Question Number 127287 by liberty last updated on 28/Dec/20
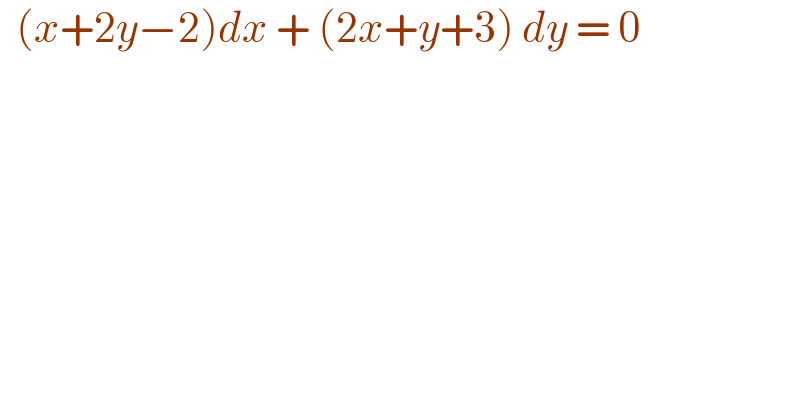
$$\:\:\left({x}+\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{2}\right){dx}\:+\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+{y}+\mathrm{3}\right)\:{dy}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 28/Dec/20

Commented by liberty last updated on 28/Dec/20
grazzi. eż
Commented by liberty last updated on 28/Dec/20
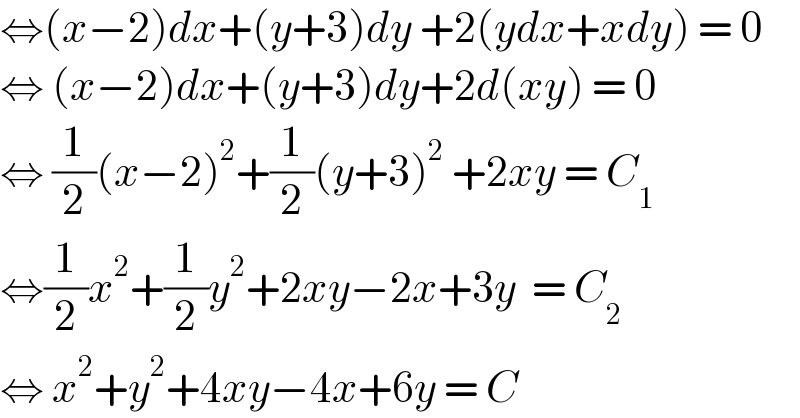
$$\Leftrightarrow\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right){dx}+\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right){dy}\:+\mathrm{2}\left({ydx}+{xdy}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right){dx}+\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right){dy}+\mathrm{2}{d}\left({xy}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({y}+\mathrm{3}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2}{xy}\:=\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \: \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{xy}−\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}{y}\:\:=\:{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{xy}−\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{6}{y}\:=\:{C} \\ $$
