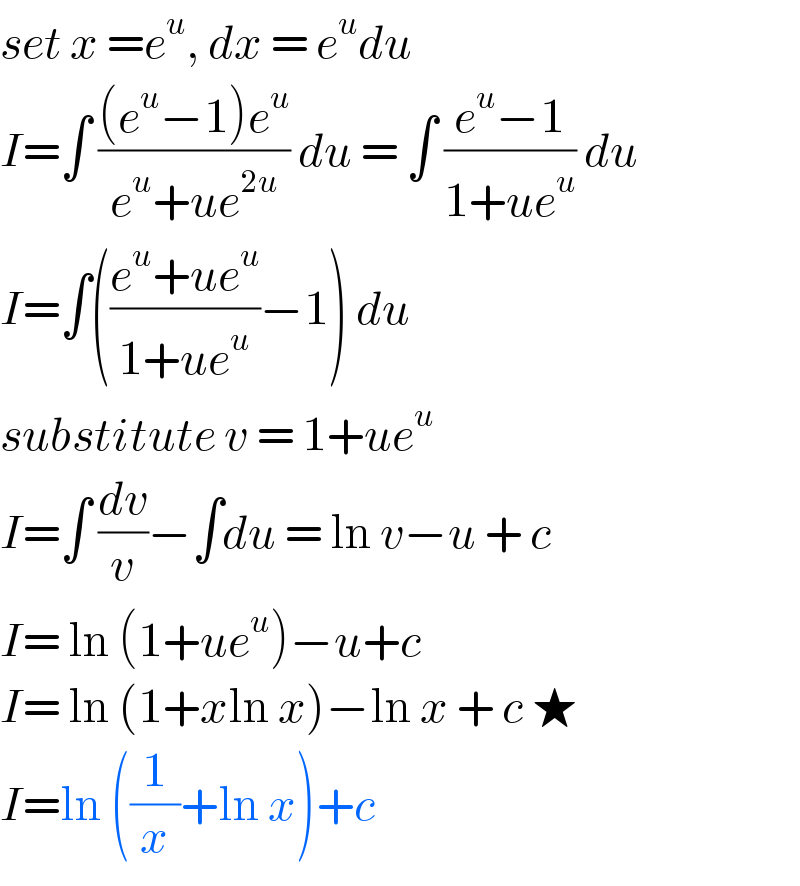
$${set}\:{x}\:={e}^{{u}} ,\:{dx}\:=\:{e}^{{u}} {du} \\ $$$${I}=\int\:\frac{\left({e}^{{u}} −\mathrm{1}\right){e}^{{u}} }{{e}^{{u}} +{ue}^{\mathrm{2}{u}} }\:{du}\:=\:\int\:\frac{{e}^{{u}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{ue}^{{u}} }\:{du} \\ $$$${I}=\int\left(\frac{{e}^{{u}} +{ue}^{{u}} }{\mathrm{1}+{ue}^{{u}} }−\mathrm{1}\right)\:{du} \\ $$$${substitute}\:{v}\:=\:\mathrm{1}+{ue}^{{u}} \\ $$$${I}=\int\:\frac{{dv}}{{v}}−\int{du}\:=\:\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−{u}\:+\:{c} \\ $$$${I}=\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{ue}^{{u}} \right)−{u}+{c} \\ $$$${I}=\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\right)−\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\:+\:{c}\:\bigstar \\ $$$${I}=\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\right)+{c}\: \\ $$
