Question Number 26837 by sorour87 last updated on 30/Dec/17
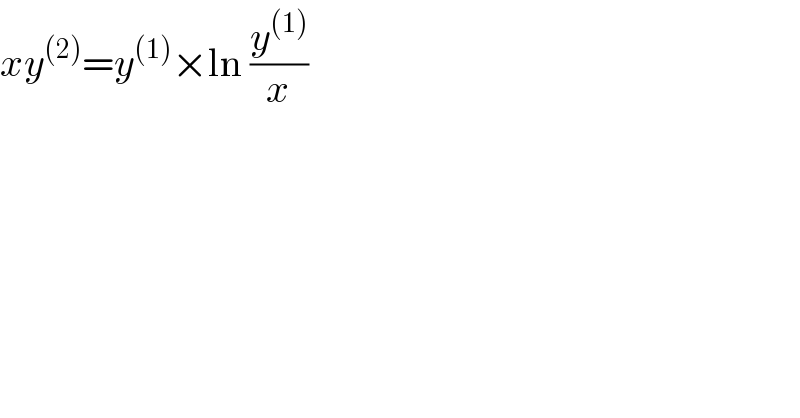
$${xy}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} ={y}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} ×\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{y}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} }{{x}} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 30/Dec/17

$${y}'={u}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${y}''={u}'\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${xu}'={u}\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{{u}}{{x}} \\ $$$${v}=\frac{{u}}{{x}}\Rightarrow{u}={vx} \\ $$$${u}'={xv}'+{v} \\ $$$${x}\left({xv}'+{v}\right)={xv}\mathrm{ln}\:{v} \\ $$$${xv}'+{v}={v}\mathrm{ln}\:{v} \\ $$$${x}\frac{{dv}}{{dx}}={v}\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−{v}\Rightarrow\frac{{dv}}{{v}\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−{v}}=\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Equation}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{solved}\:\mathrm{in}\:{v}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{then}\:{u} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:{y}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{point}. \\ $$
Commented by sorour87 last updated on 30/Dec/17
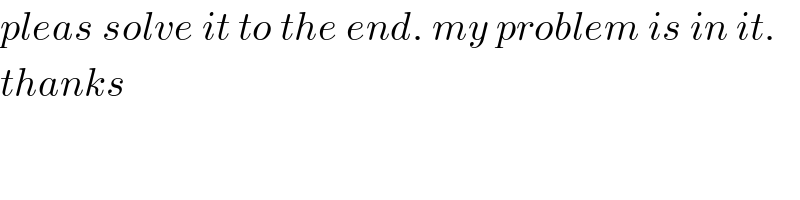
$${pleas}\:{solve}\:{it}\:{to}\:{the}\:{end}.\:{my}\:{problem}\:{is}\:{in}\:{it}. \\ $$$${thanks} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 30/Dec/17
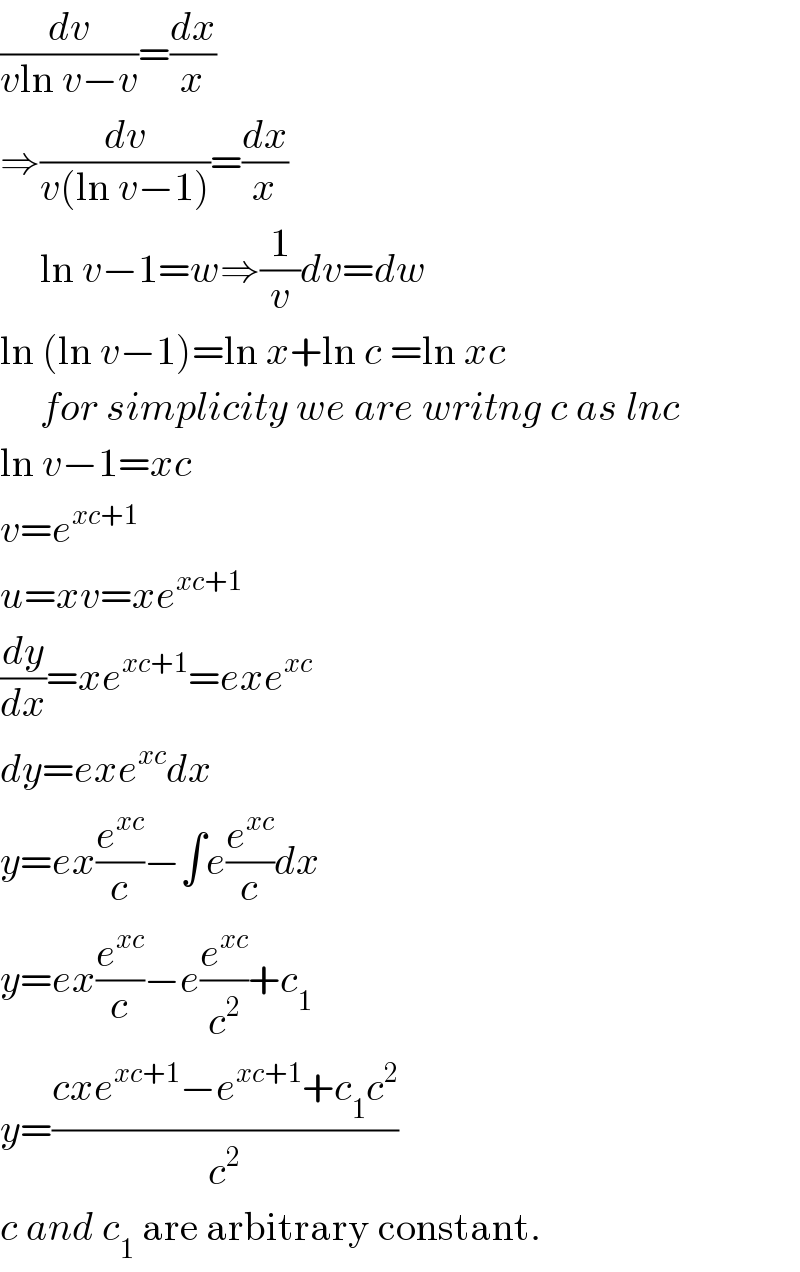
$$\frac{{dv}}{{v}\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−{v}}=\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{dv}}{{v}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−\mathrm{1}={w}\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{v}}{dv}={dw} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:{x}+\mathrm{ln}\:{c}\:=\mathrm{ln}\:{xc} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{for}\:{simplicity}\:{we}\:{are}\:{writng}\:{c}\:{as}\:{lnc} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:{v}−\mathrm{1}={xc} \\ $$$${v}={e}^{{xc}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${u}={xv}={xe}^{{xc}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={xe}^{{xc}+\mathrm{1}} ={exe}^{{xc}} \\ $$$${dy}={exe}^{{xc}} {dx} \\ $$$${y}={ex}\frac{{e}^{{xc}} }{{c}}−\int{e}\frac{{e}^{{xc}} }{{c}}{dx} \\ $$$${y}={ex}\frac{{e}^{{xc}} }{{c}}−{e}\frac{{e}^{{xc}} }{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{c}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{{cxe}^{{xc}+\mathrm{1}} −{e}^{{xc}+\mathrm{1}} +{c}_{\mathrm{1}} {c}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${c}\:{and}\:{c}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{arbitrary}\:\mathrm{constant}. \\ $$
Commented by sorour87 last updated on 30/Dec/17
$$\boldsymbol{{thank}}\:\boldsymbol{{you}}\:\boldsymbol{{very}}\:\boldsymbol{{much}} \\ $$
