Question Number 173839 by Khalmohmmad last updated on 19/Jul/22
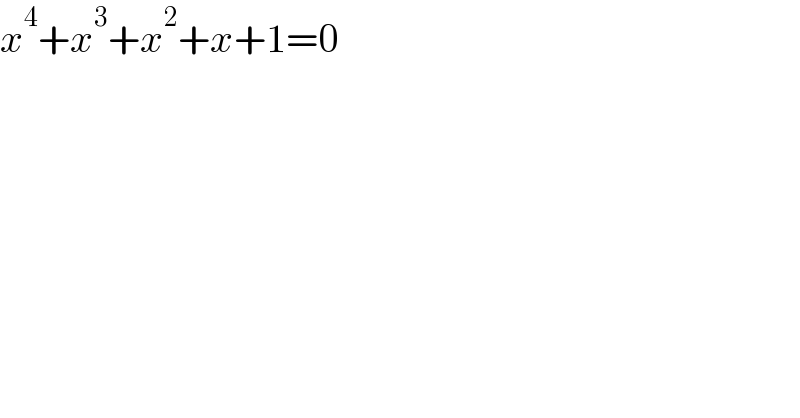
$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 19/Jul/22
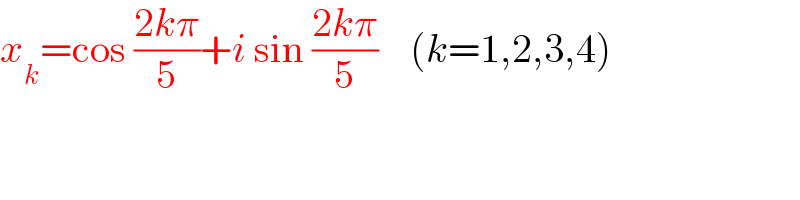
$${x}_{{k}} =\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{k}\pi}{\mathrm{5}}+{i}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{k}\pi}{\mathrm{5}}\:\:\:\:\left({k}=\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 19/Jul/22
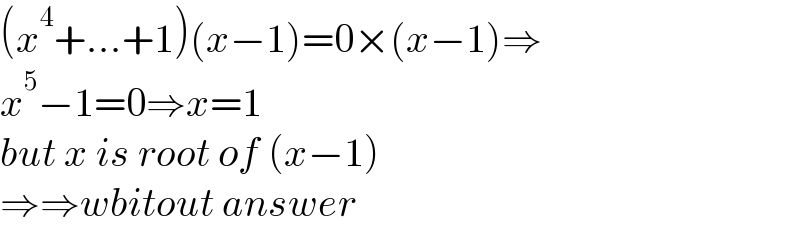
$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{4}} +…+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0}×\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\Rightarrow \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{5}} −\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${but}\:{x}\:{is}\:{root}\:{of}\:\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\Rightarrow{wbitout}\:{answer} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 19/Jul/22

$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{5}} −\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{5}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}\:{is}\:{fifth}\:{root}\:{of}\:{unity} \\ $$$${Let}\:\delta\:{is}\:{one}\:\mathrm{5}{th}\:{root}\:{of}\:{unity}. \\ $$$${All}\:{the}\:\mathrm{5}{th}\:{roots}\:{are} \\ $$$$\delta\:,\delta^{\mathrm{2}} ,\delta^{\mathrm{3}} ,\delta^{\mathrm{4}} ,\:\delta^{\mathrm{5}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{root}\:{of}\:{x}−\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{is}\:{not}\:{root} \\ $$$${of}\:{the}\:{given}\:{equation}. \\ $$$$\therefore\:\delta\:,\delta^{\mathrm{2}} ,\delta^{\mathrm{3}} ,\delta^{\mathrm{4}} \:{are}\:{the}\:{roots}\:{of}\:{the}\:{given} \\ $$$${equation}. \\ $$
Answered by BaliramKumar last updated on 20/Jul/22
![x^4 +x^3 +x^2 +x+1=(x^2 +ax+1)(x^2 +bx+1)=0 x^4 +x^3 +x^2 +x+1=x^4 +(a+b)x^3 +(ab+2)x^2 +(a+b)x+1=0 a+b=1 ab+2=1 a = (((√5)+1)/2) b = −(((√5)−1)/2) x^4 +x^3 +x^2 +x+1=[x^2 +((((√5)+1)/2))x+1][x^2 −((((√5)−1)/2))x+1]=0 x^2 +((((√5)+1)/2))x + 1 = 0 & x^2 −((((√5)−1)/2))x + 1 = 0 .....................](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q173860.png)
$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{ax}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}={x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\left({a}+{b}\right){x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\left({ab}+\mathrm{2}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({a}+{b}\right){x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$${ab}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${a}\:=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{b}\:=\:−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{1}=\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}+\mathrm{1}\right]\left[{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}+\mathrm{1}\right]=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}\:+\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\&\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}\:+\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$………………… \\ $$
