Question Number 56747 by Tawa1 last updated on 22/Mar/19
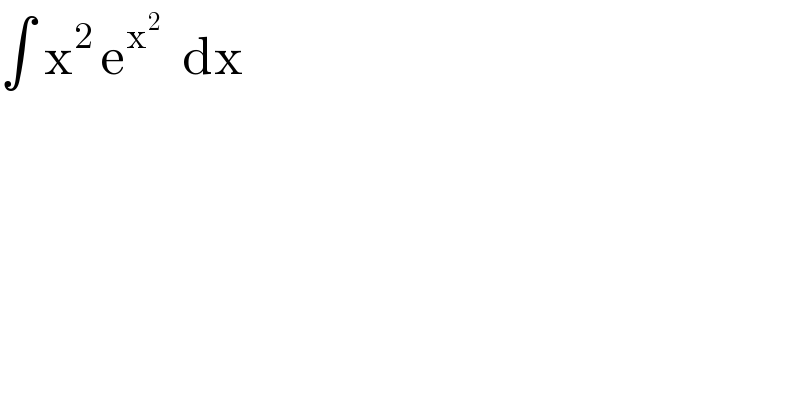
$$\int\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 22/Mar/19
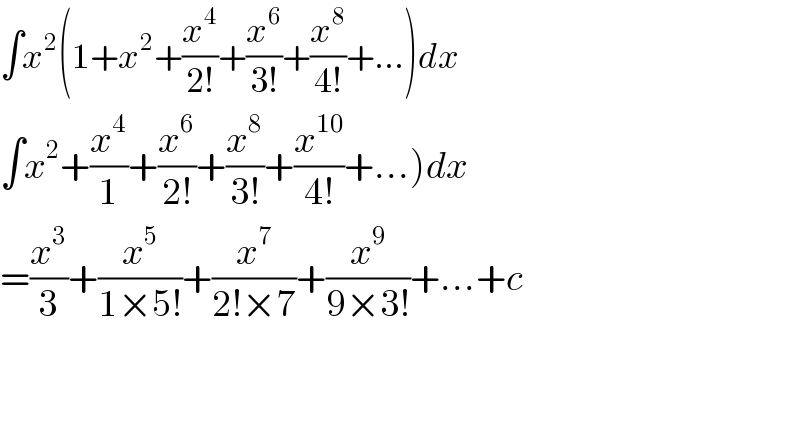
$$\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{8}} }{\mathrm{4}!}+…\right){dx} \\ $$$$\left.\int{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{8}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{10}} }{\mathrm{4}!}+…\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{5}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{7}} }{\mathrm{2}!×\mathrm{7}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{9}} }{\mathrm{9}×\mathrm{3}!}+…+{c} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
