Question Number 103014 by bobhans last updated on 12/Jul/20
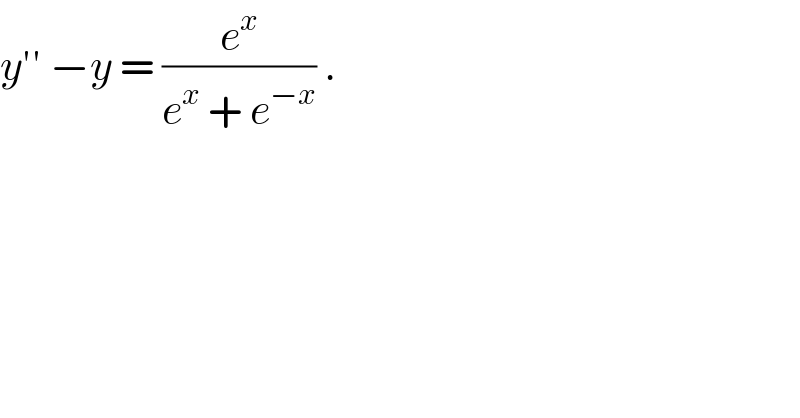
$${y}''\:−{y}\:=\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} \:+\:{e}^{−{x}} }\:. \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 12/Jul/20
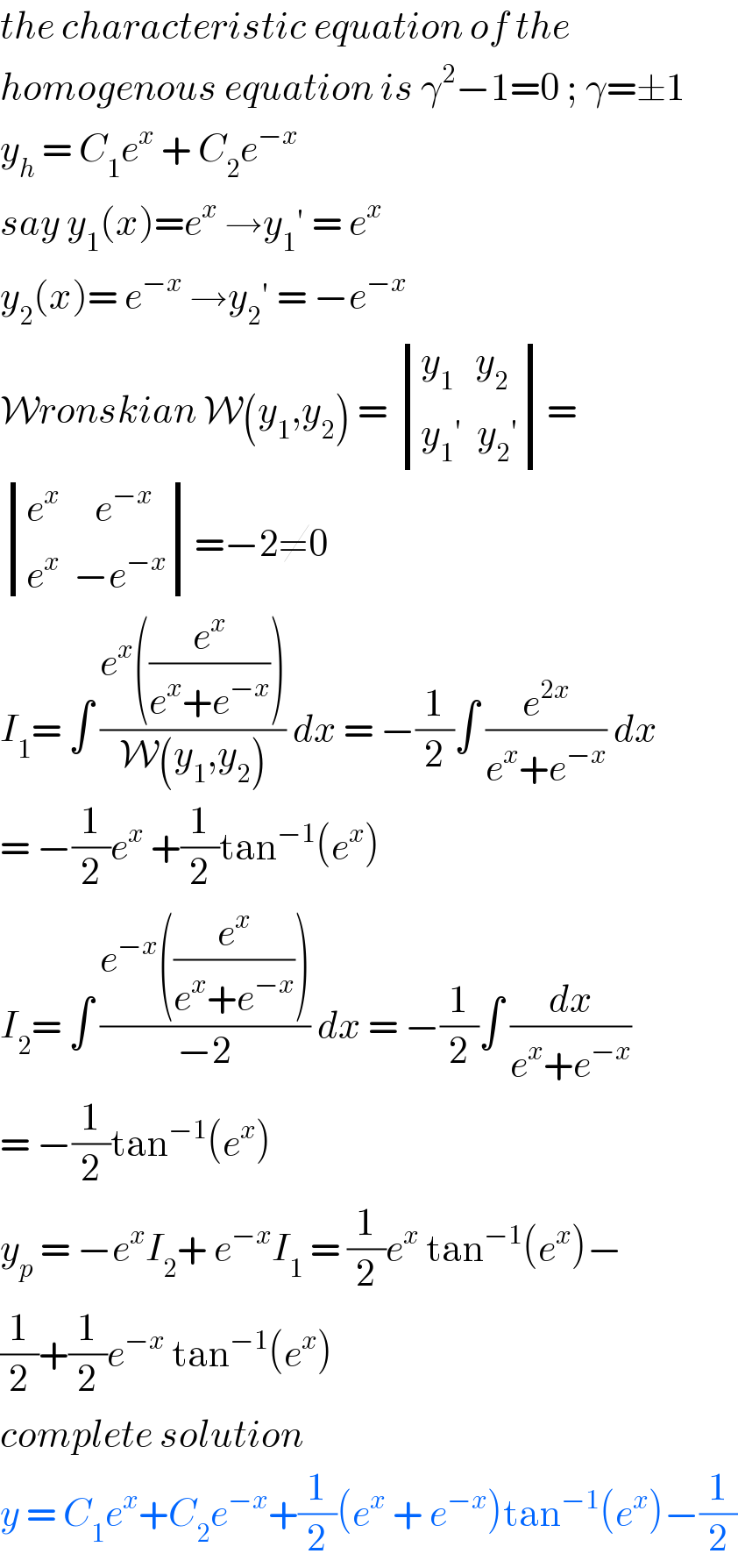
$${the}\:{characteristic}\:{equation}\:{of}\:{the} \\ $$$${homogenous}\:{equation}\:{is}\:\gamma^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:;\:\gamma=\pm\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}_{{h}} \:=\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} \:+\:{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} \: \\ $$$${say}\:{y}_{\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)={e}^{{x}} \:\rightarrow{y}_{\mathrm{1}} '\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${y}_{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right)=\:{e}^{−{x}} \:\rightarrow{y}_{\mathrm{2}} '\:=\:−{e}^{−{x}} \\ $$$$\mathcal{W}{ronskian}\:\mathcal{W}\left({y}_{\mathrm{1}} ,{y}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\:\begin{vmatrix}{{y}_{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:{y}_{\mathrm{2}} }\\{{y}_{\mathrm{1}} '\:\:{y}_{\mathrm{2}} '}\end{vmatrix}= \\ $$$$\begin{vmatrix}{{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:{e}^{−{x}} }\\{{e}^{{x}} \:\:−{e}^{−{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{2}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\int\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} \left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }\right)}{\mathcal{W}\left({y}_{\mathrm{1}} ,{y}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:{dx}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{{x}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({e}^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$${I}_{\mathrm{2}} =\:\int\:\frac{{e}^{−{x}} \left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }\right)}{−\mathrm{2}}\:{dx}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\:\frac{{dx}}{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} } \\ $$$$=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({e}^{{x}} \right)\: \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:−{e}^{{x}} {I}_{\mathrm{2}} +\:{e}^{−{x}} {I}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{{x}} \:\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({e}^{{x}} \right)− \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−{x}} \:\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({e}^{{x}} \right)\: \\ $$$${complete}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$${y}\:=\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({e}^{{x}} \:+\:{e}^{−{x}} \right)\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({e}^{{x}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by bramlex last updated on 12/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{coll}\:\mathrm{joss}\: \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 12/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{y}^{''} −\mathrm{y}\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{he}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{''} −\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\rightarrow\mathrm{r}\:=\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{be}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:=\mathrm{au}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{bu}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}\left(\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\\{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}\:=−\mathrm{2}\:\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{o}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\\{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }}\end{vmatrix}\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \right)}\:\:=_{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{t}} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{t}\:+\mathrm{t}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:\:=−\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{\mathrm{2}\left(\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \right)}\mathrm{dx}\:=_{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{t}} \:\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{t}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)}\:\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{t}^{−\mathrm{1}} }\mathrm{dt}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\:\frac{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dt} \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{t}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:=−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\right)+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \left(−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ch}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} \:+\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{ae}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{be}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{ch}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{arctan}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
