Question Number 128608 by john_santu last updated on 08/Jan/21
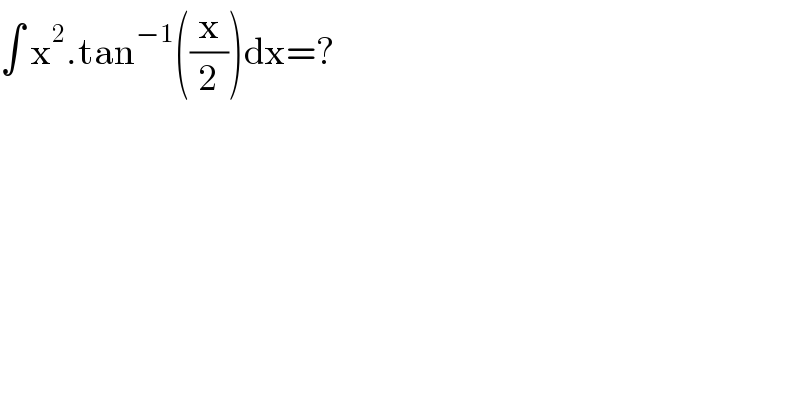
$$\int\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{dx}=? \\ $$
Answered by liberty last updated on 08/Jan/21
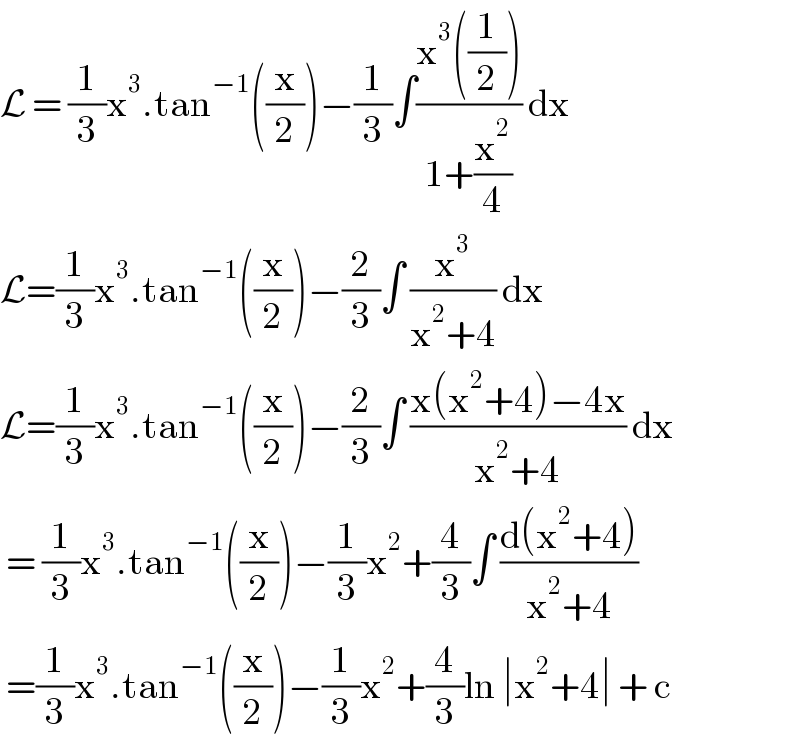
$$\mathcal{L}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}}\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathcal{L}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}}\:\mathrm{dx}\: \\ $$$$\mathcal{L}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)−\mathrm{4x}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}}\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{d}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\right)}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} .\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}\mid\:+\:\mathrm{c}\: \\ $$
