Question Number 98106 by bobhans last updated on 11/Jun/20
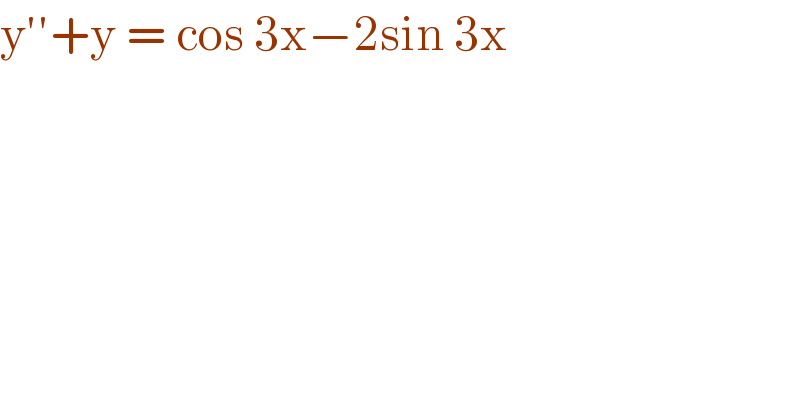
$$\mathrm{y}''+\mathrm{y}\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2sin}\:\mathrm{3x} \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 11/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{homogenous}\:\mathrm{solution}\: \\ $$$$\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\lambda\:=\:\pm\:{i} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} \:=\:\mathrm{Acos}\:\mathrm{x}\:+\:\mathrm{Bsin}\:\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{particular}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} \:=\:{a}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+{b}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} '=−\mathrm{3}{a}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{3}{b}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} ''\:=\:−\mathrm{9acos}\:\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{9}{b}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\left(−\mathrm{9acos}\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{9bsin}\:\mathrm{3x}\right)+\left(\mathrm{acos}\:\mathrm{3x}+\mathrm{bsin}\:\mathrm{3x}\right)= \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2sin}\:\mathrm{3x} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow−\mathrm{8acos}\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{8bsin}\:\mathrm{3x}\:= \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2sin}\:\mathrm{3x}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\:\begin{cases}{−\mathrm{8a}=\mathrm{1}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{a}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}}\\{−\mathrm{8b}=−\mathrm{2}\rightarrow\mathrm{b}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{generall}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{c}} \:=\:\mathrm{Acos}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{Bsin}\:\mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{3x} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 11/Jun/20

$$\left(\mathrm{eh}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{''} \:+\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\:=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{r}=\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{i}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} \:=\mathrm{acosx}\:+\mathrm{bsinx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} \:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{form}\:\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\alpha\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)+\beta\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}^{'} \:=−\mathrm{3}\alpha\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:+\mathrm{3}\beta\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{y}^{''} \:=−\mathrm{9}\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:−\mathrm{9}\beta\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right) \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}\right)\Rightarrow−\mathrm{9}\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)+\mathrm{9}\beta\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:+\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)+\beta\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:=\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)−\mathrm{2sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$−\mathrm{8}\alpha\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:+\mathrm{10}\beta\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:=\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)−\mathrm{2sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)\:\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{−\mathrm{8}\alpha\:=\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{10}\beta\:=−\mathrm{2}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\alpha\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{genearal}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{acosx}\:+\mathrm{bsinx}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{3x}\right)}\\{\beta=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}}\end{cases} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 12/Jun/20

$$−\mathrm{9}\beta+\beta=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{8}\beta=−\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow\:\beta=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
