Question Number 163075 by tounghoungko last updated on 03/Jan/22
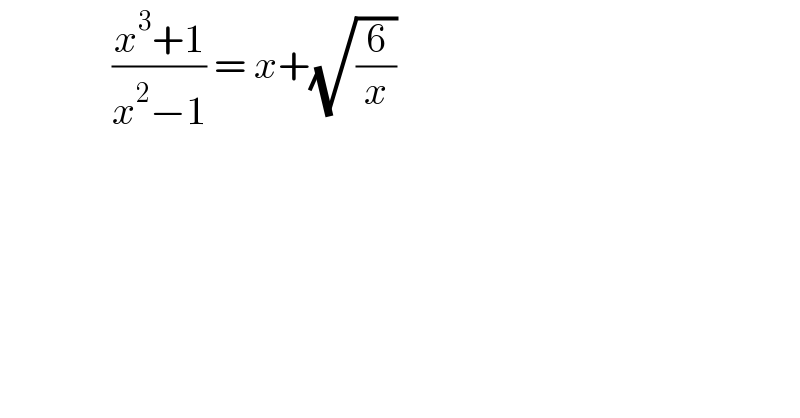
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:{x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 03/Jan/22

$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:{x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}−{x}\:=\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{6}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)={x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\mid\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${On}\:{checking}\:{it}\:{can}\:{be}\:{shown}\:{that} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{is}\:{valid}\:{root},{while}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:{is} \\ $$$${an}\:{extraneous}\:{root}. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\therefore\:\:\:\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 03/Jan/22

$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:{x}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\cancel{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}\right.}{\cancel{\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}−{x}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\:\frac{\cancel{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\cancel{{x}}+\mathrm{1}−\cancel{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\cancel{{x}}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{6}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)={x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{13}{x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\underset{\underset{\underset{\mathcal{R}{oot}} {\mathcal{E}{xtraneous}}} {\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:}} {{x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}}\:\mid\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\checkmark \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
