Question Number 94969 by bobhans last updated on 22/May/20
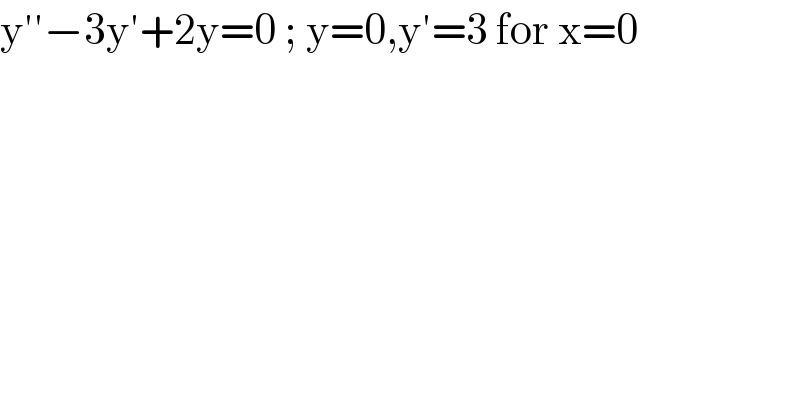
$$\mathrm{y}''−\mathrm{3y}'+\mathrm{2y}=\mathrm{0}\:;\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{0},\mathrm{y}'=\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 22/May/20
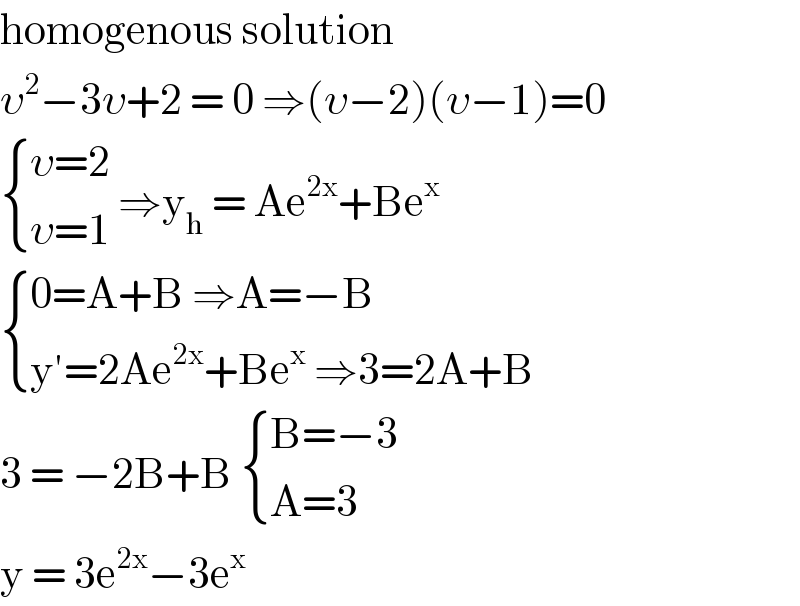
$$\mathrm{homogenous}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\upsilon^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}\upsilon+\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\left(\upsilon−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\upsilon−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\upsilon=\mathrm{2}}\\{\upsilon=\mathrm{1}}\end{cases}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} \:=\:\mathrm{Ae}^{\mathrm{2x}} +\mathrm{Be}^{\mathrm{x}} \: \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\mathrm{0}=\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{A}=−\mathrm{B}}\\{\mathrm{y}'=\mathrm{2Ae}^{\mathrm{2x}} +\mathrm{Be}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{2A}+\mathrm{B}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\:=\:−\mathrm{2B}+\mathrm{B}\:\begin{cases}{\mathrm{B}=−\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{3}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{3e}^{\mathrm{2x}} −\mathrm{3e}^{\mathrm{x}} \: \\ $$
