Question Number 185087 by SEKRET last updated on 16/Jan/23
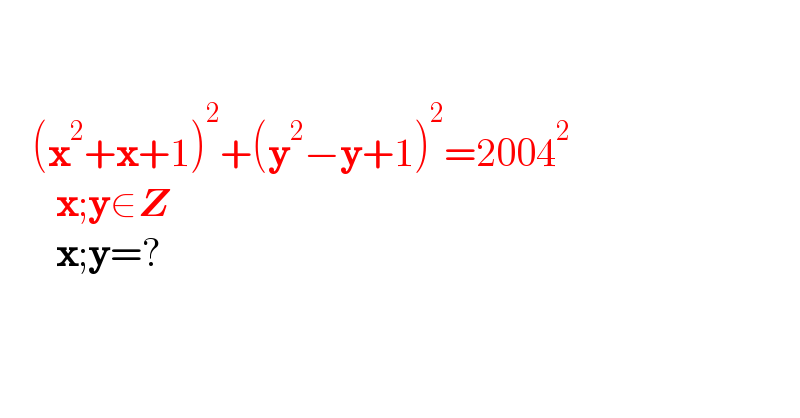
$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2004}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}};\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}\in\boldsymbol{{Z}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}};\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}=?\:\:\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 16/Jan/23
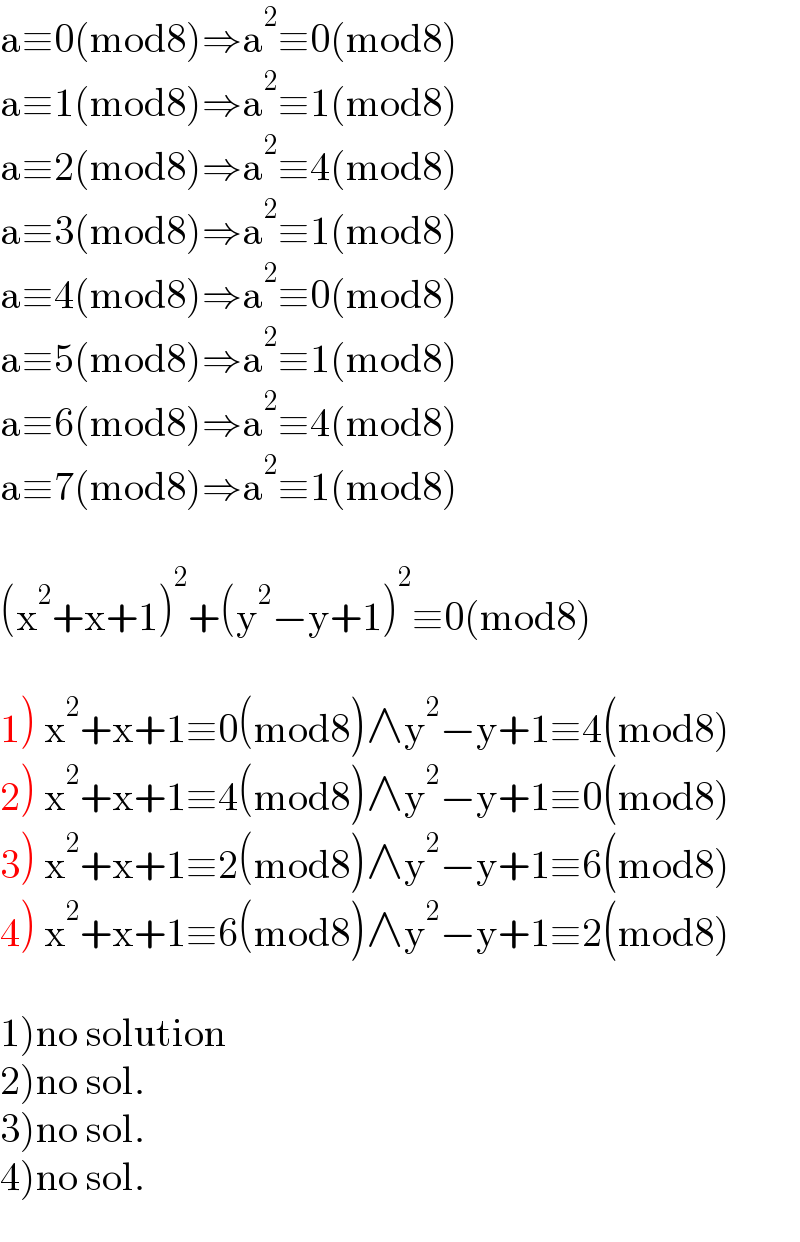
$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\equiv\mathrm{7}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\wedge\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\wedge\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\wedge\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\wedge\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{sol}. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{sol}. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{sol}. \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 17/Jan/23
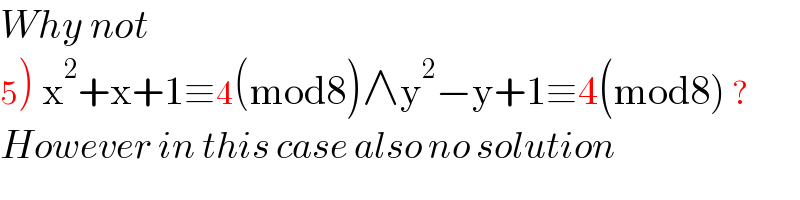
$${Why}\:{not} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\wedge\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod8}\right)\:? \\ $$$${However}\:{in}\:{this}\:{case}\:{also}\:{no}\:{solution} \\ $$
Answered by Frix last updated on 17/Jan/23
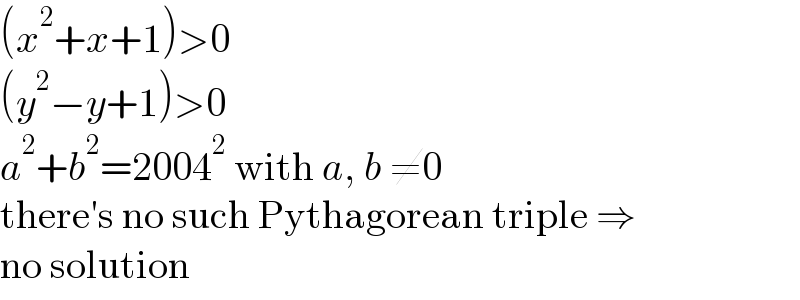
$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2004}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{with}\:{a},\:{b}\:\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{there}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{such}\:\mathrm{Pythagorean}\:\mathrm{triple}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
