Question Number 105879 by john santu last updated on 01/Aug/20
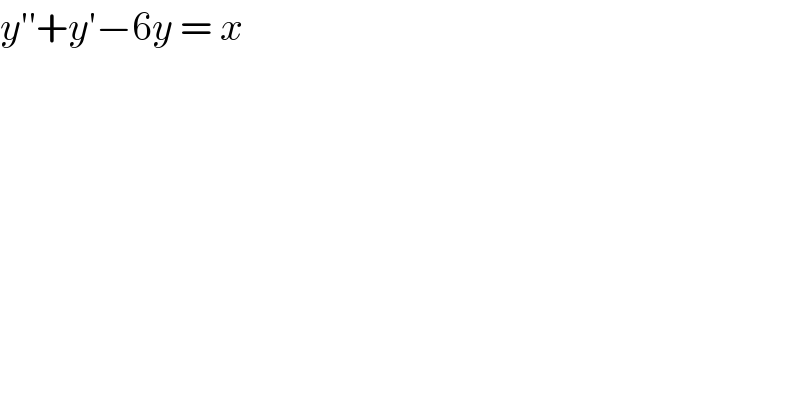
$${y}''+{y}'−\mathrm{6}{y}\:=\:{x}\: \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 01/Aug/20
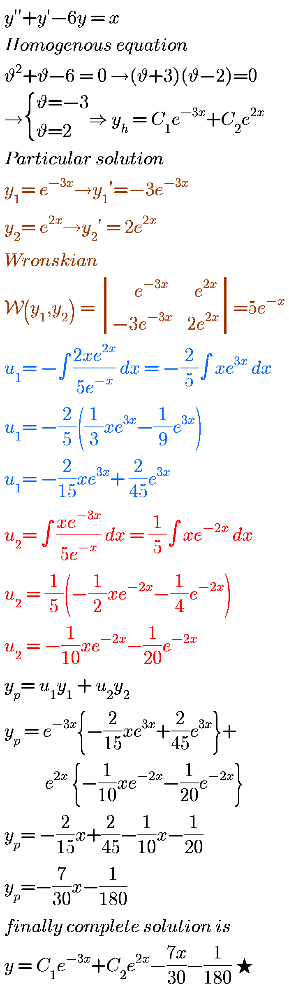
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 01/Aug/20

$$\mathrm{y}^{''} \:+\mathrm{y}^{'} −\mathrm{6y}\:=\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{''} \:+\mathrm{y}^{'} −\mathrm{6y}\:=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{r}−\mathrm{6}\:=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow\Delta\:=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{24}=\mathrm{25}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=−\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\mathrm{ae}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:+\mathrm{be}^{−\mathrm{3x}} \:=\mathrm{au}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{bu}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}\left(\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \:,\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} }\\{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{2e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:=−\mathrm{5e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{o}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} }\\{\mathrm{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{xe}^{−\mathrm{3x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}}\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{xe}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{w}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int\:\:\frac{−\mathrm{xe}^{−\mathrm{3x}} }{−\mathrm{5e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\int\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{5v}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} +\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{dx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$=−\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{10}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2o}}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{w}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{xe}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{−\mathrm{5e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\int\:\mathrm{xe}^{\mathrm{3x}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} −\int\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \mathrm{dx}\right\}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \right\} \\ $$$$=\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{45}}−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{15}}\right\}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \:\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}\:} \:+\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} ×\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{10}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \:+\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} ×\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{45}}−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{15}}\right\}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{10}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{45}}−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{15}}\:=−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{15}}\right)\mathrm{x}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{45}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{150}}\:\mathrm{x}\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{900}}\left(\mathrm{rest}\:\mathrm{simplification}!\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{ae}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:+\mathrm{b}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{3x}} −\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{150}}\mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{900}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Coronavirus last updated on 01/Aug/20
Intéressant
Answered by john santu last updated on 01/Aug/20
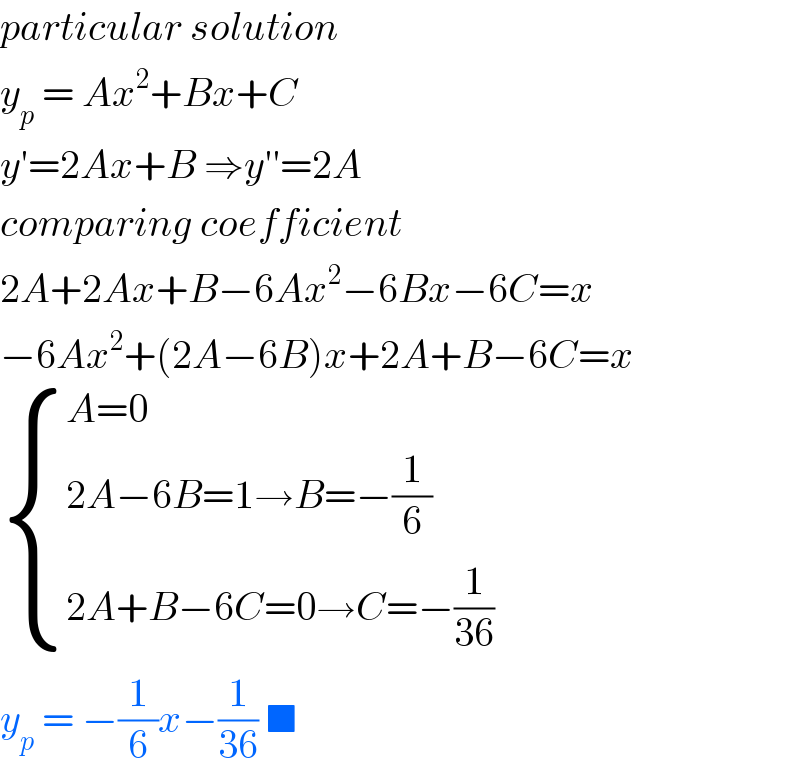
$${particular}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:{Ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{Bx}+{C}\: \\ $$$${y}'=\mathrm{2}{Ax}+{B}\:\Rightarrow{y}''=\mathrm{2}{A} \\ $$$${comparing}\:{coefficient}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{A}+\mathrm{2}{Ax}+{B}−\mathrm{6}{Ax}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6}{Bx}−\mathrm{6}{C}={x} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{6}{Ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{2}{A}−\mathrm{6}{B}\right){x}+\mathrm{2}{A}+{B}−\mathrm{6}{C}={x} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{A}=\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2}{A}−\mathrm{6}{B}=\mathrm{1}\rightarrow{B}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}}\\{\mathrm{2}{A}+{B}−\mathrm{6}{C}=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow{C}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{36}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{36}}\:\blacksquare\: \\ $$
