Question Number 130296 by sumit Singh last updated on 24/Jan/21
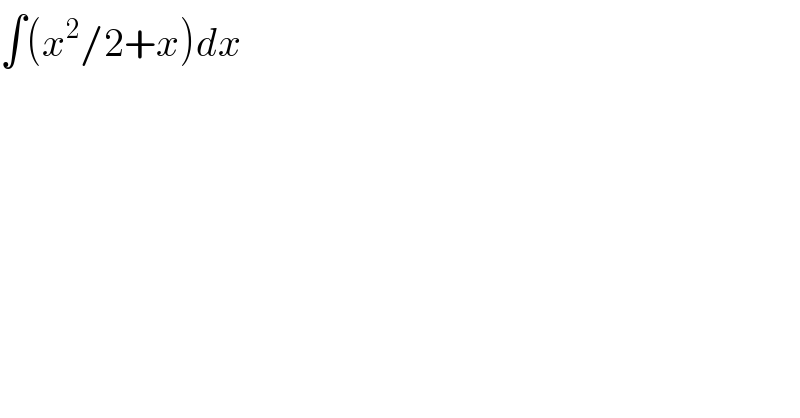
$$\int\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} /\mathrm{2}+{x}\right){dx} \\ $$
Commented by EDWIN88 last updated on 24/Jan/21
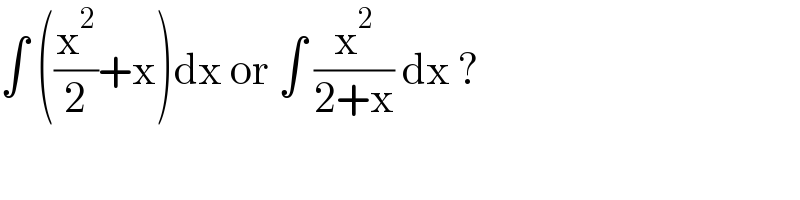
$$\int\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}\:\mathrm{or}\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{x}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:? \\ $$
Answered by benjo_mathlover last updated on 24/Jan/21
![If ∫ (x^2 /(x+2)) dx = ∫ ((x(x+2)−2x)/(x+2)) dx = (1/2)x^2 −2∫ (x/(x+2)) dx =(1/2)x^2 −2[ ∫ ((x+2−2)/(x+2)) dx ] =(1/2)x^2 −2x+4ln ∣x+2∣ + c](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q130298.png)
$$\mathrm{If}\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:=\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:\: \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\left[\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{dx}\:\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{4ln}\:\mid\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid\:+\:\mathrm{c} \\ $$
