Question Number 27032 by cmaxamuud98 @gmail.com last updated on 01/Jan/18
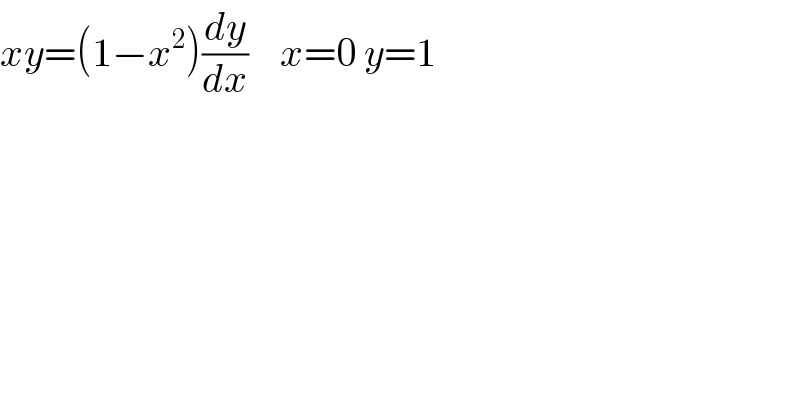
$${xy}=\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\:\:\:{x}=\mathrm{0}\:{y}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 01/Jan/18
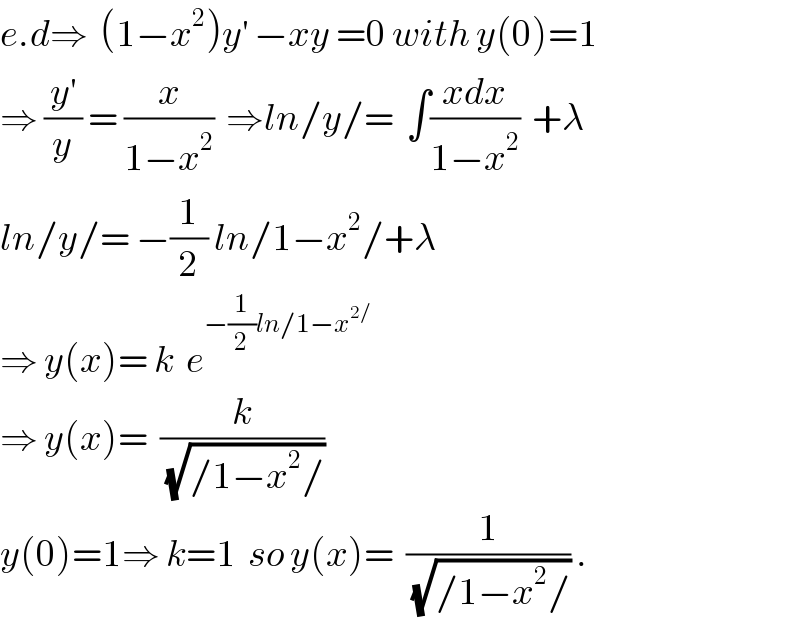
$${e}.{d}\Rightarrow\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){y}^{'} \:−{xy}\:=\mathrm{0}\:{with}\:{y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\frac{{y}^{'} }{{y}}\:=\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\Rightarrow{ln}/{y}/=\:\:\int\frac{{xdx}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:+\lambda \\ $$$${ln}/{y}/=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:{ln}/\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} /+\lambda \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{y}\left({x}\right)=\:{k}\:\:{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}/\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}/} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{y}\left({x}\right)=\:\:\frac{{k}}{\:\sqrt{/\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} /}} \\ $$$${y}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\:{k}=\mathrm{1}\:\:{so}\:{y}\left({x}\right)=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{/\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} /}}\:. \\ $$
